Fig. s5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-110622-35
- Publication
- Waxman et al., 2011 - Zebrafish retinoic acid receptors function as context-dependent transcriptional activators
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
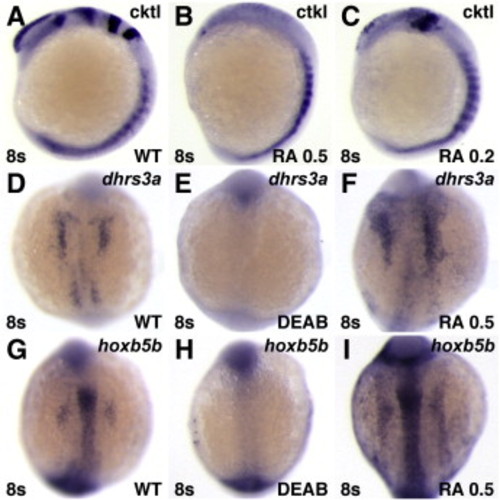
Phenotypes induced by RA treatment. (A?C) RA treatment eliminates anterior neural gene expression. Cktl of probes is the same as in Fig. 6. (A,D,G) Untreated control embryos. (B) Treatment with 0.5 ÁM RA can strongly posteriorize embryos, resulting in loss of all anterior neural markers. (C) Treatment with 0.2 μM RA can yield moderately posteriorized embryos in which the MHB is lost and the expression of krox20 in rhombomere 3 is reduced. This more modest posteriorization is remniscent of rar-vp mRNA-injected embryos (Fig. 6), though the eyes of rar-vp mRNA-injected embryos are never lost. (D?I) RA signaling positively regulates expression of dhrs3a and hoxb5b. (E, H) Treatment with DEAB inhibits dhrs3a and hoxb5b expression. (F, I) Treatment with 0.5 μM RA induces ectopic dhrs3a and hoxb5b expression. Images in A?C are lateral views with dorsal to the right. All other images are dorsal views with anterior up. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 352(1), Waxman, J.S., and Yelon, D., Zebrafish retinoic acid receptors function as context-dependent transcriptional activators, 128-140, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.