Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-110622-29
- Publication
- Waxman et al., 2011 - Zebrafish retinoic acid receptors function as context-dependent transcriptional activators
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
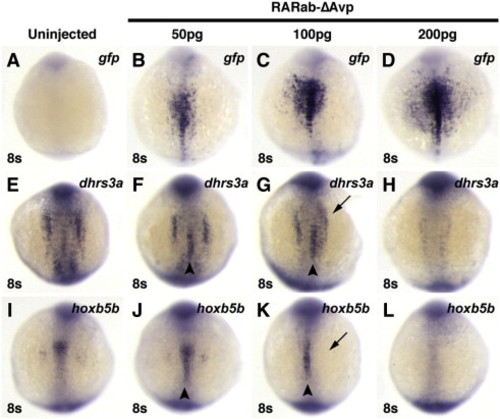
Injection of high doses of hyperactive RAR mRNA can inhibit target gene expression. Injection of increasing concentrations of rarabΔAvp mRNA increasingly activates reporter expression (A?D), but inhibits endogenous target gene expression (E?L). (A, E, I) Uninjected control embryos. (B, F, J) In embryos injected with 50 pg of rarabΔAvp mRNA, modest levels of the reporter are induced (B), as well as ectopic expression of dhrs3a and hoxb5b (arrowheads in F and J). (C, G, K) In embryos injected with 100 pg of rarabΔAvp mRNA, higher levels of the reporter are induced (C). Although ectopic activation of dhrs3a and hoxb5b is induced (arrowheads in G and K), their endogenous expression is also inhibited (arrows in G and K). (D, H, L) In embryos injected with 200 pg of rarabΔAvp mRNA, the highest levels of the reporter are induced (D), while endogenous dhrs3a and hoxb5b expression are inhibited and ectopic expression is not induced (arrowheads in H and L). All images are dorsal views with anterior up. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 352(1), Waxman, J.S., and Yelon, D., Zebrafish retinoic acid receptors function as context-dependent transcriptional activators, 128-140, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.