Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-101105-46
- Publication
- Butler et al., 2010 - Genetic and chemical modulation of spastin-dependent axon outgrowth in zebrafish embryos indicates a role for impaired microtubule dynamics in hereditary spastic paraplegia
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
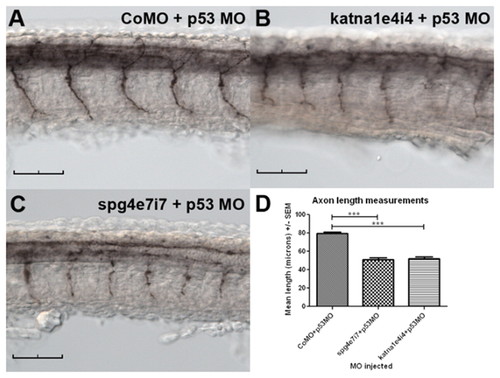
A katna1 splice-blocking (katna1e4i4) morpholino inhibits spinal motor axon outgrowth in a p53-independent manner. Embryos were injected with 1.0 pmol CoMO + 1.6 pmol p53MO (A), 0.8 pmol katna1e4i4 + 1.6 pmol p53MO (B) or 1.0 pmol spg4e7i7 + 1.6 pmol p53MO (C), fixed at 28 hpf, and then immunostained with znp-1. Both katna1 and spast splice-blocking morpholinos inhibit spinal motor axon outgrowth in a p53-independent manner (D). CoMO + p53MO (n=25), spg4e7i7 + p53MO (n=35), katna1e4i4 (n=34); statistical significance was determined using ANOVA with Bonferroni?s multiple comparison test. ***P<0.001. Scale bars: 50 μm. |
| Antibody: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | Prim-5 |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Prim-5 |