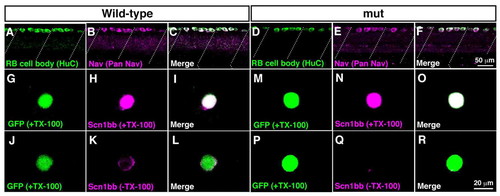
Surface expression of sodium channels is impaired in mutant RB neurons. (A-F) Wholemount immunostaining showed Nav expression in wild-type and mutant RB neurons at 2 dpf. (A) Anti-HuC labeled cell bodies of wild-type RB neurons at the dorsal spinal cord. Dotted lines represent somite boundaries. (B) Immunostaining with anti-pan Nav displayed Nav expression in wild-type spinal cord. (C) A merged image showed that all HuC-positive RB cells expressed Nav in wild-type. (D) Labeling with anti-HuC showed RB neurons in mutant spinal cord. (E) Anti-pan Nav labeled dorsally located spinal neurons in mutants. (F) All of the HuC-positive mutant RB neurons expressed Nav. (G-R) Dissociated RB neurons (GFP-positive) from 2 dpf embryos were labeled with anti-Scn1bb, with or without TX-100, which permeabilizes the plasma membrane. Note that anti-Scn1bb reacts with the extracellular domain of Scn1bb. (G-I) Scn1bb staining in the permeable condition (+TX-100) demonstrated Scn1bb expression in a wild-type RB neuron. (J-L) Labeling of Scn1bb in the impermeable condition (-TX-100) displayed surface distribution of Scn1bb in a wild-type RB cell. (M-O) Scn1bb staining with TX-100 showed Scn1bb expression in a wild-type RB neuron. (P-R) In the absence of TX-100, the surface labeling of Scn1bb was missing in a mutant RB cell, suggesting that Scn1bb exists inside the mutant cell without expression at the surface.
|

