Fig. 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-100506-45
- Publication
- Nakano et al., 2010 - Biogenesis of GPI-anchored proteins is essential for surface expression of sodium channels in zebrafish Rohon-Beard neurons to respond to mechanosensory stimulation
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
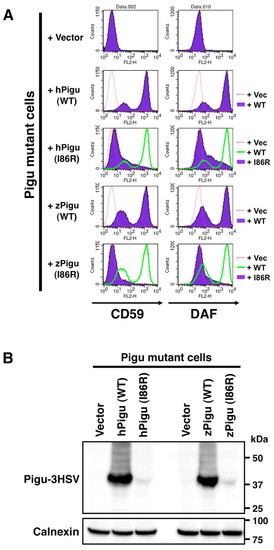
Wild-type Pigu restores the surface expression of GPI-anchored proteins in Pigu-deficient CHO cells. (A) Control or Pigu expression vectors were transfected into Pigu mutant CHO cells and the surface expressions of GPI-anchored proteins (CD59 and DAF) were estimated by flow cytometry. Surface expressions of CD59 and DAF were lower in vector-transfected Pigu mutant cells. Following transfection of human wild-type PIGU or zebrafish wild-type Pigu, surface expressions of CD59 and DAF were increased, showing that GPI transamidase activity was restored by expression of wild-type Pigu. Recovery of surface distribution of GPI-anchored proteins was not seen when transfected with human mutant (I86R) PIGU or zebrafish mutant (I86R) Pigu constructs. (B) The I86R mutation in Pigu destabilized the protein. Whole cell extracts from each pool of the transfected CHO cells were probed with anti-HSV to examine Pigu protein levels. Compared with human and zebrafish wild-type Pigu expressions, the protein levels of human PIGU (I86R) and zebrafish PIGU (I86R) were significantly lower. Calnexin is used as a loading control. |