Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-090904-45
- Publication
- Jing et al., 2009 - Zebrafish ale oko, an essential determinant of sensory neuron survival and the polarity of retinal radial glia, encodes the p50 subunit of dynactin
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
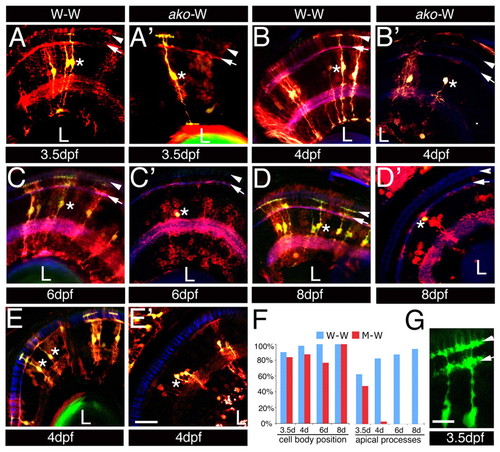
Mosaic analysis of ako Müller glia mutant phenotype. (A-E′) Transverse cryosections through retinae of mosaic zebrafish at the stages indicated below each image. Blastomere transplantations were performed using the Tg(gfap:GFPmi2001; pax6-DF4:mCFPq01) donor double transgenic line either wild type or mutant at the ako locus, as indicated at the top of each column. A non-transgenic wild-type line was used as the host. Sections were stained with an anti-GFP antibody to visualize all donor-derived cells (both CFP and GFP expression, red). Fluorescence of endogenously expressed GFP marks donor-derived Müller glia (green signal appears yellow against the red background). Sections in E,E′ are stained with the Zpr-1 antibody to visualize the photoreceptor cell layer. No defects in the morphology of Zpr-1-postitive cells in the vicinity of abnormal glial cells were observed (asterisk in E′). (F) Quantitation of mosaic analysis data. Percentages of cells with normal cell body position and apical process are provided. (G) The apical process of the wild-type Müller cell. Arrowheads and arrows indicate OLM and OPL, respectively. Asterisks indicate Müller cell perikarya. L, lens. Scale bars: 20 μm in A-E′; 10 μm in G. |