Fig. 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-050511-1
- Publication
- Shimizu et al., 2005 - Interaction of Wnt and caudal-related genes in zebrafish posterior body formation
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
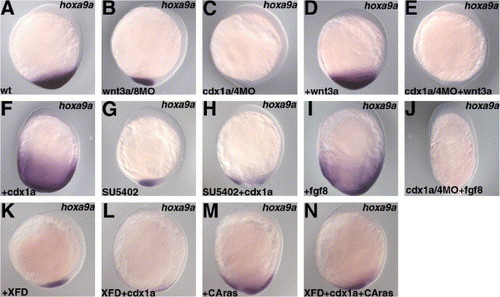
Involvement of Wnt, Cdx1a/4, and FGF in hoxa9a expression. Expression of hoxa9a at the 3-somite stage (A for the wild-type embryos). Expression of hoxa9a was reduced in the wnt3a/wnt8 morphant embryos (B) and it was not detected in the cdx1a/cdx4 morphant embryos (C). Although 6 pg of pCS2 + wnt3a plasmid injection led to increased hoxa9a expression (D), no hoxa9a expression was detected in the wnt3a-injected cdx1a/cdx4 morphant embryos (E). The hoxa9a expression was expanded in the cdx1a RNA (25 pg)-injected embryos (F), but was reduced in the SU5402-treated cdx1a RNA-injected embryos (H), as in the SU5402-treated non-injected embryos (G). The hoxa9a expression was also expanded in the 6 pg of pCS2 + fgf8-injected embryos (I), but was not detected in the embryos receiving injections of both pCS2 + fgf8- and cdx1a/4MO (J). The hoxa9a expression was reduced in the XFD RNA (500 pg)-injected (K), and XFD (500 pg) and cdx1a RNA (25 pg)-injected embryos (L). Co-injection of RNA for a constitutively active Ras (RasV12, CAras, 250 pg) with XFD (500 pg) and cdx1a RNA (25 pg) restored the expression of hoxa9a (N). (M) Expression of hoxa9a in the CAras RNA-injected embryos. Lateral views with dorsal to the right. |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Condition: | |
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage: | 1-4 somites |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 279(1), Shimizu, T., Bae, Y.K., Muraoka, O., and Hibi, M., Interaction of Wnt and caudal-related genes in zebrafish posterior body formation, 125-141, Copyright (2005) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.