- Title
-
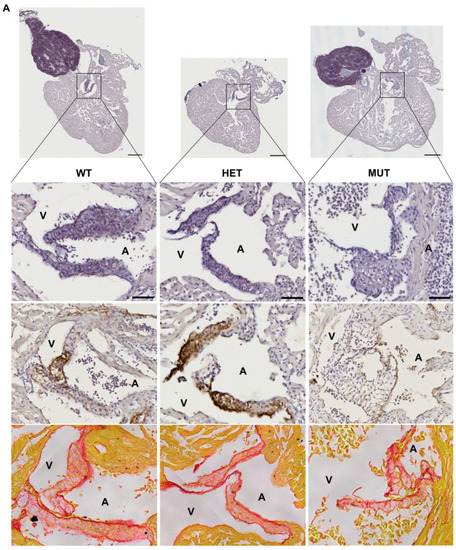
Characterization of the Zebrafish Elastin a (elnasa12235) Mutant: A New Model of Elastinopathy Leading to Heart Valve Defects
- Authors
- Hoareau, M., El Kholti, N., Debret, R., Lambert, E.
- Source
- Full text @ Cells
|
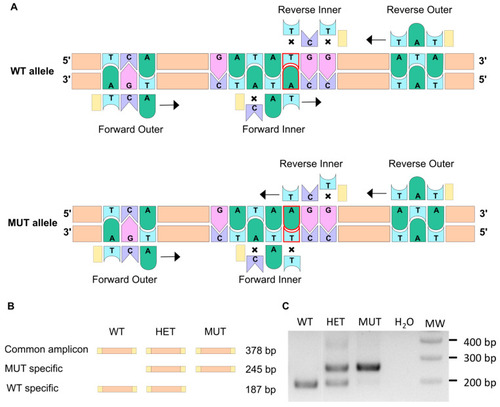
The ARMS-PCR technique allows to discriminate between WT and mutant alleles. ( |
|
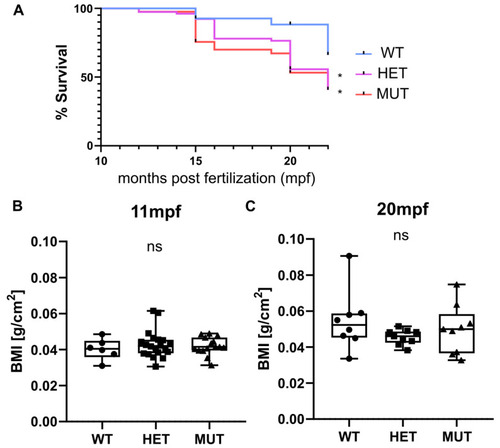
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
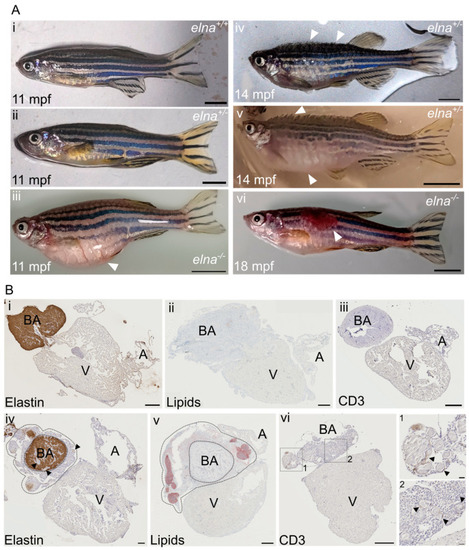
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
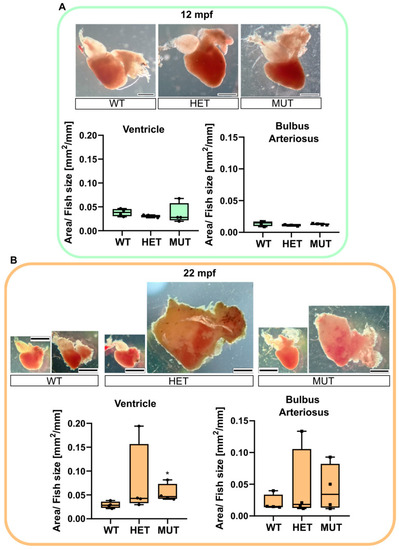
PHENOTYPE:
|