- Title
-
Oligodendrocyte origin and development in the zebrafish visual system
- Authors
- Santos-Ledo, A., Pérez-Montes, C., DeOliveira-Mello, L., Arévalo, R., Velasco, A.
- Source
- Full text @ J. Comp. Neurol.
|
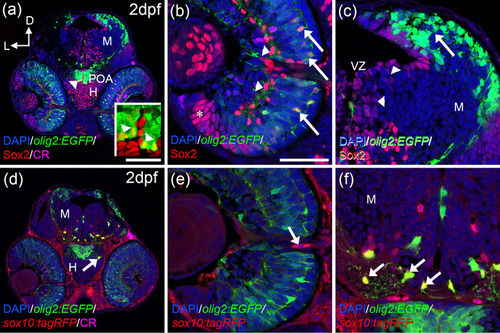
OPCs markers are detected from 2 dpf onwards. Distribution of olig2:EGFP/Sox2 (a?c) and olig2:EGFP/sox10:tagRFP (d?f) cells. olig2:EGFP and Sox2colocalize in the POA (arrowheads in a and inset in a), central outer retina (arrows in b), but not in the inner (arrowheads in c) or peripheral retina (asterisk in c). Olig2:EGFP cells are located in the dorsal optic tectum (arrow in c) but do not colocalize with Sox2 that is present in the VZ (arrowhead in c). sox10:tagRFP is absent from the retina except cells around the ON (d, arrow in e). In the hypothalamus and optic tectum, arborized olig2:EGFP cells also present sox10:tagRFP (arrows in d and f). Calretinin (CR) is present in several neurons, such as ganglion cells and is used to label the ON. D: dorsal; H: hypothalamus; L: lateral; M: mesencephalon; ON: optic nerve; POA: preoptic area; VZ: ventricular zone. Scale bar in a, d: 100 ?m; in b, c, e, f: 50 ?m |
|
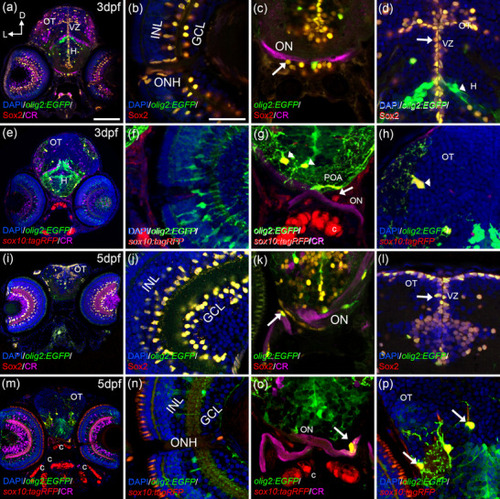
From 3 dpf onwards, OPCs cells spread throughout the visual system. At 3 dpf (a?h), olig2:EGFP/Sox2 cells are present in the INL, GCL, ONH (a, b), the optic chiasm (arrow in c), and the ventricular zones of the brain (arrow in d). Arborized olig2:EGFP cells are negative for Sox2 (arrowhead in d). sox10:tagRFP cells are present in the ONH (e, f) and the optic chiasm (e, arrow in g). Arborized olig2:EGFP/sox10:tagRFP cells are located in the POA with their projections surrounding the ON (arrowheads in g). OT also presented olig2:EGFP/sox10:tagRFP cells (arrowhead in h). At 5 dpf (i?p), olig2:EGFP/Sox2 cells are present in the INL, GCL (i, j), ON (arrow in k), and ventricular zones (arrow in l). olig2:EGFP/sox10:tagRFP cells are found in the ON with projections surrounding it (m, arrow in o), arborized olig2:EGFP/sox10:tagRFP cells are also present in the OT (arrows in p). Calretinin (CR) labels the ganglion cells and the ON. C: cartilage; D: dorsal; GCL: ganglion cell layer; H: hypothalamus; INL: inner nuclear layer; L: lateral; ON: optic nerve; ONH: optic nerve head; OT: optic tectum; POA: preoptic area; VZ: ventricular zone. Scale bar in a, e, i, m: 100 ?m; in b, c, d, f, g, h, j, k, l, n, o, p: 50 ?m |
|
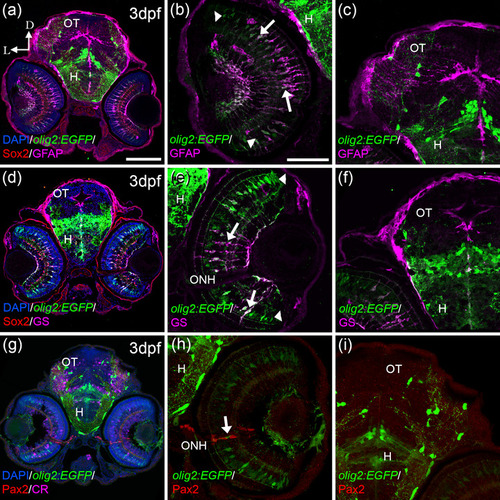
olig2:EGFP cells present other glial markers in the retina; GFAP and GS. olig2:EGFP cells also colocalized with Müller markers: GFAP (a, b) and GS (d, e) in the retina but not in the OT (c, f). Colocalization was detected mostly in the central area of the retina (arrows in band e), while cells in the periphery were just olig2:EGFP (arrowheads in b and e). olig2:EGFP cells in the periphery of the ONH do not colocalize with Pax2, typical maker for reticular astrocytes (g?i), although these two populations are very close (arrow in h). D: dorsal; L: lateral; H: hypothalamus; ONH: optic nerve head; OT: optic tectum. Scale bar in a, d, g: 100 ?m; in b, c, e, f, h, i: 50 ?m |
|
olig2:EGFP cells are differentiated from 7 dpf. In the retina at 7 dpf, olig2:EGFP cells are restricted to the PGZ and the TZ (a, b). But only the cells in the TZ colocalize with Sox2 (arrows in b). Sox2 that do not show olig2:EGFP are abundant in the proliferative areas of the brain (c, d). olig2:EGFP occasionally colocalize with Sox2 in the optic nerve chiasm at 7 dpf (arrow in c). At 7 dpf olig2:EGFP/sox10:tagRFP cells were found in the ON chiasm (e, arrow in g) and in other parts of the brain (arrows in h). Differentiated part of the retina was empty of olig2:EGFP/sox10:tagRFP cells (f). At 11 dpf, Sox2 keeps its pattern in the retina (i, j) and in the ON (arrow k). In the OT, Sox2 cells are restricted to the ventricular area (l). olig2:EGFP/sox10:tagRFP cells are abundant in the ON with obvious projections (m, arrows in o) and there are none in the retina (n). Oligodendrocytes in the OT are olig2:EGFP/sox10:tagRFP (p). Calretinin (CR) is used to label ganglionar cells and ON. D: dorsal; GCL: ganglion cell layer; INL: inner nuclear layer; L: lateral; ONH: optic nerve head; ON; optic nerve; OT: optic tectum; PGZ: proliferative germinal zone; VZ: ventricular zone. Scale bar in a, e, i, m: 100 ?m; in b, c, d, f, g, h, j, k, l, n, o, p: 50 ?m |
|
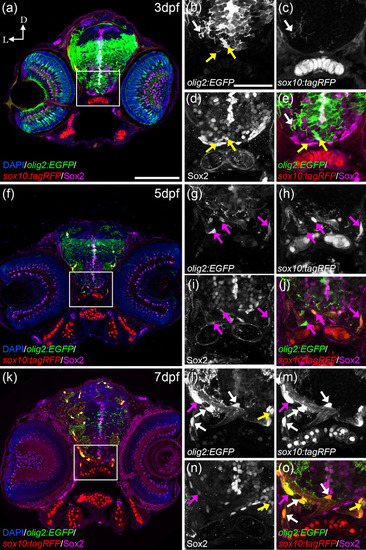
olig2:EGFP cells switch from Sox2 to sox10:tagRFP. At 3 dfp (a), olig2:EGFP cells with round morphologies and slightly arborized in the postchiasmatic ON colocalized with Sox2 but not with sox10:tagRFP (a, yellow arrows in b, d, and e). Fully arborized olig2:EGFP cells in the ventral OT colocalized with sox10:tagRFP and not with Sox2 (a, white arrows in b, c, and e). At 5 dpf (f), olig2:EGFP with elongated morphologies and arborization colocalize simultaneously with Sox2 and sox10:tagRFP (f, magenta arrows in g?j). At 7 dfp (k), arborized olig2:EGFP cells that present many projections colocalize only with sox10:tagRFP (k, white arrows in l, m, and o); while some olig2:EGFP cells with less arborization colocalize with Sox2 and sox10:tagRFP (magenta arrows in l?o) and those with round morphologies colocalized only with Sox2 and not sox10:tagRFP (yellow arrows in l, n, and o). D: dorsal; L: lateral. Scale bar in a, f, k: 100 ?m; in b, c, d, e, g, h, I, j, l, m, n, o: 50 ?m |
|
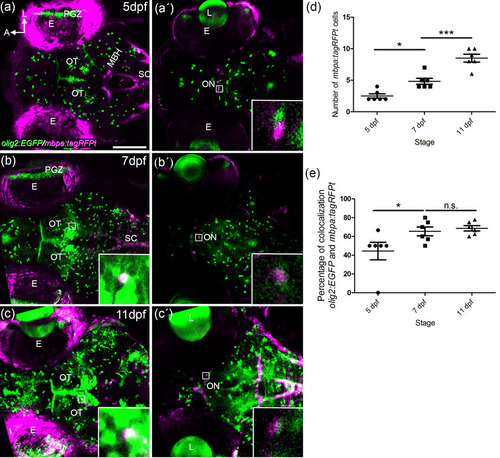
Myelination of the visual system. Confocal images of whole mount olig2:EGFP/mbpa:tagRFPt embryos at 5 (a, a?), 7 (b, b?), and 11 (c?) dpf. A 25 ?m thick stack is shown as max intensity projection in the OT area (a, b, and c) and the optic nerve chiasm (a?, b?, and c?). Detection of mbpa:tagRFPt starts at 5 dpf in the ON (a?). The number of mbpa:tagRFPt cells increase significantly from 3?4 cells at 5 dpf to 8?10 cells at 11 dpf (a?, b?, c?, quantified in d). A total of 40% olig2:EGFP colocalize with mbpa:tagRFPt at 5 dpf. This percentage increases to 60% from 5 dpf to 7 dpf (quantified in e). E: eye: L: lens; MBH; midbrain hindbrain boundary; ON: optic nerve; OT: optic tectum; PGZ: proliferative germinal zone; SC: spinal cord. Scale bar: 100 ?m |