- Title
-
Specialized neurons in the right habenula mediate response to aversive olfactory cues
- Authors
- Choi, J.H., Duboue, E.R., Macurak, M., Chanchu, J.M., Halpern, M.E.
- Source
- Full text @ Elife
|
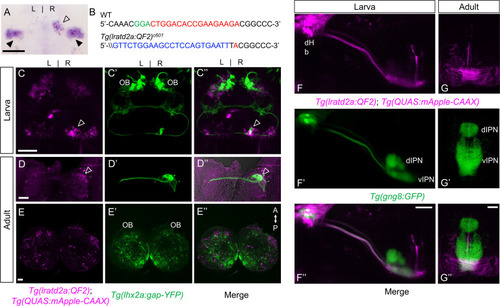
Iratd2a-expressing neurons in the right dHb connect asymmetric pathway from the olfactory bulb to ventral IPN. (A) Pattern of lratd2a expression at 5 days post fertilization (dpf), open arrowhead indicates right dHb and black arrowheads the bilateral vHb. (B) Sequences of WT (top) and transgenic fish (bottom) with QF2 integrated within the first exon of the lratd2a gene. PAM sequences are green, the sgRNA-binding site red and donor DNA blue. Confocal dorsal views of Tg(lratd2a:QF2), Tg(QUAS:mApple-CAAX) and Tg(lhx2a:gap-YFP) labeling in a (C-C??) 5 dpf larva and in transverse sections of the adult brain at 3 months post-fertilization (mpf) at the level of the (D-D??) dHb and (E-E??) olfactory bulb. Axons of lhx2a olfactory mitral cells (open arrowheads, C and D) terminate at lratd2a dHb neurons. (F-F??) Lateral view of Tg(lratd2a:QF2), Tg(QUAS:mApple-CAAX), Tg(gng8:GFP) larva at 6 dpf with mApple-labeled dHb terminals at the ventral interpeduncular nucleus (vIPN). Dorsal habenular nuclei (dHb), dorsal interpeduncular nucleus (dIPN). (G-G??) Axonal endings of lratd2a dHb neurons are restricted to the ventralmost region of the vIPN in transverse section of 2.5 mpf adult brain. Scale bar, 50 ?m. A-P, anterior to posterior; L-R, left-right; OB, olfactory bulb. |
|
Targeted genomic integration does not disrupt endogenous gene expression. Expression patterns of (A) lratd2a and (B) slc5a7a are similar in 5 dpf wild-type and heterozygous transgenic larvae. Arrowheads point to the dHb. Dorsal views, scale bars are 100 ?m. |
|
Asymmetry of lratd2a-expressing dHb neurons.(A) Dorsal views of the habenular region of three Tg(lratd2a:QF2); Tg(QUAS:GFP) larvae at 7 dpf. Each confocal image is a single focal plane (1 ?m). Brackets indicate regions of lratd2a-expressing neurons in the dHb and arrowheads point to the bilateral vHb. Scale bar, 25 ?m. (B) Quantification of lratd2a-expressing dHb neurons. Each line connecting the circles corresponds to a single larva. Mean is 13.1 ± 1.4 cells in the left dHb and 33.5 ± 2.3 cells in the right, n = 15 larvae [p < 0.0001, paired t-test]. |
|
lhx2a-expressing olfactory cells innervate lratd2a dHb neurons. Axons of lhx2a olfactory mitral cells terminate at mApple labeled lratd2a dHb neurons. Dorsal confocal views of (A) Tg(lratd2a:QF2), Tg(QUAS:mApple-CAAX); Tg(lhx2a:syp-GFP) pre-synaptic labeling (open arrowhead) in a 5 dpf larva. The synaptophysin GFP-labeled pre-synaptic boutons are distributed over approximately 5% of the region occupied by lratd2a neurons. (B) Tg(lratd2a:QF2), Tg(QUAS:mApple-CAAX); Tg(lhx2a:gap-YFP) axon terminal labeling (open arrowhead) in a transverse section of the adult brain at three mpf. Scale bar, 50 ?m. |
|
Increased activity of lratd2a-expressing dHb neurons upon exposure to aversive olfactory cues. (A?B) Average change in fluorescence (?F/F) in seconds (sec) for all lratd2a positive neurons in the larval right dHb over a 5 min interval. Yellow bars indicate consecutive 5 s intervals of vehicle or odor delivery. Solid lines represent mean responses to (A) cadaverine or (B) to chondroitin sulfate and shadings represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). (C?D) Change in the intensity of GCaMP6f fluorescence for lratd2a neurons in the right dHb in response to consecutive delivery of (C) water or cadaverine [n = 30 neurons in three larvae, 0.009 ± 0.039 ?F/F for water, 0.148 ± 0.074 ?F/F for cadaverine] and of (D) water or chondroitin sulfate [n = 43 neurons in four larvae, 0.039 ± 0.037 ?F/F for water, 0.176 ± 0.069 ?F/F for chondroitin sulfate] at seven dpf, respectively. Two-way ANOVA reveals a significant effect of time [F(1, 29) = 32.09, p < 0.0001], interaction [F(3, 87) = 3.797, p = 0.0131] but no effect of vehicle vs. odorants [F(3, 87) = 1.169, p = 0.3262] for cadaverine; and a significant effect of time [F(1, 42) = 4.754, p = 0.0349], vehicle vs. odorants [F(3, 126) = 2.825, p = 0.0414] and interaction [F(3, 126) = 4.256, p = 0.0067] for chondroitin sulfate. Post-hoc analysis by Bonferroni?s multiple comparisons. (E?G) Colocalization of fos and lratd2a transcripts in transverse sections of adult olfactory bulbs (left panels) and habenulae (middle panels) detected by double labeling RNA in situ hybridization 30 min after addition of (E) water, (F) cadaverine, or (G) alarm substance to the test tank. (E?-G?) Higher magnification images (corresponding to dashed boxes in E-G) show lratd2a (brown) coexpressed with fos (blue) in cells of the right dHb (arrowheads). Scale bars, 100 ?m. (H) Quantification of fos-expressing cells in the adult dHb after addition of water [3.58 ± 0.811 cells in the left and 5.61 ± 0.85 in the right dHb, n = 31 sections from 16 adult brains], cadaverine [5.32 ± 1.36 cells in the left and 15.73 ± 1.25 in the right dHb, n = 22 sections from 11 adult brains], or alarm substance [20.72 ± 2.70 cells in the left and 20.31 ± 2.53 in the right dHb, n = 29 sections from 17 adult brains]. For the right dHb, significantly more cells were fos positive after addition of cadaverine (p = 0.0031) or alarm substance (p < 0.0001). For the left dHb, a significant difference was only observed after addition of alarm substance (p < 0.0001). Two-way mixed ANOVA reveals a significant effect of group [F(2, 60) = 30.18, p < 0.0001], left vs. right [F(1, 30) = 13.02, p = 0.0011] and interaction [F(2, 38) = 7.881, p = 0.0014]. Post-hoc analysis by Bonferroni?s multiple comparisons. All numbers represent the mean ± SEM. |
|
Synaptic inhibition of lratd2a right dHb neurons attenuates response to cadaverine. (A) Sequences upstream of the slc5a7a transcriptional start site before (WT) and after integration of Cre (blue indicates donor DNA) at sgRNA target site (red nucleotides and PAM sequences in green). (B) Schematic diagram of intersectional strategy using Cre/lox mediated recombination and the QF2/QUAS binary system. QF2 is driven by lratd2a regulatory sequences and the slc5a7a promoter drives Cre leading to reporter/effector expression in lratd2a neurons in the right dHb. (C) Dorsal view of GFP labeling in only the right dHb after Cre-mediated recombination in a 5 dpf Tg(lratd2a:QF2), Tg(slc5a7a:Cre), Tg(QUAS:loxP-mCherry-loxP-GFP-CAAX) larva. Scale bar, 25 ?m. (D) BoTxBLC-GFP-labeled cells (open arrowhead) in the right dHb in Tg(lratd2a:QF2), Tg(slc5a7a:Cre), Tg(QUAS:loxP-mCherry-loxP-BoTxBLC-GFP) 5 dpf, 37 dpf, and 4 mpf zebrafish. Upper images show mCherry-labeled lratd2a Hb neurons, middle images show the subset of right dHb neurons that switched to GFP expression, and the bottom row are merged images. Scale bar, 50 ?m. (E) Transverse section of BoTxBLC-GFP labeled axonal endings of dHb neurons that express Cre and lratd2a in a subregion of the vIPN (bracket) in Tg(lratd2a:QF2), Tg(slc5a7a:Cre), Tg(QUAS:loxP-mCherry-loxP-BoTxBLC-GFP) 37 dpf juveniles. Scale bar, 50 ?m. (F, G) Preferred tank location prior to and after cadaverine addition of adults genotyped for absence (Cre-) or presence (Cre+) of Tg(slc5a7a:Cre). (F) Representative 1 min traces for single Cre- (blue) and Cre+ (purple) adults recorded over 10 min prior to (min 0?5) and after (min 6?10) addition of cadaverine to one end of the test tank (open arrows). (G) Preference index for all adults for an average of 2 min before (white) and for each of 3 min after (gray) the addition of cadaverine. In Cre- fish, aversive behavior was significantly increased at 2 min (p = 0.0116) and 3 min (p = 0.0344), n = 15 fish for each group. In contrast, Cre+ fish, showed no significant difference in their preferred location over time. Dashed red lines in F and G denote midpoint of test tank. Two-way ANOVA reveals significant effects of time [F(3, 27) = 29, p < 0.0001], but no effect of group [F(1, 14) = 2.381] and interaction [F(3, 33) = 1.813]. Post-hoc analysis by Bonferroni?s multiple comparisons. (H) Swimming speed during 1 min period before and after addition of alarm substance was similar for Cre- [3.68 ± 0.47 and 7.43 ± 1.1 cm/s] and Cre+ [4.02 ± 0.42 s and 7.93 ± 0.92 cm/s] adults. Two-way ANOVA reveals significant effects of time [F(1, 16) = 39.61, p < 0.0001], but no effect of group [F(1,16) = 0.2236] and interaction [F(1,16) = 0.0141]. Post-hoc analysis by Bonferroni?s multiple comparisons. (I) Duration in the upper half of the test tank prior to and after addition of alarm substance for Cre+ adults was 96.6 ± 15.72 s and 13.23 ± 3.34 s and for Cre- adults was 125.53 ± 18.6 s and 8.26 ± 2.5 s. Two-way ANOVA reveals a significant effect of time [F(1, 16) = 63.79, p < 0.0001], but no effect of group [F(1,16) = 1.048] and interaction [F(1,16) = 0.0141]. Post-hoc analysis by Bonferroni?s multiple comparisons. (J) Onset of fast swimming after application of alarm substance was observed at 25 ± 4.05 and at 22.7 ± 3.72 sec for Cre- and Cre+ fish, respectively [p = 0.679, unpaired t-test]. (K) Time interval between increased swimming speed and freezing behavior for Cre- (68.88 ± 23.36 s) and Cre+ (20.88 ± 3.93 s) adults [p = 0.051, unpaired t-test]. For H-K, all numbers represent the mean ± SEM. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Preferred tank location prior to and after cadaverine addition within each group and between groups. (A) Preferred tank location prior to and after cadaverine addition of adults genotyped for absence (Cre-, blue) or presence (Cre+, red) of Tg(slc5a7a:Cre). Preference index for all adults tested 5 min prior to (white) and 5 min after addition of cadaverine (grey and on side indicated by +). In Cre- fish, significant differences in repulsive behavior were detected after addition of cadaverine [6 min (p = 0.0084), 7 min (p = 0.0012), 8 min (p = 0.0017), 9 min (p = 0.0353) compared to the last min before addition, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, n = 15 fish]. Cre+ fish, did not show significant differences in their preferred location beyond two mins after cadaverine addition [6 min (p = 0.0302), 7 min (p = 0.0043) compared to the last min before addition, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, n = 15 fish]. (B) Preference index before and after addition of cadaverine averaged over 5 min periods for without [Cre-; ?0.1341 ± 0.0923 and ?0.6315 ± 0.0718] or with the Cre transgene [Cre+; ?0.0823 ± 0.0631 and ?0.3952 ± 0.1365], n = 15 fish per group. Two-way ANOVA reveals significant effect of time [F(3, 179) = 32.45, p < 0.0001], group [F(14, 60) = 3.4887, p = 0.0004] and interaction [F(42, 180) = 4.887, p < 0.0001]. Post-hoc analysis by Bonferroni?s multiple comparisons. Dashed red lines in A and B denote midpoint of test tank. |
|
Validation of intersectional strategy to inhibit cholinergic neurons using botulinum neurotoxin. Lateral views of (A) Tg(Xla.Tubb:QF2), Tg(QUAS:loxP-mCherry-loxP-BoTxBLC-GFP) and (B) Tg(Xla.Tubb:QF2), Tg(slc5a7a:Cre), Tg(QUAS:loxP-mCherry-loxP-BoTxBLC-GFP) larvae at 4 dpf. In the presence of Cre recombinase, cholinergic neurons in the spinal cord switch from mCherry to BoTxBLC-GFP expression, which inhibits their response to touch (refer to Video 1). Scale bars, 100 ?m. |
|
Variability in BoTxBLC-GFP labeling of dHb neurons. (A) Dorsal views of Tg(lratd2a:QF2), Tg(slc5a7a:Cre), Tg(QUAS:loxP-mCherry-loxP-BoTxBLC-GFP) zebrafish at 5, 14, and 22 dpf showing persistence and variability in labeling of lratd2a right Hb neurons. Four different individuals are shown at each stage (12 total). Scale bar, 25 ?m. (B) Quantification of BoTxBLC-GFP-expressing neurons at 5 dpf [none in left dHb, 23 ± 4.92 in right dHb], 14 dpf [1.25 ± 0.63 left, 34 ± 5.82 right] and 22 dpf [1.25 ± 0.48 left, 34.25 ± 4.52 right]. Two-way ANOVA reveals significant effects of left vs. right [F(1,3) = 245.7, p = 0.0006], but no effect of developmental stages [F(2,6) = 0.301] and interaction [F(2, 6) = 1.117]. Post-hoc analysis by Bonferroni?s multiple comparisons. Numbers represent the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. |
|
Aversive response to alarm substance is intact in BoTxBLC-GFP juvenile fish. (A) Swimming speed for 1 min before and after addition of alarm substance by Tg(lratd2a:QF2), Tg(QUAS:loxP-mCherry-loxP-BoTxBLC-GFP) 5?7 week old juveniles with or without Tg(slc5a7a:Cre). In the absence of Cre, swimming speed was 0.6 ± 0.083 cm/s before and 1.476 ± 0.295 cm/s after and, in the presence of Cre, 0.681 ± 0.10 cm/s before and 1.251 ± 0.229 cm/s after the addition of alarm substance. Two-way ANOVA reveals significant effects of time [F(1, 14) = 14.46, p = 0.0019], but no effect of group [F(1,14) = 0.141] and interaction [F(1,14) = 1.656]. Post-hoc analysis by Bonferroni?s multiple comparisons. (B) Duration in the upper half of the test tank prior to and after addition of alarm substance for Cre- adults was 105.96 ± 12.96 s and 64.89 ± 3.34 s, and for Cre+ adults was 88.57 ± 10.78 s and 55.26 ± 9.2 s. Two-way ANOVA reveals significant effects of time [F(1, 14) = 18.21, p = 0.0008], but no effect of group [F(1,14) = 3.426] and interaction [F(1,14) = 0.1316]. Post-hoc analysis by Bonferroni?s multiple comparisons. (C) The onset of fast swimming after application of alarm substance was observed at 19.33 ± 4.27 s for Cre- and at 40.8 ± 7.12 s for Cre+ fish [p = 0.015, unpaired t-test]. (D) Time interval between increased swimming speed and freezing behavior for Cre- (161.5 ± 23.8. s) and for Cre+ (147.5 ± 21.79 s) [p = 0.669, unpaired t-test], n = 15 fish for each group. Numbers represent the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ns, not significant (p > 0.05). |
|
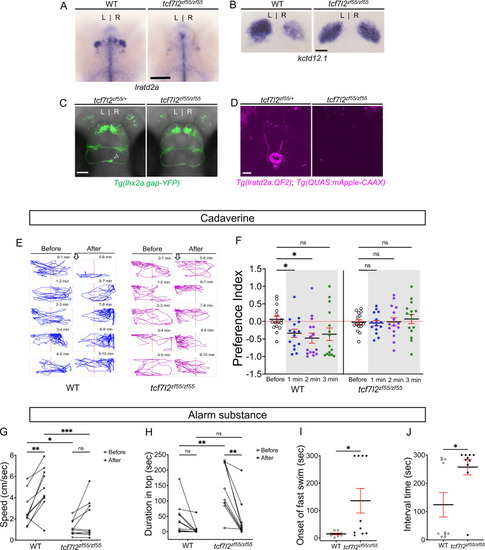
Attenuated response to aversive odorants by left-isomerized dHb mutants. (A?B) (A) Absence of lratd2a-expressing right dHb neurons and (B) right-isomerized expression of kctd12.1 in tcf7l2 mutant larvae at five dpf. (C) Dorsal views of olfactory mitral neuronal projections of Tg(lhx2a:gap-YFP) larvae at 6 dpf. Open arrowhead indicates axon terminals of mitral cells in the WT right dHb that are absent in the mutant. (D) Dorsal views of dHb neuronal projections to the ventral IPN in Tg(lratd2a:QF2), Tg(QUAS:mApple-CAAX) larvae at 6 dpf. (E) Representative traces (1 min) for tcf7l2 mutant and WT sibling adults after application of cadaverine. (F) Preference index for mutants and WT siblings for an average of 2 min before (white) and for each of 3 min after (gray) the addition of cadaverine. Only WT fish showed a significant difference in their preferred location at 1 min (p = 0.0439) and at 2 min (p = 0.0184). For each group, n = 15 adults. Two-way ANOVA reveals a significant effect of time [F(3, 24) = 3.665, p = 0.046], group [F(1, 14) = 6.197, p = 0.026] and interaction [F(3, 30) = 7.953, p = 0.001]. Post-hoc analysis by Bonferroni?s multiple comparisons. Dashed red lines denote midpoint of test tank. (G) Swimming speed for 30 s before and after addition of alarm substance was1.13 ± 0.22 cm/s and 1.89 ± 0.56 cm/s for tcf7l2 homozygotes and 2.84 ± 0.48 cm/s and 4.88 ± 0.63 cm/s for their WT siblings, n = 10 fish for each group. Two-way ANOVA reveals significant effects of time [F(1, 9) = 19.31, p = 0.0021] and group [F(1, 9) = 13.91, p = 0.0047], but no effect of interaction [F(1, 9) = 3.933]. Post-hoc analysis by Bonferroni?s multiple comparisons. (H) Duration in the upper half of the test tank prior to and after addition of alarm substance for tcf7l2 adults was 143.58 ± 24.80 s and 38.77 ± 19.56 s and 43.68 ± 16.35 s and 8.19 ± 6.16 s for their WT siblings, n = 10 fish for each group. Two-way ANOVA reveals significant effects of time [F(1, 9) = 3755, p = 0.0002], group [F(1, 9) = 12.42, p = 0.0065] and interaction [F(1, 9) = 5.877, p = 0.0383]. Post-hoc analysis by Bonferroni?s multiple comparisons. (I) Onset of fast swimming after application of alarm substance occurred at 15 ± 2.65 s for WT and at 136 ± 44.86 s for tcf7l2 fish [p = 0.015, unpaired t-test]. (J) The time interval between increased swimming speed and freezing behavior was 124.2 ± 43.13 s for WT and 257.3 ± 27.43 s for tcf7l2 fish [p = 0.018, unpaired t-test]. For F-J, all numbers represent the mean ± SEM. |
|
Preferred tank location prior to and after cadaverine addition within each group and between groups. (A) Preference index for tcf7l2 homozygous mutants and their WT siblings after addition of cadaverine (grey and on side indicated by +). Behavior was monitored prior to and after cadaverine addition for 5 min periods. Only WT adults showed a significant difference in their location 5 min afterwards compared to the min before its addition [at 6 min (p = 0.0003), 7 min (p < 0.0001), 8 min (p = 0.0067), 9 min (p = 0.0479) and 10 min (p = 0.0215), Wilcoxon signed-rank test, n = 15 adults for each group]. (B) Preference index before and after addition of cadaverine averaged over 5 min periods for WT [?0.0986 ± 0.0637 and ?0.3574 ± 0.1571] and tcf7l2 adults [0.152 ± 0.0514 and 0.0361 ± 0.1015], n = 15 fish. Two-way ANOVA reveals significant effect of time [F(3, 152) = 34.41, p < 0.0001], group [F(14, 60) = 17.38, p < 0.0001] and interaction [F(42, 180) = 5.786, p < 0.0001]. Post-hoc analysis by Bonferroni?s multiple comparisons. Dashed red lines in A and B denote midpoint of test tank. |
|
Enhanced reactivity to alarm substance in mutants with right-isomerized dHb. (A) Asymmetric expression pattern of kctd12.1 is right-isomerized in bsx homozygotes at five dpf. (B) Projections of Tg(lhx2a:gap-YFP) labeled olfactory mitral cells terminate bilaterally (open arrowheads) in the dHb of bsxm1376 homozygous mutants at five dpf. (C) In bsx mutants, axons from both left (open arrowhead) and right dHb lratd2a neurons project to the same region of the vIPN. Scale bar, 50 ?m. (D) Bilateral fos-expressing neurons in right-isomerized mutants. fos (blue) and lratd2a (brown) transcripts in the olfactory bulbs (upper panels) and dHb (bottom panels) of 10-month-old bsxm1376 heterozygotes and homozygous mutants detected by RNA in situ hybridization 30 min after addition of cadaverine to the test tank. Brackets indicate fos-expressing cells. Scale bar, 100 ?m. (E) Quantification of fos-expressing cells in the dHb after application of cadaverine in bsxm1376/+ [9.47 ± 2.37 cells on the left and 15.41 ± 2.19 cells on the right, n = 17 sections from nine adults] and bsxm1376/m1376 adults [17.64 ± 1.59 cells on the left and 18.5 ± 1.76 cells on the right, n = 14 sections from eight adults]. Two-way mixed ANOVA reveals significant effect of group [F(1, 16) = 5.178, p = 0.037] and left vs. right [F(1, 16) = 6.885, p = 0.0184], but no effect of interaction [F(1, 10) = 3.85]. Post-hoc analysis by Bonferroni?s multiple comparisons. (F) Preference index for bsx adults for an average of 2 min before (white) and for each of 3 min after (gray) the addition of cadaverine. Both bsx homozygotes and heterozygotes showed reduced responsiveness to cadaverine. Two-way ANOVA reveals significant effect of interaction [F(3, 34) = 5.483, p = 0.005], but no effect of time [F(3, 25) = 0.987] and group [F(1, 14) = 2.728]. Post-hoc analysis by Bonferroni?s multiple comparisons. (G) Swimming speed for 30 s before and after addition of alarm substance. In heterozygous adults, swimming speed was 1.22 ± 0.31 cm/s before and 3.52 ± 0.44 cm/sec after and, in homozygotes, 0.46 ± 0.08 cm/s before and 2.80 ± 0.37 cm/s after, n = 15 adults for each group. Two-way ANOVA reveals significant effect of time [F(1, 14) = 113.4, p < 0.0001], but no effect of group [F(1, 14) = 4.459] and interaction [F(1, 14) = 0.0023]. Post-hoc analysis by Bonferroni?s multiple comparisons. (H) Duration in the upper half of the test tank prior to and after addition of alarm substance for bsxm1376/m1376 adults was 194.86 ± 25.66 s and 51.89 ± 14.84 s and was 63.55 ± 10.11 s and 7.95 ± 3.24 s for bsxm1376/+, n = 15 fish for each group. Two-way ANOVA reveals significant effect of time [F(1, 14) = 44.35, p < 0.0001], group [F(1, 14) = 22.45, p = 0.0003] and interaction [F(1, 14) = 20.89, p = 0.0004]. Post-hoc analysis by Bonferroni?s multiple comparisons. (I) Onset of fast swimming after application of alarm substance was observed at 33.13 ± 19.19 s in bsxm1376/+ and at 37.73 ± 4.27 s in bsxm1376/m1376 fish [p = 0.816, unpaired t-test]. (J) Time interval between increased swimming speed and freezing behavior for bsxm1376/+ (103.1 ± 30.75 s) and for bsxm1376/m1376 (186.7 ± 28.23 s) [p = 0.055, unpaired t-test]. For E-J, all numbers represent the mean ± SEM. |
|
Preferred tank location prior to and after cadaverine addition within each group and between groups. (A) Preferred tank location of bsxm1376 adults after addition of cadaverine (grey and on side indicated by +). Behavior was monitored prior to and after cadaverine addition for 5 min periods. bsxm1376/+ heterozygotes showed a mild increase in aversive behavior only in the first min after its addition [6 min (Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p = 0.0302), n = 15 adults for each group]. (B) Preference index before and after addition of cadaverine averaged over 5 min periods for bsxm1376/+ [0286 ± 0.077 and ?0.0926 ± 0.0812] and bsxm1376/m1376 adults [?0.0651 ± 0.0494 and 0.0773 ± 0.0561]. Two-way ANOVA reveals a significant effect of odor delivery [F(3, 149) = 5.323, p = 0.0031], group [F(14, 60) = 6.827, p < 0.0001] and interaction [F(42, 180) = 3.128, p < 0.0001]. Post-hoc analysis by Bonferroni?s multiple comparisons. Numbers represent the mean ± SEM. Dashed red lines in A and B denote midpoint of test tank. |