- Title
-
Reduced Acrolein Detoxification in akr1a1a Zebrafish Mutants Causes Impaired Insulin Receptor Signaling and Microvascular Alterations
- Authors
- Qi, H., Schmöhl, F., Li, X., Qian, X., Tabler, C.T., Bennewitz, K., Sticht, C., Morgenstern, J., Fleming, T., Volk, N., Hausser, I., Heidenreich, E., Hell, R., Nawroth, P.P., Kroll, J.
- Source
- Full text @ Adv Sci (Weinh)
|
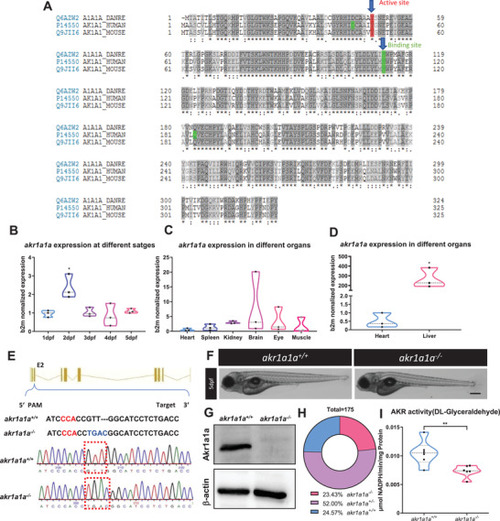
Sequence alignment of Akr1a1a across different species and generation of Akr1a1a knockout zebrafish by using CRISPR‐Cas9 technology. A) The amino acid alignment showed a high similarity between the different species on the active site (red frame) and binding site (green); first line: zebrafish AKR1a1a; second line: human AKR1a1; third line: mouse AKR1a1. B) |
|
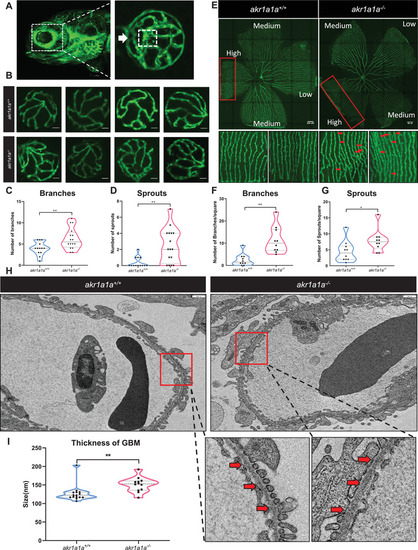
Retinal vasculature and renal alterations in |
|
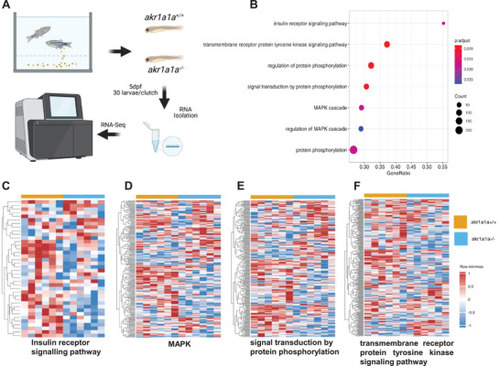
Down‐regulated insulin receptor signaling pathway and downstream pathways in |
|
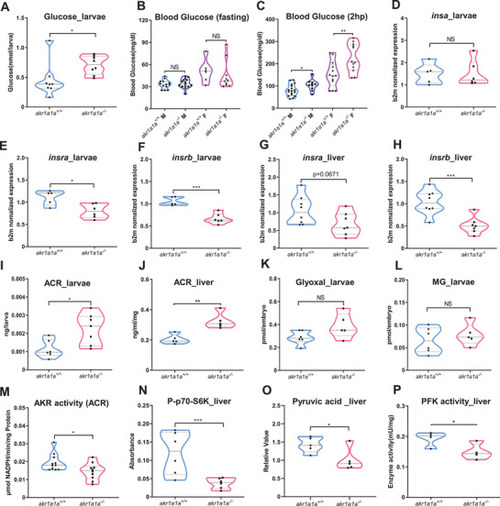
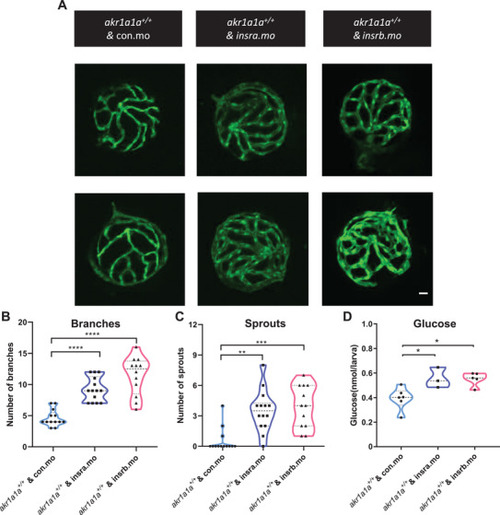
Altered glucose and insulin related gene expression in |
|
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
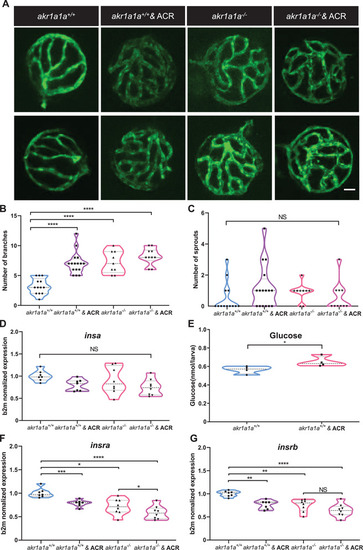
ACR induced alterations on retinal hyaloid vasculature and downregulation of |
|
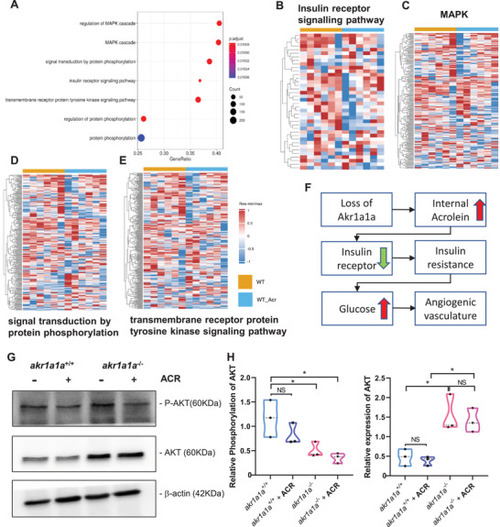
Down‐regulated insulin receptor signaling pathways in |
|
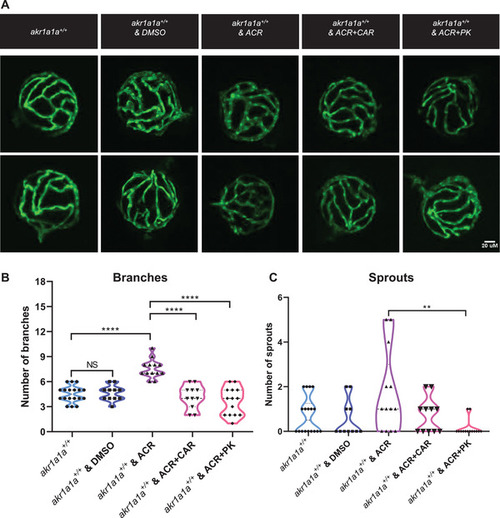
Carnosine and PK11195 can alleviate the effects caused by ACR on retinal hyaloid vasculature at 5 dpf. A) Representative confocal images of hyaloid vasculature. White scale bar: 20 µm. B) Quantification of hyaloid vasculature showed significant increasing numbers of branches in PHENOTYPE:
|