- Title
-
Dkk1 Controls Cell-Cell Interaction through Regulation of Non-nuclear β-Catenin Pools
- Authors
- Johansson, M., Giger, F.A., Fielding, T., Houart, C.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Cell
|
Dkk1 Disrupts Collective Cell Migration Independently of Cell Fate (A) Expression of (B) Progression of axial cells. Confocal maximum projections from shield to 80% epiboly stages in transgenic (C) Maximum projections of anterior axial cells from time-lapse confocal imaging of (D) Tracking of migrating axial cells from (E) Dkk1 cell migration behavior is independent of transcriptional regulation of β-catenin target genes. 24 h post-fertilization (hpf) embryos (left) and confocal maximum projections of EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Dkk1 Controls Organization of Filamentous Actin (A) Single-plane confocal images of the axis in (B) The loss of filamentous actin boundary organization induced by Dkk1 is not dependent on planar cell polarity (PCP) signaling. Single-plane confocal images of (C) Axial boundary straightness was quantified in phalloidin-labeled PHENOTYPE:
|
|
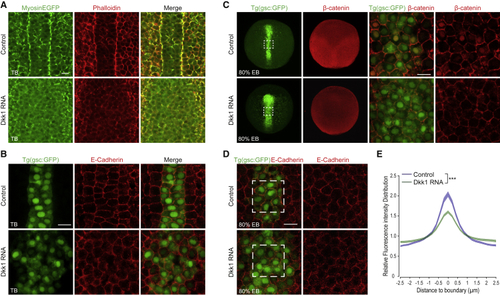
Dkk1 Reduces Cell Adhesion (A) Single-plane confocal imaging, dorsal view, of tail bud stage embryos (n = 6 of each condition) ubiquitously expressing EGFP-tagged myosin light chain (MyosinEGFP, green) stained with phalloidin (red) labeling filamentous actin. Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) Single-plane confocal images of axial cells in (C) Distribution of endogenous β-catenin (red) in (D) (E) Quantification of E-cadherin distribution across boundaries between neighboring axial (green) cells. Normalized intensity distributions across cell-cell boundaries show that Dkk1 expression reduces E-cadherin intensity at cell boundaries and broadens lateral distribution of E-cadherin intensity. Normalized intensity distributions were calculated for boundaries between six neighboring cells in five embryos for both control and Dkk1-expressing embryos. ∗∗∗p < 0.001. p value was calculated using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. |
|
Dkk1 Impacts Cell Shape and Orientation (A) Axial cell angles were measured in dorsally oriented tail bud stage (B) Dkk1-RNA-injected embryos (n = 6,176 cells) are less elongated and have a larger cell area than control embryos (n = 6,227 cells). Aspect ratio and cell area were quantified in |
|
Loss of Dkk1 Increases Cell Adhesion and Polarization (A and B) Single-plane confocal images of (C) Single-plane confocal images of β-catenin antibody-stained |
|
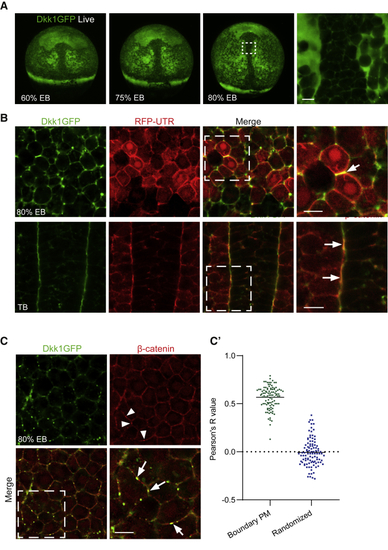
Ubiquitous Expression of GFP-Tagged Dkk1 Reveals Polarized Distribution of Dkk1 Protein at Tissue and Subcellular Levels (A) Live (B) Subcellular localization of Dkk1GFP in 80% epiboly (EB) and tail bud (TB) stage fixed embryos. Single-plane high magnification confocal images are shown of the region of interest in dashed white frames. Localization of Dkk1GFP to actin-rich membrane junctions was visualized by coexpression with red fluorescent protein-tagged actin-binding utrophin (RFP-UTR, red). Arrow highlights Dkk1GFP and RFP-UTR colocalization at a cell-cell junction. n = 6 for each condition. Scale bar, 20 μm. (C) Dkk1GFP colocalizes with plasma membrane-associated β-catenin (red)-positive puncta. Embryos were fixed shortly after heat shock. Arrowheads highlight β-catenin positive puncta (red), which colocalize with Dkk1GFP (arrows). (C’) Quantification of colocalization (n = 10). Mean Pearson’s R value is 0.60 for Dkk1-β-catenin and 0.03 for the randomized control. Scale bar, 20 μm. |
|
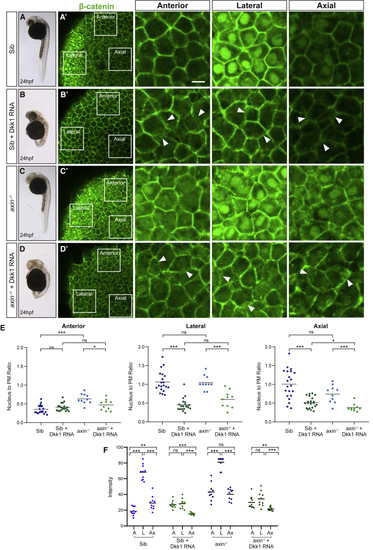
Dkk1 Sequesters β-Catenin at the Plasma Membrane (A–D) Sibling and (E) Nucleus to plasma membrane (PM) β-catenin (green) fluorescence intensity ratios quantified in anterior, lateral, and axial cells in sibling (Sib) and (F) Absolute levels of β-catenin nuclear expression, calculated by fluorescence intensity in 10 cells in each of the three regions per embryo. A, anterior; L, lateral; and Ax, axial. p |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 51(6), Johansson, M., Giger, F.A., Fielding, T., Houart, C., Dkk1 Controls Cell-Cell Interaction through Regulation of Non-nuclear β-Catenin Pools, 775-786.e3, Copyright (2019) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell