- Title
-
Odd skipped related 1 is a negative feedback regulator of Nodal-induced endoderm development
- Authors
- Terashima, A.V., Mudumana, S.P., Drummond, I.A.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
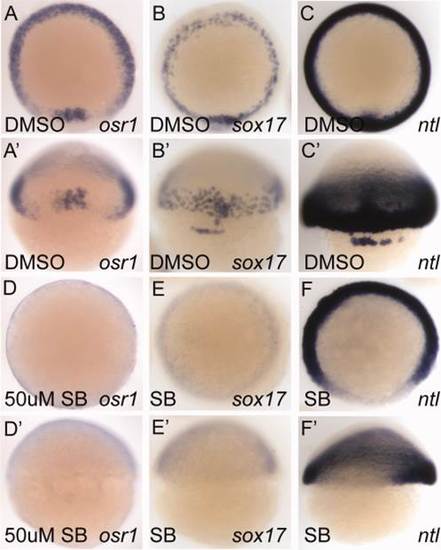
Pharmacological inhibition of Nodal signaling by SB505124 prevents osr1 expression. A?F: Animal pole views. A′?F′: Dorsal views. osr1 expression in the germ ring (A) and shield (A′) is absent in embryos treated with 50 µM SB505124 from 2.5 hpf until the embryo was fixed at shield stage (6 hpf, D, D′). sox17 expression (B, B′) in the endoderm and forerunner cells (B′) is also absent in SB505124-treated embryos (E, E′) demonstrating that a complete block of Nodal signaling is achieved by SB505124. ntl expression (C, C′) requires Nodal signaling only in the most dorsal region (F, F′). |
|
osr1 expression is disrupted in Nodal signaling mutants. A?D: Animal pole views. A′?D′: Dorsal views of the shield. At shield stage, osr1 is expressed in the shield and germ ring of the embryo (A, A′). Maternal zygotic one eyed pinhead (MZoep) mutants, which lack all Nodal signaling, show a complete loss of osr1 expression (B, B′). Mutants bonnie and clyde(bon) and schmalspur(sur), which have reduced Nodal signaling, show a reduction of osr1 expression (C, C′ and D, D′, respectively). |
|
osr1 expression is induced by ectopic Nodal signaling. Embryos were injected with either squint or tar*/Acvr1b RNA at 1-cell stage fixed at 4.5 hpf. A?F: Animal pole views. A: osr1 is normally expressed in the margin of the embryo. Both squint and tar* can induce ectopic expression of osr1 in animal pole cells. Ectopic expression of sox17 (D?F) in these embryos confirms ectopic activation of Nodal signaling. |
|
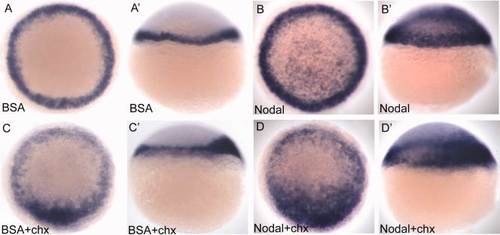
osr1 is a direct target of Nodal signaling. A?D: Animal pole view. A′?D′: Lateral view, dorsal to the right. Embryos (4 hpf) were injected with 2 ng recombinant mouse Nodal protein (B, B′) or 400 ng BSA (A, A′). Half of the injected embryos were treated with 50 µg/ml cycloheximide (C, C′, D, D′), and all were fixed after 1 hr and 20 min. Nodal protein strongly induces ectopic osr1 expression in the animal pole of the embryo (B, B′). Ectopic expression is induced in the presence of cycloheximide indicating that osr1 is a direct target of Nodal signaling (D, D′). |
|
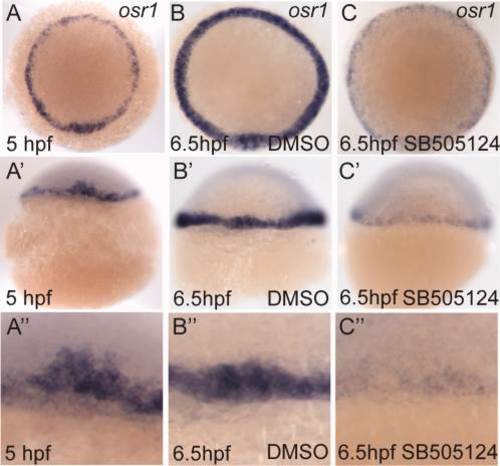
Nodal signaling is required to maintain osr1 expression. A-C: Animal pole views. At 5 hpf (A, A′, A′′) osr1 is expressed in the margin of the embryo. Embryos treated with 50 µM SB505124 from 5 hpf to 6.5 hpf show a dramatic reduction in levels of osr1 mRNA (C, C′, C′′) as compared to DMSO-treated controls (B, B′, B′′) indicating that osr1 mRNA is degraded in the absence of Nodal signaling. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Loss of osr1 increases the number of sox32-expressing endoderm cells. sox32-expressing cells were counted in osr1 morphants and embryos injected with a control morpholino. A, B: Lateral views of control and osr1 morphant embryos, respectively (dorsal is on the right). Cells were counted in identical-sized windows (area = 0.05 mm2) (A′, B′) on both lateral sides and the dorsal side (shield). C: Average number of cells per 0.05mm2 on each side. D: Welch′s t-test analysis indicates that osr1 morphant embryos show a significant increase in the number of sox32-expressing cells. n=7 (control); n=10 (osr1 MO). Scale bar in A′, B′ = 0.1 mm. |
|
osr1 expression is independent of sox32 and acts to limit endodermal cell differentiation. A, B: Lateral views, dorsal on the right. A′, B′: Animal pole views, dorsal bottom. osr1 expression in the germ ring (A, A′) is unaffected in sox32 morphant embryos, which lack all endoderm derivatives. C?J: Animal pole views, dorsal bottom. foxa2 expression in control (C), osr1 knockdown (D), sox32 knockdown (E), and combined osr1, sox32 knockdown (F) reveals increased foxa2-expressing cells in osr1- and combined osr1-, sox32-deficient embryos. sox17 expression in control (G), osr1 knockdown (H), sox32 knockdown (I), and combined osr1, sox32 knockdown (J) reveals increased sox17-expressing cells in osr1- and combined osr1-, sox32-deficient embryos. |