- Title
-
nanos3 maintains germline stem cells and expression of the conserved germline stem cell gene nanos2 in the zebrafish ovary
- Authors
- Beer, R.L., and Draper, B.W.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
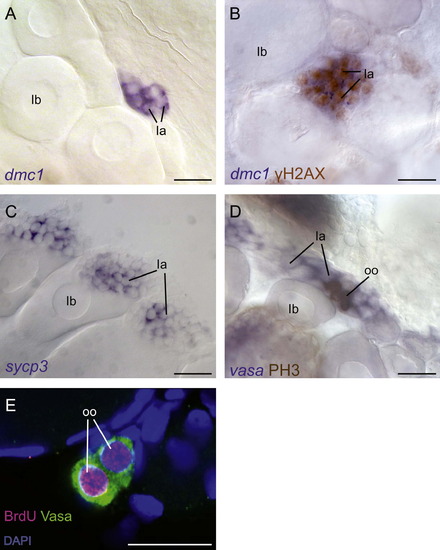
Mitotic and early meiotic germ cells are present in the adult ovary. (A?D) RNA in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry shows that dmc1 expressing cells (blue) are present in the adult ovary (A), and that these cells are also positive for γH2AX protein (brown), which labels cells containing double-strand DNA breaks (B). RNA in situ hybridization shows that sycp3 expressing cells are present in the adult ovary (C). (D) Mitotic germ cells are present in the adult ovary as vasa RNA positive germ cells (blue) co-labeled for phosphorylated histone H3 (PH3; brown). (E) BrdU+ Vasa+ <20 μm germ cells are present in the adult ovary. All images are from whole mount preparations. Scale bars: 50 μm (A?D), 20 μm (E). Stage Ia oocytes (Ia), stage Ib oocytes (Ib) and oogonia (oo). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
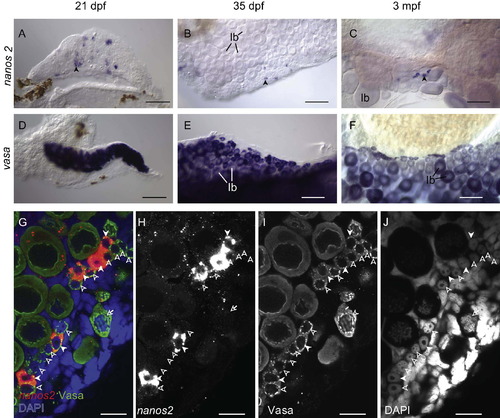
nanos2 is expressed in a small subset of pre-meiotic oogonia. (A?C) RNA in situ hybridization shows that nanos2 (blue staining in A) is expressed in a subset of <20 μm germ cells, in comparison to vasa (blue staining in D) that is expressed in all germ cells. While nanos2-expressing cells are initially randomly distributed at 21 dpf (A), they become restricted to the lateral edges of the ovary by about 35 dpf (B). In adult ovaries, nanos2 continues to be expressed in a subset of <20 μm germ cells (C) as compared to vasa, which is expressed in all germ cells (F). Arrows in A?C identify single nanos2-expressing cells. (G?J) Fluorescent in situ hybridization for nanos2 mRNA and immunohistochemistry for Vasa protein (G) confirms that all nanos2-expressing cells (red in G; white in H) are germ cells, as they also express Vasa (green in G; white in I). Nuclear morphology, as revealed by DAPI staining (blue in G; white in J) indicates that nanos2 is expressed in a subset of pre-meiotic oogonia, which have characteristic uncondensed chromatin and prominent nucleoi. In G?J, nanos2-expressing cells, nanos2-negative oogonia, and meiotic oocytes, are indicated by filled arrowheads, empty arrowheads, and arrows, respectively. All images are from whole mount preparations. Stage Ib oocyte (Ib); Scale bars: 100 μm (A?F), 20 μm (G?J). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
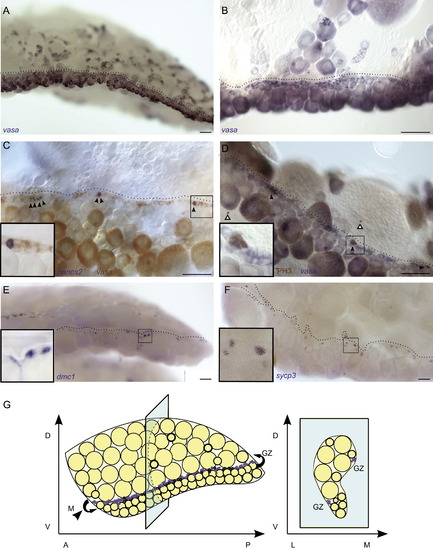
The germinal zone is the (A and B) vasa RNA in situ hybridization demonstrates that the <20 μm germ cell population in 3 mpf adult ovaries localizes to the germinal zone (dotted line) which is readily identifiable at low magnification (A), and higher magnification (B). (C) Two color RNA in situ hybridization shows that nanos2-expressing cells (blue, indicated by arrowheads) co-localize with the vasa-expressing <20 μm cells (red) in the germinal zone. (D) RNA in situ and immunohistochemistry co-staining reveal that all mitotic germ cells (brown PH3+ and blue vasa+, indicated by black arrowhead) are located in the germinal zone. White arrowheads indicate PH3+vasa- somatic cells. (E and F) dmc1+ cells (blue in E), and sycp3+ cells (blue in F) localize to the germinal zone. Insets in C?F show higher magnification of boxed region. All images are from whole mount preparations. (G) Three-dimensional illustration of an adult ovary. <20 μm cells are indicated in purple. A-anterior, P-posterior, D-dorsal, V-ventral, L-lateral, M-medial and GZ-germinal zone. Scale bars: 100 μm (A, E and F), 50 μm (B?D). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
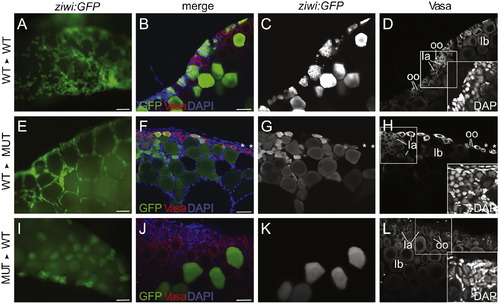
nanos3 is required cell-autonomously in the <20 μm germ cell population. (A?L) Genetic germline chimeras were created by transplanting Tg(ziwi:EGFP) donor germ cells into EGFP-negative hosts, and the contribution of EGFP+ germ cells was analyzed at 60 dpf. (A, E and I) Low magnification images, where donor derived cells are green. All others panels are higher magnification confocal images. (A?D) In controls, wild-type Tg(ziwi:EGFP) germ cells were able to equally contribute to the <20 μm germ cell population as wild-type host germ cells (WT′WT, n=10). (E-H) Wild-type Tg(ziwi:EGFP) germ cells are the only <20 μm germ cells detected in a nanos3 mutant host ovary (WT′MUT, n=5). (I?L) Conversely, nanos3 mutant; Tg(ziwi:EGFP) donor germ cells are not able to contribute to the <20 μm germ cell population in wild-type host ovaries (MUT′WT, n=2). B, F and J show merged images of EGFP expressing donor cells (green), Vasa expressing germ cells (red), and DNA (blue). C, G, and K, show endogenous GFP expression. D, H and L show Vasa protein localization, and inset shows the DNA morphology of DAPI stained cells boxed in main image. All images are from whole mount preparations. Scale bars: 200 μm (A, E and I), 20 μm (B, F and J). Stage Ia oocytes (Ia), stage Ib oocytes (Ib) and oogonia (oo). |
|
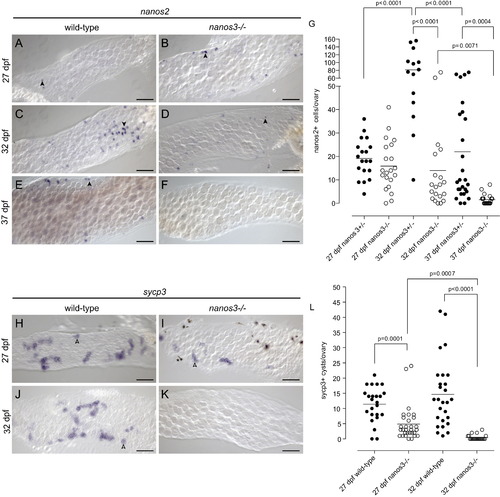
nanos2+ and sycp3+ cells are not maintained in nanos3 mutant juvenile ovaries. (A?G) Analysis of nanos2-expressing cells by in situ hybridization in wild-type and nanos3 mutant 27?37 dpf ovaries. nanos2+ cells are easily detected in wild-type and mutant ovaries at 27 dpf. (A and B). At 32 dpf, nanos2+ cells are easily detectable in both wild-type and mutant ovaries, but are more abundant in wild-type (C-D). However, by 37 dpf nanos2+ cells are not detected in mutants, but are present in wild-type ovaries (E and F) Arrowheads identify representative nanos2-expressing cells in A?E. (G) Quantification of nanos2+ cells per ovary in wild-type and mutant ovaries. (H?L) Analysis of sycp3 expressing germ cell cysts by in situ hybridization in wild-type and mutant ovaries from 27?37 dpf. Actively differentiating sycp3 expressing germ cell cysts are present in both wild-type and mutant tissue at 27 dpf (H and I). By 32 dpf sycp3+ cysts cannot be detected in mutant ovaries (J and K). Arrowheads identify representative sycp3 expressing germ cell cysts (blue) in H?J, while an asterisk in I identifies a representative melanocyte pigment cell (black). (L) Quantification of sycp3+ cysts per ovary in wild-type and mutant ovaries. All images are from whole mount preparations. Scale bars: 50 μm. p-values indicate statistically significant differences. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
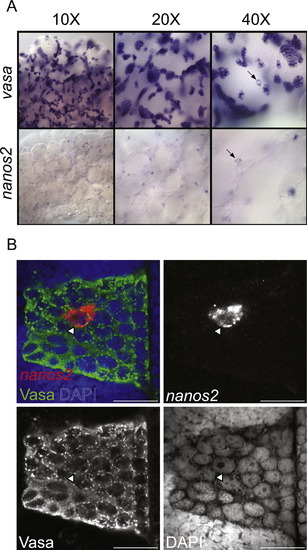
nanos2 is expressed in a subset of pre-meiotic spermatogonia. (A) RNA in situ hybridization shows that nanos2 (blue staining in second row) is expressed in a subset of early germ cells, in comparison to vasa (blue staining in top row) that is expressed in all germ cells. vasa mRNA is expressed in all early spermatogonia and spermatocytes, while nanos2 expression restricted to clusters of 3?4 cells that are randomly distributed throughout the testis. (B) Fluorescent in situ hybridization for nanos2 mRNA and immunohistochemistry for Vasa protein confirms that all nanos2-expressing cells (red) are germ cells, as they are also express Vasa (green). Nuclear morphology, as revealed by DAPI staining (blue) indicates that nanos2 is expressed in a subset of pre-meiotic spermatogonia, which have characteristic uncondensed chromatin and prominent nucleoli. In A and B nanos2-expressing cells are indicated by arrows. All images are from whole mount preparations. Scale bar: 20 μm. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 374(2), Beer, R.L., and Draper, B.W., nanos3 maintains germline stem cells and expression of the conserved germline stem cell gene nanos2 in the zebrafish ovary, 308-318, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.