- Title
-
The Methyltransferases PRMT4/CARM1 and PRMT5 Control Differentially Myogenesis in Zebrafish
- Authors
- Batut, J., Duboé, C., and Vandel, L.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
- Probe
- MGC:110669
- Supplier
|
PRMT5 and CARM1 are differentially expressed during zebrafish embryogenesis. (A?D) CARM1 and PRMT5 in situ hybridization at the indicated stages. (A) Animal view (av), lateral view (lv, dorsal to right for 6 hpf, anterior to left for 24 hpf) and dorsal views (dv, anterior to top) of whole-mount zebrafish in situ hybridization. (B) Dorsal view (anterior to top) of CARM1 and PRMT5 expression during somitogenesis. (C) Dorsal flat-mounts of 14 ss embryos stained for CARM1 and PRMT5. A magnified region is shown on the right. (D) Transverse sections (30 μm) of the magnified region in (C) showing undetectable PRMT5 expression in adaxial cells (arrow), whereas CARM1 is ubiquitously expressed in the somite. *, Presomitic Mesoderm (PSM); ss, somite stage. |
|
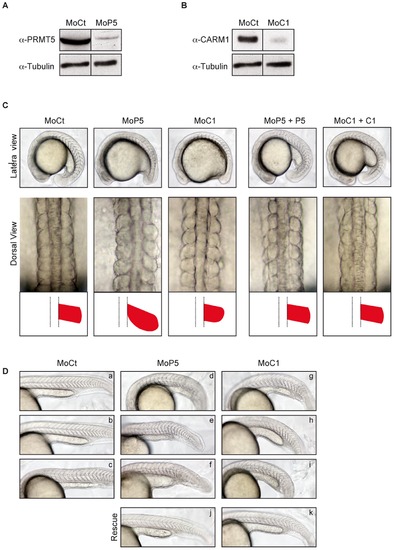
PRMT5 and CARM1 morphants exhibit distinct and specific phenotypes. (A, B) One-cell embryos were injected with 6 ng of either a control morpholino (MoCt), or a morpholino against PRMT5 (MoP5) or CARM1 (MoC1). Embryos were collected at 14 ss and were processed for immunoblotting to detect (A) PRMT5 and (B) CARM1 expression. Tubulin was used as a loading control. (C) Lateral (anterior to left) and dorsal view (anterior to top) of 14?16 ss zebrafish embryos injected with the indicated morpholino. Rescue experiments by injection of the cognate mRNA are shown to the right (MoP5+P5, MoC1+C1). Schematic representations of each somite are shown below the corresponding dorsal view. Mo, morpholino. (D) Phenotypes of 24 hpf embryos injected with increasing doses (3-6-12 ng) of Control (MoC, a?c), PRMT5 (MoP5, d?f) or CARM1 (MoC1, g?i) morpholinos or 6 ng of morpholino against PRMT5 or CARM1 co-injected with their corresponding mRNA (MoP5+P5, j and MoC1+C1, k) for rescue experiment. Embryos were visualized at 24 hpf. Lateral view, anterior to the left. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
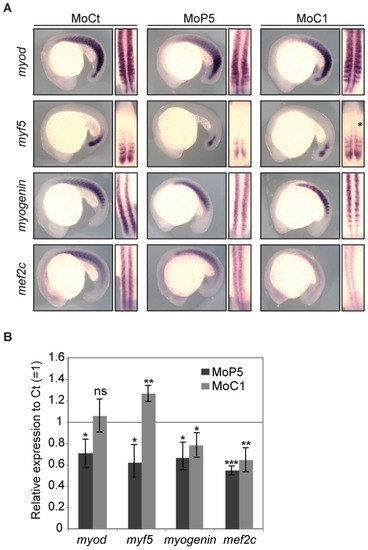
PRMT5 and CARM1 regulate myogenic factor expression. Expression of myod, myf5, myogenin and mef2c at 18 ss in embryos injected with the indicated Mo by (A) whole-mount in situ hybridization (lateral view, anterior to left; a dorsal view, anterior to top, is shown on the right; *, anterior expression of myf5 in CARM1 morphant) or (B) real time PCR. Error bars represent standard deviations. *, P<0.01 statistically significant; **, P<0.001, very statistically significant; ***, P<0.0001, extremely statistically significant; ns, not statistically significant, using a t-test. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
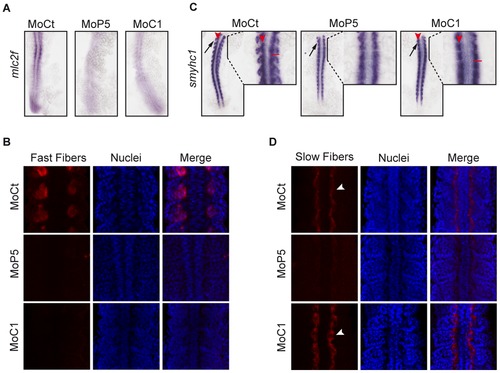
CARM1 and PRMT5 differentially control slow and fast myogenesis. (A, C) Dorsal flat-mounted 14 ss embryos (anterior to top) injected with the indicated Mo were analyzed by whole-mount in situ hybridization for (A) mlc2f and (C) smyhc1 or (B, D) immunohistochemistry for (B) fast fibers, (D) slow fibers. In (C) a magnification of the area indicated by the black line is shown to the right of each panel. Arrow or white arrowhead, lateral expression; red arrowhead, medial expression; red bar, length of one somite. (B, D) Z-stack sections of the most anterior somites are shown. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
CARM1 controls slow fiber localization. (A, B) One-cell stage embryos were injected with a CARM1 morpholino (MoC1) or a control morpholino (MoCt) and were analyzed at 24 hpf by whole-mount immunohistochemistry for slow fibers. (A) Lateral views, anterior to the left of 3D confocal reconstructions projected over four somites, (A2) single confocal scans at the dorsoventral level of the notochord and (A3) corresponding cross-section views. (B) Rostral cross-sections (50 μm) of 22 ss embryos injected with the indicated morpholino. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
CARM1 and PRMT5 control cell cycle arrest during development. (A) Dorsal flat-mounted of 14 ss embryos (anterior top) injected with the indicated Mo or co-injected with the corresponding mRNA for rescue experiments were analyzed by immunohistochemistry for mitotic cells with an anti phospho-H3 (Ser10) antibody. (B) Representation of the number of mitotic cells per somite. Error bars represent standard deviations. ***, P<0.0001 extremely statistically significant; ns, not statistically significant, using a t-test. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
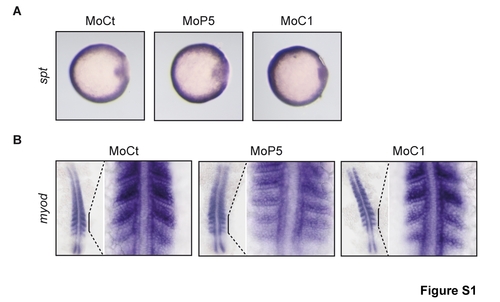
PRMT5 and CARM1 regulate myogenic factor expression. (A?B) In situ hybridization of embryos with the indicated mRNA probe and injected with the indicated Mo (A) at the shield stage or (B) at 14 ss. (A) Animal view (dorsal to right). (B) Dorsal flat-mounted embryos stained for myod with a magnified region to the right. |
|
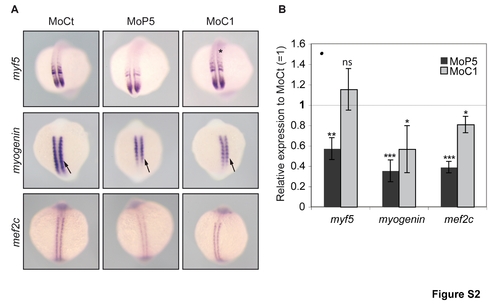
PRMT5 and CARM1 regulate specifically myogenic factors expression at 14-somite stage (14 ss). Whole-mount in situ hybridization of embryos injected at one-cell stage with the indicated morpholino (Mo). Experimentrs were done twice with n = 20 for each condition. Embryos were collected at 14 ss and were analyzed for myogenic factors expression by (A) in situ hybridization, lateral view, anterior to the left or by (B) real time PCR with standard deviations relative to a control morpholino. Q-PCR procedures are detailed in the methods section. (A) Asterisk, anterior expression of myf5 in CARM1 morphant; arrow, down regulation of myogenin expression in the posterior somites in PRMT5 morphant. (B) Error bars represent standard deviations. *, P<0.01; **, P<0.001; ***, P<0.0001; ns, not statistically significant. |
|
Knock down of CARM1 or PRMT5 does not affect their mutual expression. One-cell stage embryos injected with either a control morpholino (MoCt), or a morpholino against PRMT5 (MoP5) or against CARM1 (MoC1) (left panels). Mos were co-injected with either PRMT5 mRNA (MoP5+P5) or CARM1 (MoC1+C1) (right panels). Embryos were collected at 14-somite stage and analyzed for CARM1 and PRMT5 expression by in situ hybridization. Note that PRMT5 expression is strongly enhanced in MoP5-injected embryos (white asterisk), which can be rescued by the co-expression of PRMT5 mRNA (black asterisk). |
|
PRMT5 and CARM1 mRNAs rescue specifically myogenin expression affected by their cognate morpholino(*). One-cell stage embryos were injected with either a morpholino control (MoCt), or a morpholino against PRMT5 (MoP5) or CARM1 (MoC1), alone or in combination with either PRMT5 or CARM1 mRNA. Embryos were collected at 14-somite stage and were analyzed for myogenin expression by in situ hybridization. Experiments were done twice (n = 22 for each condition). |
|
CARM1 (C1) and PRMT5 (P5) control myogenesis differentially. (A,B) One-cell stage embryos were injected with the indicated morpholino (Mo) or a control Mo (MoCt) and were analyzed by whole-mount immunohistochemistry for (A) slow fibers and (B) fast fibers at 18-somite stage. Lateral views, anterior to the left. Both slow and fast fiber formation require PRMT5 (n = 12). CARM1 is necessary for fast fiber specification but does not affect slow fiber specification (n = 15). Antibodies used were: F310 fast Myosin Light Chain (DSHB), F59 slow Myosin Heavy Chain (DSHB) and appropriate Alexa Fluor-conjugated secondary antibodies (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, US). Nuclei were stained with TO-PRO3 (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, US) according to the manufacturer′s protocol. |