- Title
-
Zebrafish cdx1b regulates differentiation of various intestinal cell lineages
- Authors
- Chen, Y.H., Lu, Y.F., Ko, T.Y., Tsai, M.Y., Lin, C.Y., Lin, C.C., and Hwang, S.P.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
cdx1b is expressed in the intestine. A: A 100-hr post-fertilization (hpf) embryo hybridized with a cdx1b antisense RNA probe. B-E: Histological analyses of paraffin sagittal sections of a cdx1b antisense RNA-hybridized embryo. Scale bars = 100 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
cdx1b antisense morpholino oligonucleotide (MO) knockdown analyses. A-D: Wild type (A) and cdx1b MO-injected (B-D) 72 hr post-fertilization (hpf) embryos. E-H: Wild-type (E) and cdx1b MO-injected (F-H) 96-hpf embryos. I-L: Histological analyses of paraffin sagittal sections of a 96-hpf cdx1b-4mm-MO-injected embryo. Higher magnifications depicting the intestinal bulb (J), mid-intestine (K), and posterior intestine (L). M-P: Histological analyses of paraffin sagittal sections of a 96-hpf cdx1b morphant. Higher magnifications depicting the intestinal bulb (N), mid-intestine (O), and posterior intestine (P). Arrows indicate locations of goblet cells in the mid-intestine (K,O). Scale bars = 100 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Inhibition of cdx1b function affects the development of goblet cells in the intestine. A-D: Wild type (A), cdx1b-4mm MO-injected (B), and cdx1bMO-injected (C, D) 102-hr post-fertilization (hpf) embryos were hybridized with agr2 antisense RNA probes. E-H: Wild type (E), cdx1b-4mm MO-injected (F), and cdx1b MO-injected (G, H) 102-hpf deyolked embryos that had been hybridized with agr2 antisense RNA probes. I-L: Wild type (I), cdx1b-4mm MO-injected (J), and cdx1b MO-injected (K, L) 102-hpf embryos were stained with alcian blue. M-P: Higher magnifications of alcian blue-stained paraffin sagittal sections corresponding to the mid-intestine (M, O) and posterior intestine (N, P) of 102-hpf cdx1b-4mm MO-injected (M, N) and cdx1b MO-injected (O, P) embryos. Arrows indicate locations of alcian blue-stained goblet cells in the intestine. Q-T: Wild type (Q), cdx1b-4mm MO-injected (R), and cdx1b MO-injected (S, T) 120-hpf embryos were stained with alcian blue. U: Comparison of agr2-expressing goblet cell numbers in the intestine of 102-hpf wild type (n = 28), cdx1b-4mm MO-injected (n = 28), and cdx1b MO-injected (n = 21) embryos. V: Comparison of alcian blue-stained goblet cell numbers in the intestine of wild type (n102 = 20; n120 = 21), cdx1b-4mm MO-injected (n102 = 23; n120 = 21), and cdx1b MO-injected (n102 = 22; n120 = 23) embryos from 102 (red bars) and 120 hpf (green bars). W: Comparison of the percentages of intestinal goblet cell numbers reveals decreased goblet cell numbers in cdx1b MO-injected (n = 7) embryos compared to wild type (n = 5) and cdx1b-4mm MO-injected (n = 5) embryos. Error bars indicate standard errors. Student's t-test was conducted to compare cdx1b MO-injected embryos with either wild type or cdx1b-4mm MO-injected embryos. *P < 0.001 in both comparisons. An, anus; gc, goblet cell; mc, mucus cell; ov, otic vesicle; ph, pharynx. Scale bars = 100 μm. |
|
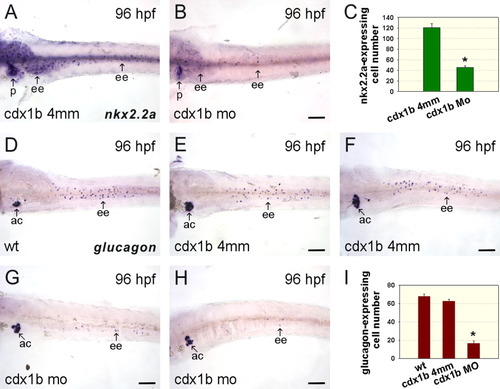
Knockdown of cdx1b function affects the development of enteroendocrine cells in the intestine. A, B: cdx1b-4mm MO-injected (A) and cdx1b MO-injected (B) 96-hr post-fertilization (hpf) deyolked embryos hybridized with nkx2.2a antisense RNA probes. C: Comparison of nkx2.2a-expressing enteroendocrine cell numbers in cdx1b-4mm MO-injected (n = 21) and cdx1b MO-injected (n = 21) embryos. D-H: Wild type (D), cdx1b-4mm MO-injected (E, F), and cdx1b MO-injected (G, H) 96-hpf deyolked embryos hybridized with glucagon antisense RNA probes. I: Comparison of glucagon-expressing enteroendocrine cell numbers in wild type (n = 15), cdx1b-4mm MO-injected (n = 31), and cdx1b MO-injected (n = 29) embryos. Error bars indicate standard errors. Student's t-test was conducted to compare cdx1b MO-injected embryos with either wild type or cdx1b-4mm MO-injected embryos. *P < 0.001 in both comparisons. Ac, pancreatic α cells; ee, enteroendocrine cells; p, pancreas. Scale bars = 100 μm. |
|
Knockdown of cdx1b function affects PepT1 expression in enterocytes. A-C: Wild type (A), cdx1b-4mm MO-injected (B), and cdx1b MO-injected (C) 80-hr post-fertilization (hpf) embryos hybridized with PepT1 antisense RNA probes. D-F: Wild type (D), cdx1b-4mm MO-injected (E), and cdx1b MO-injected (F) 96-hpf embryos hybridized with PepT1 antisense RNA probes. G: Q-PCR indicated decreased PepT1 expression in cdx1b morphants compared to wild type and cdx1b-4mm MO-injected embryos from 80 to 102 hr of development. Error bars indicate standard errors. Results from duplicated experiments are shown. Significant differences between ΔΔCt values based on Student's t-test were used to indicate different gene expressions expressed as fold changes. Student's t-test was conducted to compare cdx1b MO-injected embryos with either wild type or cdx1b-4mm MO-injected embryos.*P < 0.05 in both comparisons. H, I: cdx1b-4mm MO-injected (H) and cdx1b MO-injected (I) 102-hpf embryos hybridized with PepT1 antisense RNA probes. Ib, intestinal bulb. Scale bars = 100 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) revealed abnormal ultrastructural morphology in the intestine of cdx1b morphants. A-D: EM sagittal sections of the intestinal bulb (A, C) and mid-intestine (B, D) of 80-hr post-fertilization (hpf) wild type (A, B) and cdx1b MO-injected (C, D) embryos. E-H: EM sagittal sections of the intestinal bulb (E, G) and mid-intestine (F, H) of 96-hpf wild type (E, F) and cdx1b MO-injected embryos (G, H). Arrows indicate the locations of goblet cells in the mid-intestine. Scale bars =10 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Overexpression of cdx1b increased goblet cell numbers in the intestine. A-D: Wild type (A), lacZ mRNA-injected (B), and cdx1b mRNA-injected (C, D) 98-hr post-fertilization (hpf) deyolked embryos hybridized with agr2 antisense RNA probes. E-H: Wild type (E), CMV-GFP-injected (F), and CMV-cdx1b-injected (G, H) 98-hpf deyolked embryos stained with alcian blue. The arrowhead in G indicates secreted mucin in the lumen. I: Comparison of agr2-expressing goblet cell numbers in the intestine of lacZ (n = 20) and cdx1b (n = 20) ectopically expressed embryos. J: Comparison of alcian blue-stained goblet cell numbers in the intestine of GFP (n = 20) and cdx1b (n = 20) ectopically expressed embryos. Error bars indicate standard errors. *P < 0.001. Gc, goblet cell. Scale bars =100 μm. |
|
Effects of ectopic cdx1b expression on the development of enteroendocrine cells in the intestine. A-E: Wild type (A), CMV-GFP-injected (B, C), and CMV-cdx1b-injected (D, E) 96-hr post-fertilization (hpf) deyolked embryos hybridized with glucagon antisense RNA probes. F: Comparison of glucagon-expressing enteroendocrine cell numbers between CMV-GFP-injected (n = 29) and CMV-cdx1b-injected (n = 27) embryos. Error bars indicate standard errors. *P < 0.001. Ac, pancreatic α cells; ee, enteroendocrine cells. Scale bars = 100 μm. |
|
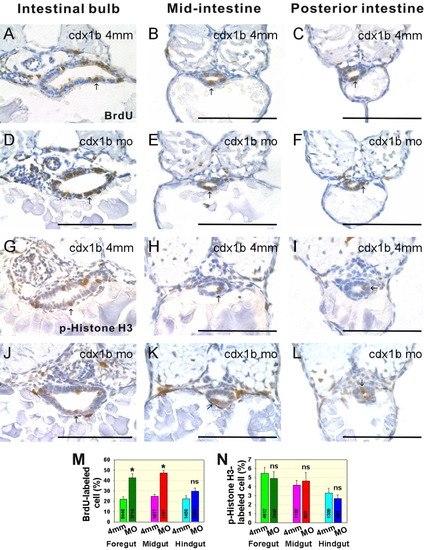
Cell proliferation affected in cdx1b morphants. A-F: BrdU-labeled paraffin transverse sections corresponding to the intestinal bulb (A, D), mid-intestine (B, E), and posterior-intestine (C, F) of respective 72-hr post-fertilization (hpf) cdx1b-4mm-MO-injected (A-C) and cdx1b MO-injected (D-F) embryos. Arrows indicate BrdU-labeled cells. G-L: p-Histone H3-stained cryostat transverse sections corresponding to intestinal bulb (G, J), mid-intestine (H, K), and posterior-intestine (I, L) of respective 72-hpf cdx1b-4mm-MO-injected (G-I) and cdx1b MO-injected (J-L) embryos. Arrows indicate p-Histone H3-stained cells. M: Comparison of the percentages of BrdU-labeled cells in the intestinal bulb, mid-intestine, and posterior-intestine of cdx1b-4mm-MO-injected (n=8) and cdx1b MO-injected (n=9) embryos. N: Comparison of the percentages of p-Histone H3-stained cells in the intestinal bulb, mid-intestine, and posterior-intestine of cdx1b-4mm-MO-injected (n = 5) and cdx1b MO-injected (n = 6) embryos. Total cell number counted for intestinal bulb, mid-intestine, and posterior intestine of both 72-hpf cdx1b -4mm-MO-injected and cdx1b MO-injected embryos are shown. Error bars indicate standard errors. *P < 0.001. Ns, not significant. Scale bars = 100 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
TUNEL assay revealed a low level of apoptosis in cdx1b morphants. A-I: Paraffin sagittal sections corresponding to the intestinal bulb (A, D, G), mid-intestine (B, E, H), and posterior-intestine (C, F, I) of respective 72-hr post-fertilization (hpf) wild type (A-C), cdx1b-4mm-MO-injected (D-F), and cdx1b MO-injected (G-I) embryos treated with TUNEL reactions using FITC-dUTP (green). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Embryos in A-C and G-I are oriented with the anterior to the left, while those in D-F are oriented with the anterior to the right. Scale bars = 100 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
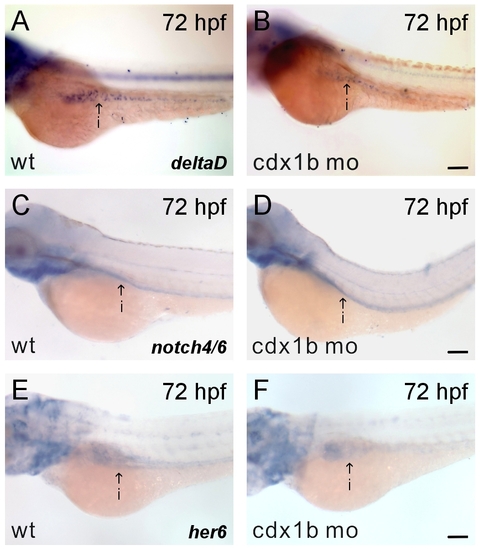
Notch signaling was not affected in cdx1b morphants. A-F: Respective 72-hr post-fertilization (hpf) wild type (A, C, E) and cdx1b MO-injected (B, D, F) embryos hybridized with delta D (A, B), notch4/6 (C, D), or her6 (E, F) antisense RNA probes. I, intestine. Scale bars = 100 μm. |
|
Comparison of sox2 expression patterns in wild type and cdx1b MO-injected embryos. A-D: Respective 72-hr post-fertilization (hpf) wild type (A,C) and cdx1b MO-injected (B,D) embryos hybridized with sox2 antisense RNA probes. Higher-magnification images are shown in C and D. Es, esophagus; ph, pharynx; sb, swim bladder. Scale bars= 100 μm. |