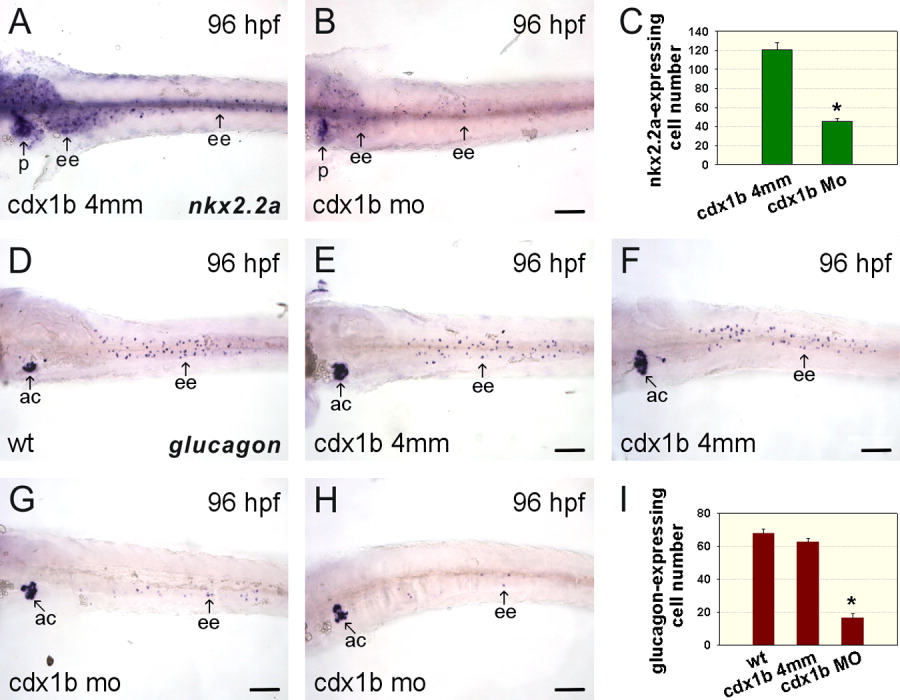
Fig. 4 Knockdown of cdx1b function affects the development of enteroendocrine cells in the intestine. A, B: cdx1b-4mm MO-injected (A) and cdx1b MO-injected (B) 96-hr post-fertilization (hpf) deyolked embryos hybridized with nkx2.2a antisense RNA probes. C: Comparison of nkx2.2a-expressing enteroendocrine cell numbers in cdx1b-4mm MO-injected (n = 21) and cdx1b MO-injected (n = 21) embryos. D-H: Wild type (D), cdx1b-4mm MO-injected (E, F), and cdx1b MO-injected (G, H) 96-hpf deyolked embryos hybridized with glucagon antisense RNA probes. I: Comparison of glucagon-expressing enteroendocrine cell numbers in wild type (n = 15), cdx1b-4mm MO-injected (n = 31), and cdx1b MO-injected (n = 29) embryos. Error bars indicate standard errors. Student's t-test was conducted to compare cdx1b MO-injected embryos with either wild type or cdx1b-4mm MO-injected embryos. *P < 0.001 in both comparisons. Ac, pancreatic α cells; ee, enteroendocrine cells; p, pancreas. Scale bars = 100 μm.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Dev. Dyn.