- Title
-
Recapitulation of human betaB1-crystallin promoter activity in transgenic zebrafish
- Authors
- Hou, H.H., Kuo, M.Y., Luo, Y.W., and Chang, B.E.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
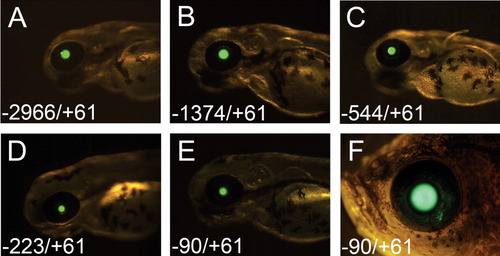
Promoter activity of the human βB1-crystallin gene demonstrated by expression of EGFP (enhanced green fluorescent protein) in transient transgenic experiments in zebrafish. A-E: Constructs of serially deleted promoter fragments shown in Figure 1 were analyzed in zebrafish embryos. The reporter gene, EGFP, was specifically observed to be expressed in the whole lens in most embryos. F: Some F0 transient transgenic fish were raised to adulthood, and showed robust expression of EGFP in the lens (F, here with the construct of the -90/+61-bp promoter). |
|
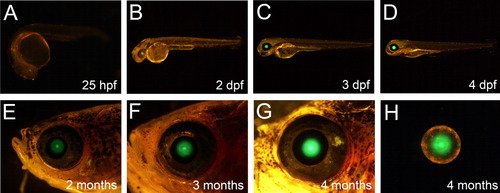
A stable line of transgenic zebrafish with integration of the -90/+61-bp human βB1-crystallin promoter-EGFP chimeric gene reiterates the specific human βB1-crystallin promoter activity. A-D: Expression of EGFP is detectable in the lens from the 25-hr post-fertilization (hpf) stage (A) and persists in the early embryo stages (B-D). E-H: When examined from 2- to 4-month stages (E-G), however, the expression of EGFP had abruptly ceased in the cortical region of the adult lens (H). |
|
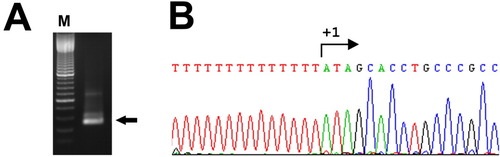
Mapping of the transcriptional initiation site of the human βB1-crystallin gene in a stable line of transgenic zebrafish. A: The -90/+61-bp human βB1-crystallin promoter-integrated stable line of transgenic zebrafish was utilized to define the transcriptional initiation site. 5'RACE was performed, and the PCR product showed a major band (arrow indicated). M: 100-bp DNA marker. B: The precise initiation site was revealed by sequencing, beginning with an A base. |
|
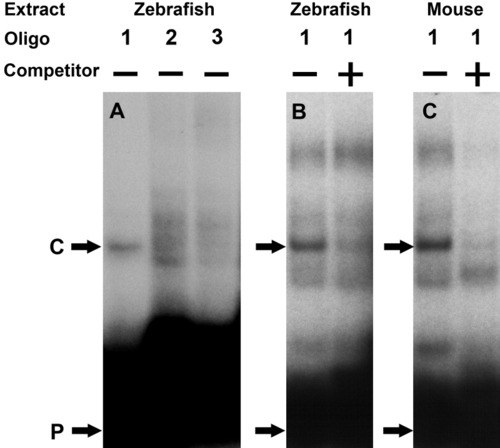
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) demonstrating a cis-regulatory element in the proximal promoter region. A: Oligonucleotides (1, 2, 3) harboring the -98/-19-bp proximal promoter region were tested with zebrafish embryo extract. B,C: The specificity of the DNA-protein complex was further analyzed using zebrafish embryos and mouse lens nuclear extract in the presence of non-radioactive competitive probes. The probes and specific DNA-protein complexes are, respectively, indicated by the letters P and C. The precise sequences of these oligonucleotides are marked in Figure 6A. |
|
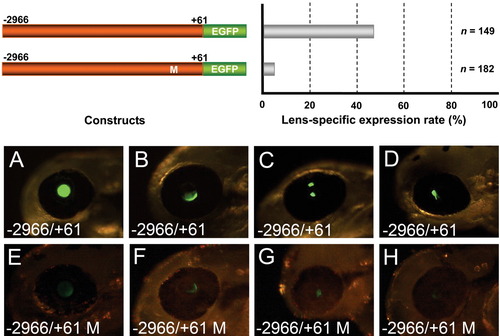
Maf binding cis-element is crucial for the upstream promoter activity of the human βB1-crystallin gene. Top: A point mutation was introduced in the single Maf binding site of the human $beta;B1-crystallin promoter. The mutated and wild-type upstream promoter -2,966/+61-bp fragments were analyzed in zebrafish by transient transgenic assay. Mutation of the Maf binding site severely impeded the human βB1-crystallin promoter function as reflected by the decrease in percentage of injected embryos that express EGFP in the lens. A-D: With the wild-type construct, intensive expression of EGFP is shown in the whole lens of most embryos (A), and in a few embryos with mosaic patterns (B-D). E-H: Embryos injected with the mutated construct show highly mosaic patterns and the reporter gene, EGFP, is faintly expressed. |