Fig. 4
|
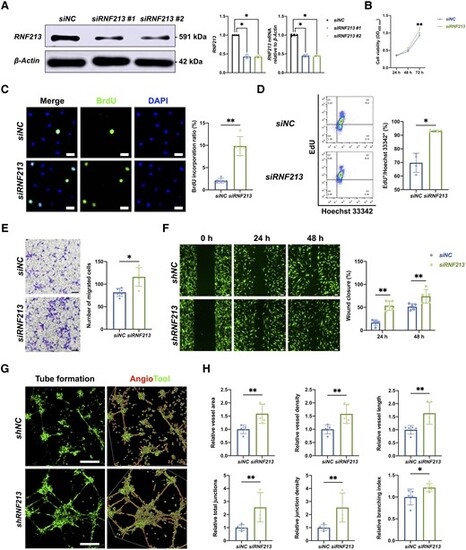
Endothelial RNF213 knockdown promotes HBMEC proliferation, migration and angiogenesis. (A) Two designed siRNA/shRNA sequences were used to mimic RNF213 loss-of-function conditions, which were confirmed by western blot (siNC versus siRNF213 #1: n = 4, 1.00 ▒ 0.00 versus 0.43 ▒ 0.05, P = 0.0286; siNC versus siRNF213 #2: n = 4, 1.00 ▒ 0.00 versus 0.42 ▒ 0.03, P = 0.0286) and qRT-PCR analyses (siNC versus siRNF213 #1: n = 4, 1.00 ▒ 0.03 versus 0.45 ▒ 0.04, P = 0.0286; siNC versus siRNF213 #2: n = 4, 1.00 ▒ 0.03 versus 0.45 ▒ 0.02, P = 0.0286). (B) The siRNF213-treated human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMECs) showed greater cell viability than the siNC-treated HBMECs at 48 h (n = 6, 0.47 ▒ 0.03 versus 0.52 ▒ 0.05, P = 0.0931) and also showed significantly greater cell viability at 72 h (n = 6, 0.93 ▒ 0.07 versus 1.09 ▒ 0.06, P = 0.004) based on the results of CCK-8 assays. (C) A BrdU incorporation assay was conducted to measure the proliferation of siNC- and siRNF213-treated HBMECs. The siRNF213-treated HBMECs showed a significantly greater BrdU incorporation ratio than the siNC-treated HBMECs (n = 5, 2.09 ▒ 0.47 versus 9.84 ▒ 1.89%, P = 0.0079). Scale bar = 20 Ám. (D) Flow cytometry was used to assess the proliferation of siNC- and siRNF213-treated HBMECs after labelling with EdU and Hoechst 33342. The siRNF213-treated HBMECs showed a significantly greater cell proliferation ratio than the siNC-treated HBMECs (n = 4, 69.75 ▒ 6.07 versus 93.15 ▒ 0.62%, P = 0.0286). (E) Transwell assays were performed to measure vertical HBMEC migration. siRNF213-treated HBMECs showed greater vertical migration than siNC-treated HBMECs (n = 6, 86.25 ▒ 38.92 versus 124.75 ▒ 57.69, P = 0.0152). Scale bar = 100 Ám. (F) A wound healing assay was used to measure horizontal HBMEC migration. The siRNF213-treated HBMECs showed markedly greater horizontal migration than the siNC-treated HBMECs at 24 h (n = 5, 16.16 ▒ 6.44 versus 55.45 ▒ 9.20, P = 0.0079) and 48 h (n = 5, 49.76 ▒ 5.26 versus 73.36 ▒ 14.78, P = 0.0079). Scale bar = 100 Ám. (G) A tube formation assay was performed to measure HBMEC angiogenesis. AngioTool software was used to automatically detect the vessel length (red) and junctions (green). Scale bar = 100 Ám. (H) The siRNF213-treated HBMECs showed significantly greater vessel area (n = 5, 1.00 ▒ 0.16 versus 1.59 ▒ 0.36, P = 0.0079), vessel density (n = 5, 1.00 ▒ 0.17 versus 1.58 ▒ 0.36, P = 0.0079), vessel length (n = 5, 1.00 ▒ 0.16 versus 1.63 ▒ 0.42, P = 0.0079), total number of junctions (n = 5, 1.00 ▒ 0.22 versus 2.56 ▒ 1.13, P = 0.0079), junction density (n = 5, 1.00 ▒ 0.23 versus 2.54 ▒ 1.12, P = 0.0079), and branching index values (n = 5, 1.00 ▒ 0.18 versus 1.22 ▒ 0.09, P = 0.0317) than the siNC-treated HBMECs. Each dot represents one sample. The means ▒ SDs are shown. The dashed line indicates the region of interest. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001. |