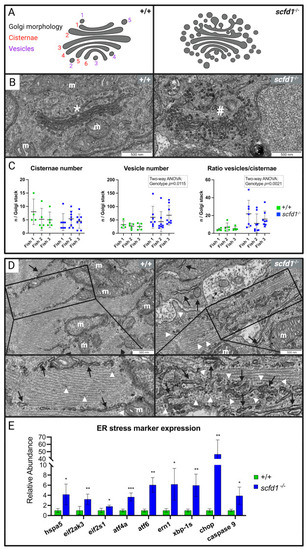
Altered cardiomyocyte Golgi apparatus and reticular network morphology, and upregulation of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress markers in scfd1 mutant hearts at 3 dpf. (A) Schematic of normal (left, wildtype (WT; +/+) and altered (right, scfd1vcc44−/−) Golgi morphology with delineation of Golgi cisternae and vesicles. (B) High magnification electron micrographs showing representative examples of ordered Golgi stack (*) in +/+ (left) and highly vesiculated Golgi stack (#) in scfd1 mutant (right); m = mitochondria. (C) Scatter graphs showing increased vesiculation and vesicle/cisternae ratio in Golgi stacks of scfd1 mutants in comparison to +/+ (n = 4–5 Golgi stacks per fish in +/+, n = 7–8 Golgi stacks per fish in scfd1−/−). (D) Low and high magnification electron micrographs showing normal smooth ER/sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR; black arrows) with occasional clusters of free ribosomes (white arrow heads) in WT cardiomyocytes (left) vs. fractionated, dispersed, and variably sized ER/SR (black arrows), and increased presence of free and membrane-bound ribosomes (white arrow heads) in scfd1vcc44−/− mutants (right). (E) Column graph showing significantly elevated transcriptional expression of ER stress markers in scfd1vcc44−/− embryos relative to their expression in WT; n = 5 samples of 30 pooled 3 dpf embryos per genotype. Zebrafish orthologs and mammalian counterparts: hspa5 = GRP78, eif2ak3 = PERK, eif2s-1 = eIF2a, atf4a = ATF4, atf6 = ATF6, ern1 = IRE1. * if p= 0.05-0.001; ** if p= 0.001-0.0001; *** if p<0.0001. Created with BioRender.com.
|

