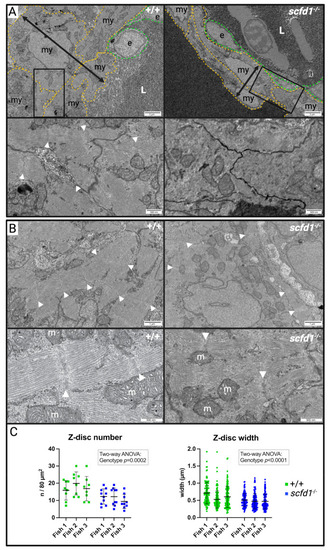
Figure 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-231030-120
- Publication
- Huttner et al., 2023 - Loss of Sec-1 Family Domain-Containing 1 (scfd1) Causes Severe Cardiac Defects and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
Homozygous |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Protruding-mouth |