Figure 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-230814-224
- Publication
- Barlow et al., 2023 - The zebrafish mutant dreammist implicates sodium homeostasis in sleep regulation
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
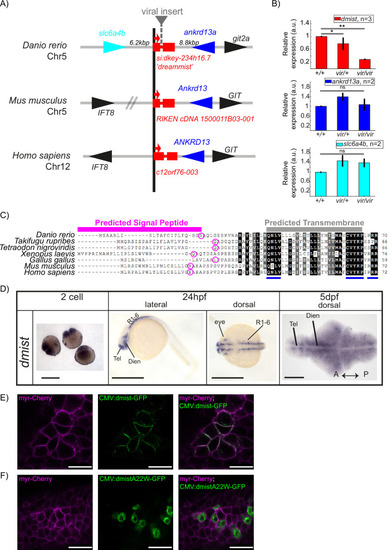
dmist encodes a conserved vertebrate single-pass transmembrane protein. (A) dmist mutants harbour a viral insertion in the first intron of si:key-234h16.7. dmist is syntenic with Ankrd13 and GIT orthologs in mouse, human, and zebrafish. (B) RT-qPCR of dmist (red) show reduced expression of dmist and not the 5? and 3? flanking zebrafish genes, slc6a4b (cyan) and ankrd13a (blue), in dmistvir/vir larvae compared to dmistvir/+ and dmist+/+ siblings. **p<0.01, *p<0.05; ns p>0.05; one-way ANOVA, Tukey?s post hoc test. Data shows mean ± SEM normalised to the wild-type mean. (C) dmist_Dr contains an open-reading frame encoding a 70 amino acid protein that is conserved across vertebrates. All identified homologues have a predicted signal peptide sequence (magenta line), signal peptide cleavage site (magenta circle), and predicted transmembrane domain (grey), with additional highly conserved C-terminal motifs (blue lines). Identical amino acids in all species are shown in black; similar amino acids (80?99% conserved across species) are shown in grey. (D) In situ hybridisation using a dmist antisense probe reveals dmist is maternally deposited as it is detected at the two-cell stage. At 24 hpf, expression is restricted to regions containing neuronal precursors, and at 5 dpf expression is widespread throughout the brain. Tel, telencephalon; Dien, diencephalon; R1-6, rhombomeres 1?6; A, anterior; P, posterior. Scale bars = 0.5 mm (two-cell and 24 hpf), 0.1 mm (5 dpf). (E, F) Representative confocal image of 90% epiboly embryo co-injected at the one-cell stage with mRNA encoding membrane-RFP (magenta) and a plasmid encoding either C-terminal tagged Dmist-GFP (E, green) or DmistA22W-GFP (F, green). Scale bar = 25 ?m |