Figure 8
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-230711-27
- Publication
- Lescouzčres et al., 2023 - A multilevel screening pipeline in zebrafish identifies therapeutic drugs for GAN
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
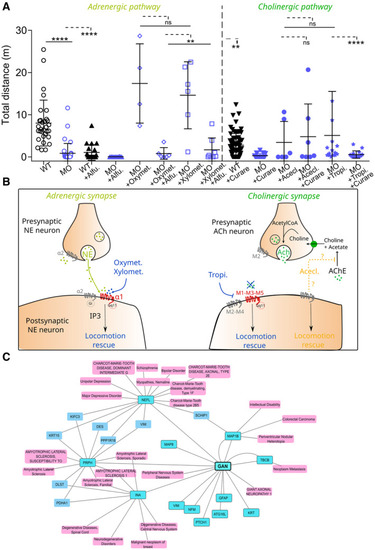
Specificity of the Hits for on‐target effects at the NMJid='emmm202216267-li-0028'> Box plots representing the effect of adrenergic (left, Oxymet., Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride; Xylomet., Xylometazoline Hydrochloride) and cholinergic (right, Acecl., Aceclidine Hydrochloride; Tropi., Tropicamide) Hits, in the presence of pathway‐specific blockers (Alfu., Alfuzosin, Curare) added as pretreatment. Each dot represents individual values for non‐injected WT embryos, MO‐injected larvae and MO‐injected larvae treated with the Hits ± blockers. In the absence of normality of distribution of the data, a nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis with Dunn's multiple comparison test is applied; means with ± standard deviation are represented; Proposed mechanisms of action of the adrenergic (left) and cholinergic (right) Hits on associated synapses. G‐coupled receptors are represented at the pre‐ or postsynaptic membrane according to their localization. Hits whose locomotion rescue action is expected to be dependent on direct action on receptors are shown in blue. Conversely, Hit whose action is assumed to be independent of its role as an agonist is shown in orange. NE, Norepinephrin; ACh, Acetylcholine; AChE, Acetylcholine‐esterase. Interaction's network between GAN and human diseases. Gigaxonin's substrates (dark blue) and associated diseases (light pink) were manually added to the initial list. The gene‐disease‐associated interactions with (KRT15, VIM, DES) are not displayed because too numerous, but they seem principally associated with cancer. The network of diseases closest to GAN mainly includes NMD. We distinguish several groups of neuromuscular pathologies, including numerous CMT forms, motor neuron pathology (ALS) and myopathies. |