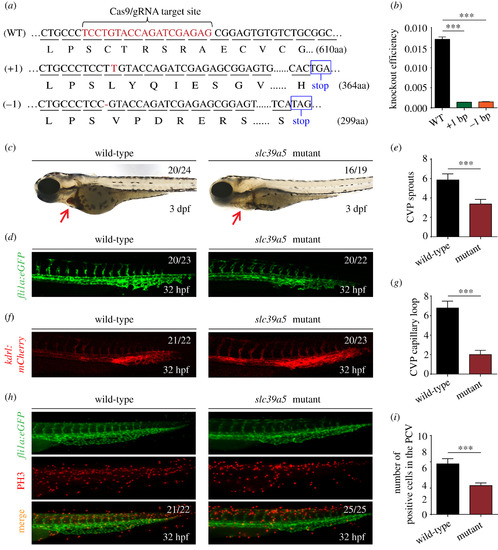
Targeting strategy and characterization of slc39a5 knockout zebrafish. (a) DNA and corresponding amino acid sequences of the wild-type (WT) slc39a5 allele and the slc39a5 allele after inserting one nucleotide (+1) or deleting one nucleotide (?1) using CRISPR/Cas9-based editing. Both the insertion and the deletion introduce a premature stop codon. (b) Summary of slc39a5 mRNA measured using qPRC in the WT, +1, and ?1 slc39a5 mutant lines (n = 3 sets of 50 pooled embryos/group). (c) Representative images of a wild-type and mutant embryo at 3 dpf. Note the significantly smaller heart with reduced cardiac blood flow in the mutant embryo (arrow). (d?e) Representative images of the CVP in wild-type (left) and mutant (right) Tg(fli1a:eGFP) (d) and summary of CVP sprouting in these embryos (e). (f?g) Representative images of the CVP in wild-type (left) and mutant Tg(kdrl:mCherry) (f) and summary of capillary loops in the CVP (g) in these embryos. (h) Representative images of PH3 immunostaining in the CVP of wild-type and mutant Tg(fli1a:eGFP) embryos. (i) Summary of PH3-positive cells in the CVP of wild-type and mutant Tg(fli1a:eGFP) embryos at 32 hpf. ***p < 0.001.
|

