Fig. S7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-190812-42
- Publication
- Chen et al., 2019 - Cerebrovascular Injuries Induce Lymphatic Invasion into Brain Parenchyma to Guide Vascular Regeneration in Zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
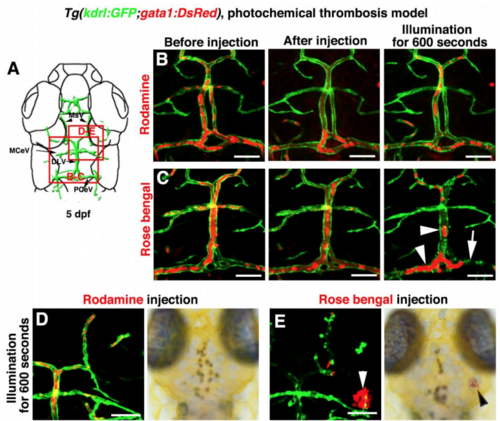
Photochemically induced thrombosis and hemorrhage in the zebrafish brain, Related to Figure 7 and Video S6. (A–C) Illustration of top layer brain vasculature at 5 dpf indicate image areas in panels. All images are dorsal view, anterior upward (A). Injection of Rhodamine followed by illumination was ineffective to the brain blood vessels (B, n=9/9). Injection of Rose bengal followed by a 600-second illumination caused thrombosis and damage to local brain blood vessels in the illuminated area (C, n=16/17). Arrowheads indicate the clogged erythrocytes. Arrow indicates damage to PCeV blood vessel. (D–E) In contrast to the Rhodamine injection (D, n=10/10), Rose Bengal injection followed by a 600-second illumination caused cerebral hemorrhage (E, arrowheads, n=10/12). Scale bar, 50 μm. DLV, dorsal longitudinal vein; MCeV, middle cerebral vein; MsV, mesencephalic vein; PCeV, posterior (caudal) cerebral vein |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 49(5), Chen, J., He, J., Ni, R., Yang, Q., Zhang, Y., Luo, L., Cerebrovascular Injuries Induce Lymphatic Invasion into Brain Parenchyma to Guide Vascular Regeneration in Zebrafish, 697-710.e5, Copyright (2019) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell