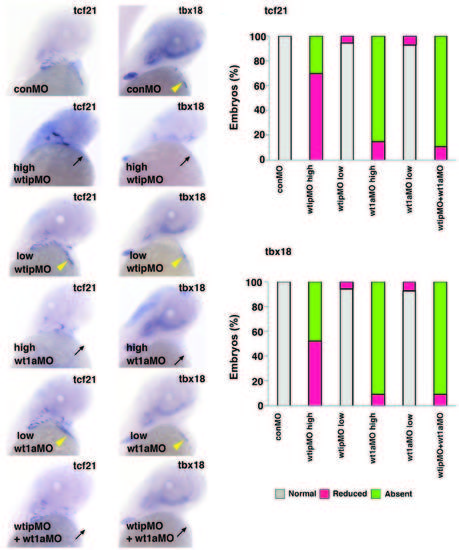
Wt1a and Wtip cooperate for PE formation. Ventral view of 48 hpf whole-mount in situ hybridization of (A,C,E,G,I,K) tcf21 and (B,D,F,H,J,L) tbx18 expression in control (yellow arrowhead, A,B), high concentration of wtipMO (black arrow, C,D; 1.035 pmol/embryo), sub-threshold concentration of wtipMO (yellow arrowhead, E,F; 0.259 pmol/embryo), high concentration of wt1aMO (black arrow, G,H; 1.15 pmol/embryo), sub-threshold concentration of wt1aMO (yellow arrowhead, I,J; wt1aMO, 0.288 pmol/embryo), sub-threshold concentrations of wt1aMO (1.15 pmol/embryo)+wtipMO (0.259 pmol/embryo; black arrow, K,L) in PE at 48 hpf. With high concentrations of wt1aMO, PE marker expressions were reduced or absent (black arrow, for tcf21; G,M, and for tbx18; H,N). With wtipMO, PE marker expressions were reduced (for tcf21, M and for tbx18, N) or absent (black arrow, for tcf21; C,M, and for tbx18; D,N). Sub-threshold doses for each MO had no effect on tcf21 (yellow arrowhead, E,I,M) or tbx18 (yellow arrowhead, F,J,N) expression in PE. In the wtip and wt1a double morphants, tcf21 and tbx18 were severely reduced (black arrow, for tcf21; K,M and for tbx18; L,N) or no longer expressed (for tcf21 and for tbx18) in the cardiac region. These data indicate that Wtip is associated with Wt1a and influences PE specification. Wt1a, Wilm′s tumor 1a; Wtip, Wilm′s tumor 1 interacting protein; PR, proepicardial organ; hpf, hours post fertilization; tcf21, transcription factor 21; tbx18, Tbox 18; wtipMO, wtip morpholino oligonucleotide.
|

