Fig. S1
|
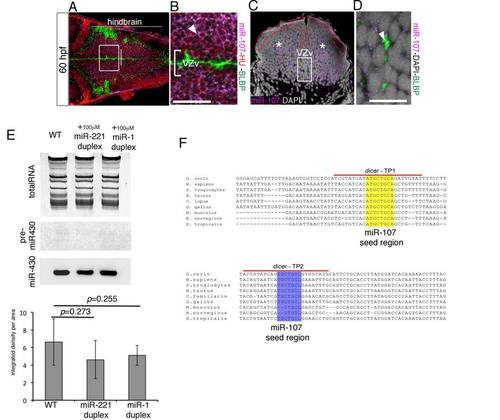
miR-107 pattern expression and gain-of-function experiment, related to Figure 1 and Figure 2. (A-B) Confocal coronal sections of a whole-mount 60 hpf embryo immunostained for HU and BLBP proteins and developed for miR-107 in situ hybridization. (B) High magnification of the white square insert in (A). The white arrow indicates miR-107 and HU double positive cells. (C) 15 µm hindbrain cross-section of a 60 hpf embryo at the level of the otic vesicle (OV) indicated by the white line in (A). Red dashed line highlights the lack of miR-107 in the ventricular hindbrain region. White stars indicate miR-107 positive expression in the mantle area of the hindbrain. (D) High magnification of the region boxed in (C) stained with anti-BLBP antibody. Arrowhead shows BLBP expression in miR-107 negative cells. (E) Northern Blot showing miR-430 biogenesis in 24 hpf embryos injected as indicated. WT (un-injected embryos) were used as controls. The image is representative of three experiments. Quantification of miR-430 mature sequence levels in each experimental condition measured as integrated intensity per area. (F) ClustalW partial alignment of the conserved dicer 3′UTR sequences containing 2 binding sites for miR-107. dicer-TP1 and dicer-TP2 highlight the regions where target protector morpholinos were designed. dicer-TP1 protects the 8 bp miR-107 seed region binding site (yellow); dicer-TP2 protects the 7 bp miR-107 seed region binding site (purple). Scale bars= 50µm. |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 32(5), Ristori, E., Lopez-Ramirez, M.A., Narayanan, A., Hill-Teran, G., Moro, A., Calvo, C.F., Thomas, J.L., Nicoli, S., A Dicer-miR-107 Interaction Regulates Biogenesis of Specific miRNAs Crucial for Neurogenesis, 546-60, Copyright (2015) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell