Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-131010-8
- Publication
- D'Aniello et al., 2013 - Depletion of Retinoic Acid Receptors Initiates a Novel Positive Feedback Mechanism that Promotes Teratogenic Increases in Retinoic Acid
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
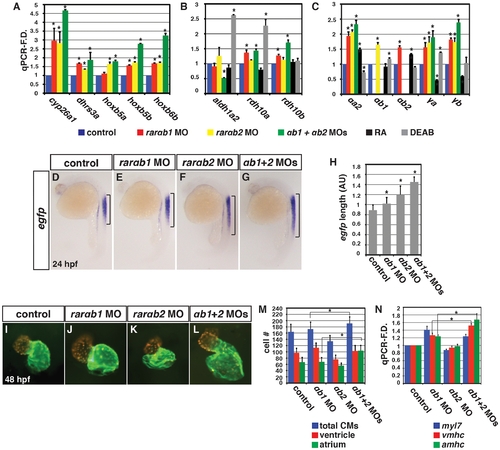
Concurrent depletion of RARαb1 and RARαb2 promotes increased RA signaling and atrial CM number. qPCR for (A) RA signaling responsive gene, (B) RA metabolizing gene, and (C) zebrafish rar expression in control sibling, RARαb1 deficient, RARαb2 deficient, RARαb1+RARαb2 (suboptimal doses) deficient, RA treated, and DEAB treated embryos at the 8 s stage. (D?G) ISH for egfp expression in Tg(12XRARE-ef1a:EGFP)sk72 embryos. Brackets indicate the length of egfp expression in the spinal cord. (H) Measurements of the length in arbitrary units (AU) of egfp expression in the spinal cord of Tg(12XRARE-ef1a:EGFP)sk72 embryos. (I?L) Hearts from control and RARαb depleted Tg(-5.1myl7:DsRed-NLS)f2 embryos. Images are frontal views. Red indicates ventricle. Green indicates atrium. (M) Mean CM number from Tg(-5.1myl7:DsRed-NLS)f2 hearts at 48 hpf. (N) qPCR for CM marker gene expression at 48 hpf. While modest increases in vmhc expression in RARαb1+RARαb2 deficient embryos were observed relative to RARαb1 (suboptimal dose) deficient embryos, corresponding increases in ventricular CM number were not observed. |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | Prim-5 to Long-pec |