Fig. 9
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-110811-20
- Publication
- Wright et al., 2011 - DeltaC and DeltaD interact as Notch ligands in the zebrafish segmentation clock
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
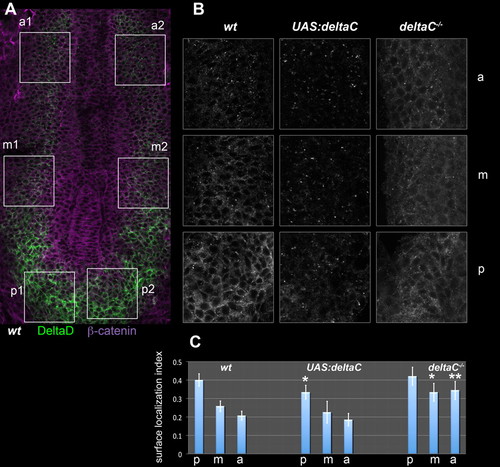
The subcellular localisation of DeltaD is controlled by DeltaC. (A) PSM of a flat-mounted wild-type (wt) zebrafish embryo immunostained for DeltaD (green) and β-catenin (magenta). Boxes show the left and right anterior (a), middle (m) and posterior (p) PSM regions that were sampled for quantitative analysis. (B) Enlargements of the corresponding boxed a, m and p regions from wild-type, DeltaC-overexpressing [heat-shocked Tg(UAS:dlc)cj2;Tg(hsp70l:Gal4vp16)vu22, ′UAS:deltaC′] and DeltaC-defective (dlctw212b/tw212b, ′deltaC-/-′) embryos; the DeltaD staining is shown in each case. (C) DeltaD surface localisation index computed for each region in each genotype. Values are means of n samples (left and right sides of n/2 embryos), where n=28 for wild type, n=10 for DeltaC overexpressing, and n=20 for DeltaC defective. Error bars show 95% confidence intervals. *, P<0.01; **, P<0.0001; versus the corresponding region of the wild type (one-tailed t-test). |