Fig. 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-100408-10
- Publication
- Veldman et al., 2010 - Tuba1a gene expression is regulated by KLF6/7 and is necessary for CNS development and regeneration in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
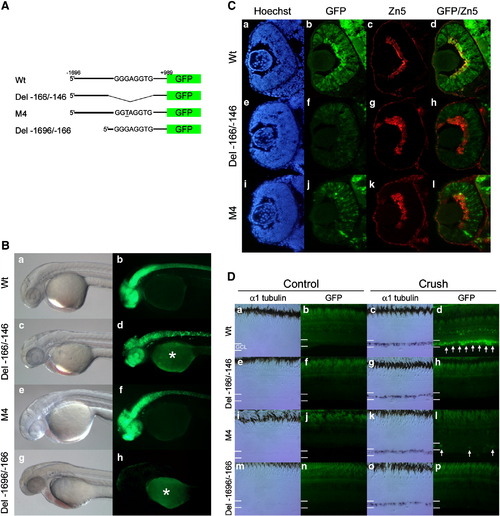
The G/C-rich enhancer is necessary for tuba1a promoter-transgene expression during RGC development and optic nerve regeneration. (A) Schematic representations (not to scale) of the reporter constructs used to create the transgenic lines. Wt transgene includes the 1.696 kb tuba1a promoter with an intact G/C-rich enhancer. Del - 166/-146 transgene contains an internal 20 basepair deletion removing the G/C-rich enhancer. M4 transgene contains the M4 point mutation (underlined) within the G/C-rich enhancer. Del - 1696/-166 transgene contains a deletion of most of the promoter sequence upstream of the G/C-rich enhancer. (B) Representative bright field (a, c, e, and g) and fluorescent images (b, d, f, and h) of the transgenic lines at 36–48 hpf. Note the similar expression of GFP in the CNS in Wt, Del - 166/-146 and M4 constructs. Del - 1696/-166 exhibits no detectable GFP expression after 24 h post fertilization. In the fluorescent images there is variable auto-fluorescence in the yolk marked with an asterisk (*). (C) Transgenic fish harboring the Wt, Del-166/-146 or M4 mutant promoters driving GFP expression were harvested at 48 hpf. Retinal sections were stained with the nuclear dye Hoechst (a, e, and i), examined for GFP expression (b, f, and j) and stained with the Zn5 antibody that identifies differentiating RGCs (c, g, and k). Merged images showing GFP and Zn5 staining are also shown (d, h, and l). Note the Wt promoter-transgene is strongly expressed in the differentiating retinal ganglion cells, while Del - 166/-146 and M4 promoters exhibited a significant reduction in the number of GFP positive cells in the GCL. Three fish per line and two lines per transgene were assayed with similar results. (D) Transgenic fish harboring the Wt, Del-166/-146, M4 or Del-1696/-166 promoters driving GFP expression had their right optic nerve crushed on day 0. Six days later, left (control) and right (crush) retinas were isolated and assayed for endogenous tuba1a (α1Tubulin) mRNA by in situ hybridization (a, c, e, g, i, k, m, and o) or transgene promoter activity by GFP fluorescence (b, d, f, h, j, l, n, and p), respectively. In situ hybridization for tuba1a expression and GFP images are from adjacent retinal sections. At least three independent lines were assayed for each transgene, except M4 for which only two lines were identified. Three fish from each line were tested, all of which gave similar results. Note that although endogenous tuba1a (α1Tubulin) expression is highly induced following optic nerve crush in all fish tested only transgenic fish harboring the Wt tuba1a promoter show strong transgene GFP induction following optic nerve crush. White arrows indicate GFP positive RGCs, residing in the ganglion cell layer (GCL). |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Condition: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | Prim-25 to Adult |
Reprinted from Molecular and cellular neurosciences, 43(4), Veldman, M.B., Bemben, M.A., and Goldman, D., Tuba1a gene expression is regulated by KLF6/7 and is necessary for CNS development and regeneration in zebrafish, 370-383, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mol. Cell Neurosci.