Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-090817-11
- Publication
- McMahon et al., 2009 - Lmx1b is essential for survival of periocular mesenchymal cells and influences Fgf-mediated retinal patterning in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
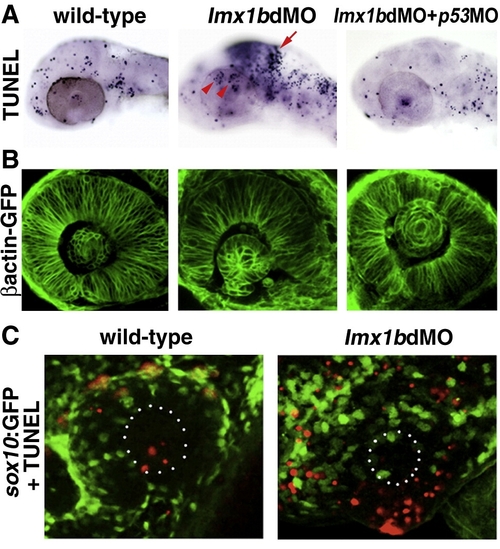
Lmx1b loss of function induces apoptosis of Lmx1b expressing cells. (A) TUNEL staining of apoptotic cells (dark blue, top row) in lmx1bdMO morphants and lmx1bdMO morphants co-injected with p53MO and analyzed at 36 hpf. Red arrow indicates increased apoptosis in the midbrain?hindbrain boundary. Red arrowheads show increased periocular cell death in lmx1bdMO eyes. (B) Eye morphology in embryos corresponding to the above panel as visualized in the betaactinGFP transgenic line. (C) TUNEL staining (red) in sox10:GFP-positive neural crest cells (green) in wild-type and lmx1bdMO morphant eyes. White dots in B outline the lens. |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | Prim-25 |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Prim-25 |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 332(2), McMahon, C., Gestri, G., Wilson, S.W., and Link, B.A., Lmx1b is essential for survival of periocular mesenchymal cells and influences Fgf-mediated retinal patterning in zebrafish, 287-298, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.