Fig. 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-090714-7
- Publication
- Weiser et al., 2009 - Rho-regulated Myosin phosphatase establishes the level of protrusive activity required for cell movements during zebrafish gastrulation
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
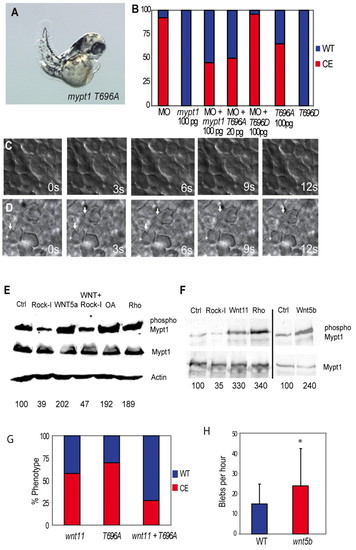
Rock and non-canonical Wnts mediate the inhibitory phosphorylation of Mypt1. (A) mypt1 T696A mRNA (100 pg) expression elicits gastrulation defects in zebrafish embryos. (B) Quantification of convergent extension (CE) defects in mypt1 T696A- and T696D-injected embryos and rescue of the MO phenotype. Red indicates a CE defect; blue indicates a normal body axis length. (C) Lack of protrusive activity of dorsal mesodermal cells in mypt1 T696A-injected embryos at bud stage. s, seconds. (D) Increased protrusive activity of dorsal mesodermal cells in wnt5b (100 pg)-injected embryos at bud stage. Arrows indicate bleb-like protrusions. (E) Western blot of HEK 293 lysates expressing myc-tagged Mypt1 treated with WNT5A-conditioned medium, or control-conditioned medium. Cells were also either co-transfected with ca-rhoA or treated with Rock inhibitor (Rock-I) or the phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid (OA) and blotted for Mypt1, phospho-Mypt1, Mypt1 and Actin. (F) Myc-tagged Mypt1 was immunoprecipitated from zebrafish embryos and blotted for Mypt1 and phospho-Mypt1. Embryos were also injected with 10 pg ca-rhoA, 100 pg wnt11, 100 pg wnt5b mRNA or treated with Rock inhibitor. Numbers beneath the lanes in E,F indicate the percentage of phospho-Mypt1 relative to the control. (G) Quantification of the rescue of the wnt11 (100 pg) overexpression phenotype by co-expression of mypt1 T696A (100 pg) mRNA. (H) Induction of blebbing of dorsal mesodermal cells at bud stage in wnt5b (100 pg)-injected embryos. *, P<0.05. |