|
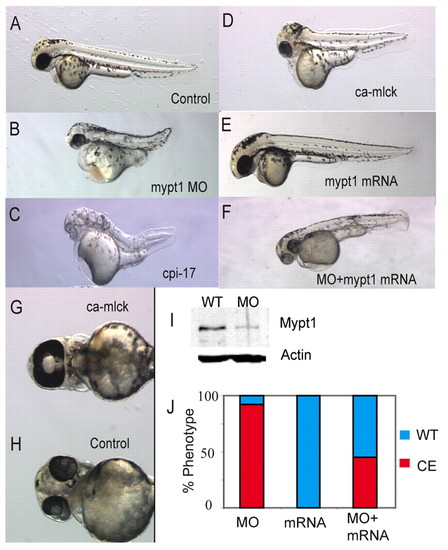
Myosin phosphatase is required for body axis elongation in zebrafish. (A-F) Dorsal views of 48 hpf zebrafish embryos injected with (A) control, (B) 1 ng mypt1 MO, (C) 200 pg cpi-17 mRNA, (D) 100 pg ca-mlck mRNA, (E) 100 pg of human MYPT1 mRNA. (F) A partially rescued embryo injected with 100 pg human MYPT1 mRNA and 1 ng mypt1 MO. (G,H) Ventral views of the head of 48 hpf zebrafish embryos showing a ca-mlck-injected embryo displaying cyclopia (G) and a control embryo (H). (I) Western blot showing endogenous Mypt1 levels in the presence and absence (WT) of 1 ng mypt1 MO. (J) Quantification of the truncated body axis phenotype in morphant and mRNA-injected embryos. The y-axis displays the percentage of embryos exhibiting a severe axis extension defect (red) or normal axis extension (blue). The x-axis displays the injected reagent.
|