Fig. 2
|
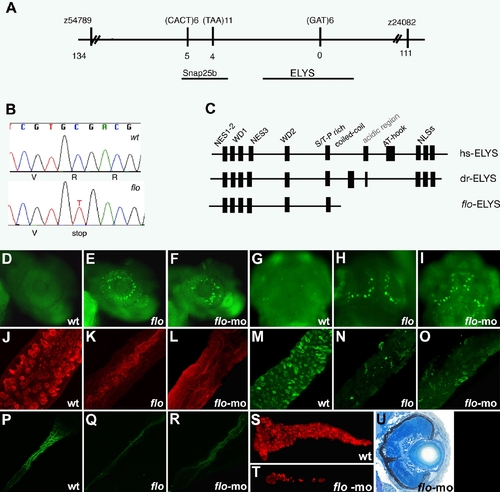
The flo locus encodes zebrafish elys. (A) Schematic representation of the genomic region surrounding the flo locus. The names of the polymorphic markers with the corresponding number of recombinants are listed. (B) DNA sequence analysis showing the cytosine to thymidine transition encoding the premature stop codon in the elysti262c allele. (C) Schematic representation of the functional domains of the human (hs) and zebrafish (dr) Elys protein and the protein encoded by the elysti262c allele (flo-ELYS). (D?I) Acridine orange staining showing apoptotic cells in the retina and growth plate of the optic tectum of 48 hpf flo (E,H) and elys-morpholino injected (F,I) larvae but not wt (D,G). (J?R) Confocal projections through the posterior intestine of 96 hpf larvae showing wheat-germ agglutinin positive goblet cells in the epithelium of the posterior intestine of wt (J) but not flo (K) or elys-morpholino injected (L) larvae; secretory cells in wt (M) but not flo (N) or elys-morpholino (O) injected larvae; enterocytes in wt (P) but not flo (Q) or elys-morpholino (R) injected larvae. (S?T) Carboxy-peptidase A positive cells are abundant in the 5 dpf wt (S) but not in elys-morpholino injected (T) exocrine pancreas. (U) Histological cross section through the retina of a 4 dpf elys morpholino injected larva showing retinal disorganization that is comparable to the 4 dpf flo retina (Figure 1H). |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | Long-pec to Day 5 |