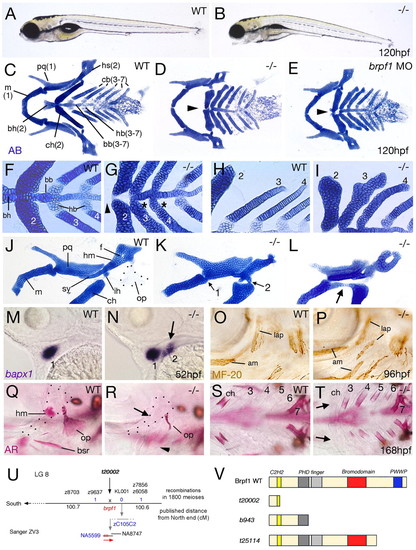
Zebrafish brpf1 mutants display anterior shifts in pharyngeal arch identities. Genotypes of fish are indicated in upper right corners (WT, wild type; -/-, homozygous brpf1 mutant; MO, brpf1 morphant), stages in lower right corners. (A,B) Lateral views of live larvae. (C-L) Cartilaginous elements of visceral skeleton stained with Alcian Blue (AB). (C-I) Ventral views; neurocranium has been removed. Numbers of pharyngeal arches are indicated (1-7). Arrowheads (D,E,G) point to absent basihyal (bh) of mutant arch 2. In addition, arches 3 and 4 of the brpf1 mutant lack hypobranchials (hb) (G, asterisks), intermediate elements that (in wild-type larvae) are characteristic for arches 3-7, but absent in arches 1 and 2 (C,F). Furthermore, the distal ends of the mutant ceratobranchials (cb) (I; 3,4) have acquired the shape and organization of the ceratohyal (ch) of the second arch of wild-type larvae (H; 2). (J-L) Lateral views of arches 1 and 2. Arrows in K point to joints between ventral and dorsal elements (compare with N). Arrow in L points to fusion between Meckel's cartilage (m) of arch 1 and the transformed ceratohyal (ch) of arch 2, an ultimate sign of segmental identity. Note the variable loss of cartilage dorsal of the foramen (f) (K,L), the reduction of the symplectic extension (sy) of the transformed hyosymplectic (hs) and its fusion with the interhyal (ih) (K), which is an arch 2-specific linker element absent in arch 1 (J), giving the hyosymplectic a spatial organization more similar to that of the palatoquadrate (pq). (M,N) Lateral views of head region ventral to eyes after in situ hybridization for bapx1, a first arch joint marker. Arrow points to ectopic bapx1 expression in arch 2 of the brpf1 mutant. (O,P) Lateral views of head region posterior to eyes after immunostaining of pharyngeal muscles with anti-MF20 antibody. (Q-T) Lateral (Q,R) and ventral (S,T) views of heads after staining of bone matrix with Alizarin Red (AR). Arrows point to absent ossification in ceratohyal (ch, ventral element; R) and hyomandibula (hm, dorsal element; T) of arch 2 in the mutant. In addition, the branchiostegal rays (bsr) and the opercle (op) dermal bones associated with the ventral and dorsal element of arch 2, respectively, are absent (arrowhead in R) or reduced. Furthermore, ceratobranchials (cb) of arches 3-6 display ectopic central ossifications (T), as in the wild-type ceratohyal of arch 2 (S). By contrast, arch 7 appears normal (S,T), with characteristic pharyngeal teeth formation (Van der Heyden et al., 2001). (U) Genetic and physical map of the t20002 allele of zebrafish brpf1. The three brpf1 exons on genomic fragment NA5599 are indicated in red. (V) Schematic of predicted wild-type and t20002, b943 and t25114 mutant Brpf1 proteins, with the C2H2, PHD finger, bromo and PWWP domains in different colors. am, adductor mandibulae; bb, basibranchial; ih, interhyal; lap, levator arcus palatini.
|

