Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-060620-5
- Publication
- Villablanca et al., 2006 - Control of cell migration in the zebrafish lateral line: Implication of the gene "Tumour-Associated Calcium Signal Transducer," tacstd
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
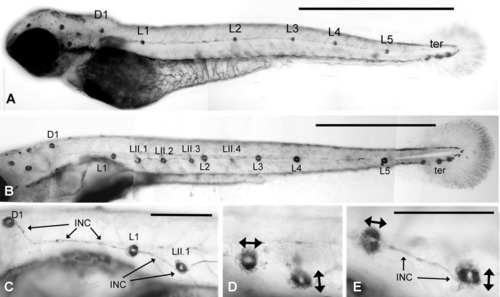
Alkaline phosphatase labeling of neuromasts. A: Normal pattern of neuromasts in a 2-day-old embryo. L1-L5 and the terminal neuromasts are derived form primI. D1, the first neuromast of the dorsal line, is derived from primII. B: Normal pattern in a 6-day-old larva. Consecutive primI neuromasts are connected by a thin trail of interneuromastic cells. Four additional neuromasts have been added by primII: LII.1-LII.4. The dorsal line comprises three additional neuromasts along the dorsal midline (out of focus). C: The trail of primI interneuromastic cells (INC) is continuous with the primI neuromast L1 but appears pushed away by the derivatives of primII (D1 and LII.1). D,E: The phosphatase activity reveals neuromast anisotropy, with the primI neuromasts being polarized along the antero-posterior axis while the primII neuromasts are polarized in a dorso-ventral direction (double arrows). Scale bars = 1 mm (A,B), 250 μm (C-E). |