- Title
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Ascorbic Acid, Vanillic Acid, and Ferulic Acid in Dopaminergic Neurons of Zebrafish
- Authors
- Hedayatikatouli, F., Kalyn, M., Elsaid, D., Mbesha, H.A., Ekker, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Biomedicines
|
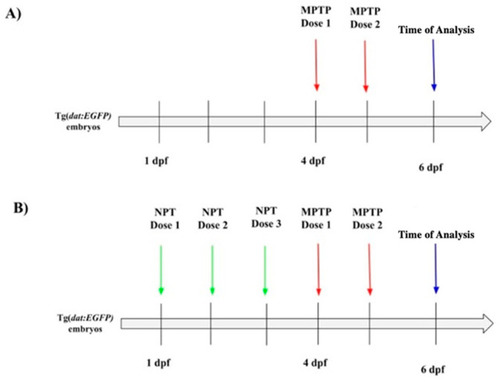
Timeline of the neuroprotective treatment and MPTP neurotoxin exposure in zebrafish larvae. ( |
|
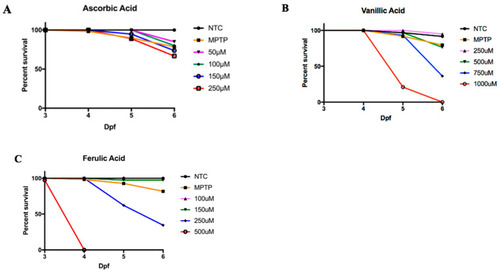
Zebrafish larvae survival following exposure to MPTP with pre-treatment with ( |
|
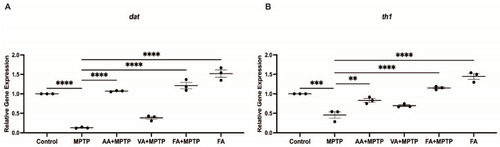
Effects of neuroprotective compounds on EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
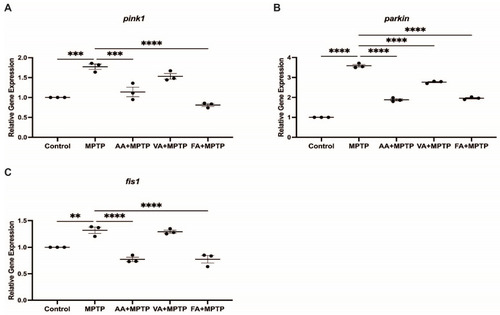
Effects of natural phenolic compounds on mRNA level of genes related to mitochondrial fission. Relative gene expression of ( |
|
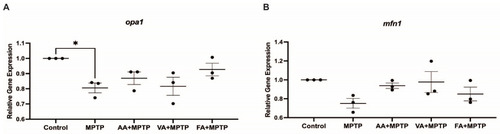
Effects of natural phenolics compounds on mRNA level of genes related to mitochondrial fusion. Relative gene expression of ( |
|
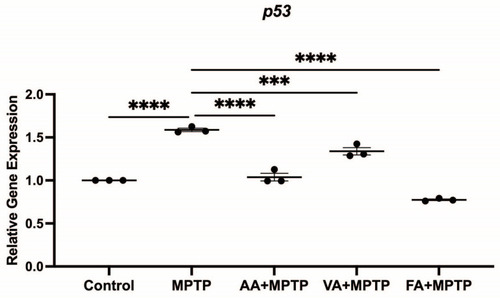
Effects of neuroprotective compounds on mRNA level |
|
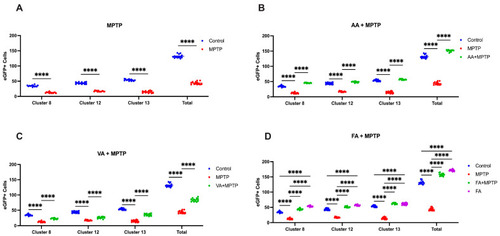
Effects of MPTP, ascorbic acid, vanillic acid, and ferulic acid on three DAnergic clusters located in the vDC of 6 dpf Tg( |
|
Quantification of DAnergic neurons within the vDC of zebrafish larvae. Developing Tg( PHENOTYPE:
|
|
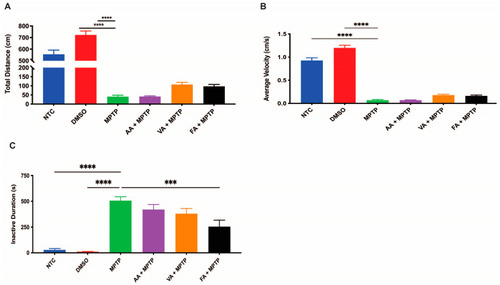
Restorative effects of ascorbic acid, vanillic acid, and ferulic acid on behavior. The swimming activity of 6 dpf larvae (n = 20) in NTC, DMSO, MPTP, ascorbic acid, vanillic acid, and ferulic acid solutions was assessed for ( PHENOTYPE:
|