- Title
-
Zebrafish nampt-a mutants are viable despite perturbed primitive hematopoiesis
- Authors
- Pomreinke, A.P., Müller, P.
- Source
- Full text @ Hereditas
|
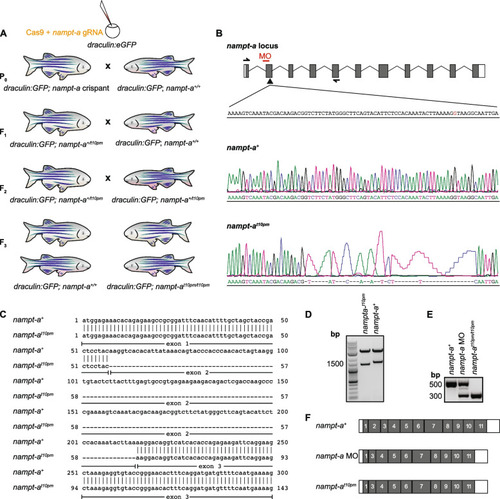
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated generation of |
|
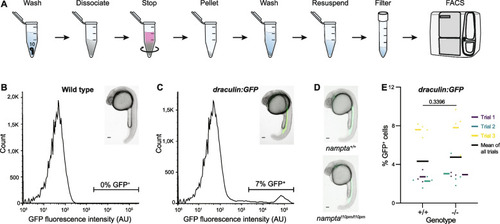
The EXPRESSION / LABELING:
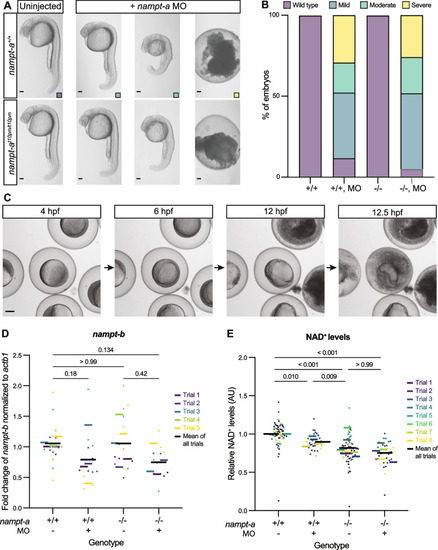
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
|
|
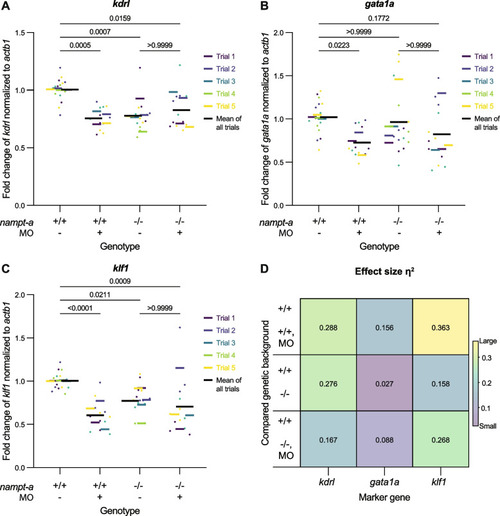
Expression of hemangioblast/endothelial and erythrocyte maturation markers in |