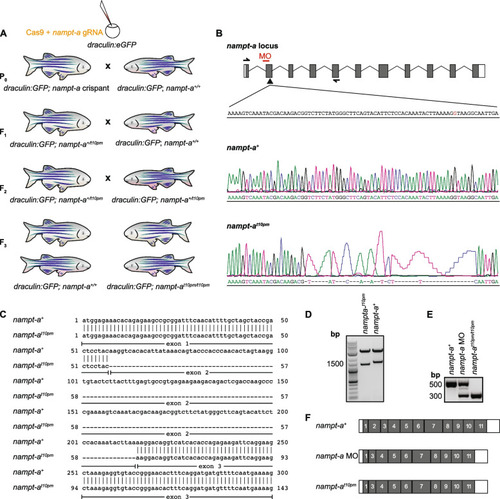
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated generation of nampt-a mutants for comparison to morpholino-induced mis-spliced transcripts. A To generate homozygous nampt-at10pm mutants using CRISPR/Cas9, draculin:GFP embryos were injected with Cas9 and gRNA targeting exon 2 of the nampt-a gene. P0nampt-a crispants were backcrossed to draculin:GFP fish, and heterozygous mutant progeny was raised to adulthood (F1). Of these fish, the nampt-at10pm mutant allele was identified to have exon 2 absent in the mature transcript. F1 fish were backcrossed to draculin:GFP to further eliminate potential off-target mutations. F2 fish were in-crossed to establish homozygous nampt-at10pm mutants (F3). F3 progeny homozygous for the wild-type allele nampt-a+ were also raised to serve as controls for the genetic background. B Schematic of the nampt-a locus. Boxes represent exons, white bars represent UTRs, and thin black lines represent introns. The arrowhead marks the gRNA target site for CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutagenesis. The red bar indicates the morpholino (MO) binding site at the 3’ splice site of the intron 1 and exon 2 splice junction on nampt-a pre-mRNA. Half-headed arrows represent the primer-annealing sites used to amplify and sequence nampt-a mature mRNA from exon 1 to exon 5. The inlet represents a short segment of the exon 2 sense strand including the 5’ splice site ‘G’ in red between exon 2 and intron 2. Lower panels show Sanger sequences of wild-type nampt-a and the nampt-at10pm allele with a 47 bp indel. C Alignment of wild-type nampt-a+ and nampt-at10pm cDNA shows that exon 2 is absent in nampt-at10pm mutant transcripts. D Cloning of wild-type nampt-a+ and nampt-at10pm into the pCS2( +) vector with subsequent release of inserts by restriction digestion shows that the nampt-at10pm allele is shorter than the wild-type cDNA. E PCR products amplified from wild-type nampt-a, nampt-a morphants (nampt-a MO), and nampt-at10pm/t10pm cDNA using primers shown in (B) indicate similar splicing defects in morphants and mutants, albeit substantial wild-type mRNA is still present in the morphants. F Schematic of nampt-a wild-type mature mRNA aligned to nampt-a morphant and nampt-at10pm mutant mature mRNA. Exons are shown in gray and UTRs in white boxes. Exon 2 is spliced out in both loss-of-function approaches
|

