- Title
-
Loss of Ripk3 attenuated neutrophil accumulation in a lipopolysaccharide-induced zebrafish inflammatory model
- Authors
- Wen, W., Chen, J., Zhou, Y., Li, G., Zhang, Y.
- Source
- Full text @ Cell Death Discov
|
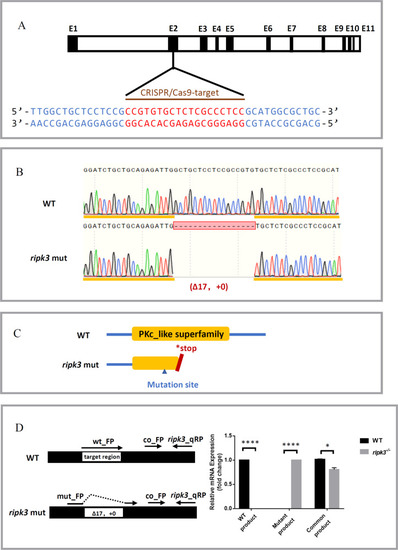
Generation of the ripk3 knockout zebrafish line.
A CRISPR target of ripk3. The CRISPR/Cas9 target sequence was designed on the second exon of ripk3, and mutations were created using CRISPR-Cas9 technology. B Mutation form of ripk3-deficient larvae. A mutation strain with 17 bp deletion in the ripk3 gene (?17 bp, +0) was applied in this study. C Protein changes upon ripk3 mutation. In the ripk3-deficient larvae, a premature stop codon was generated and disrupted the PKc_like superfamily protein domain. D Validations of the ripk3 mutation. Q-PCR revealed that the WT or mutant product of ripk3 mRNA could only be detected in the WT or ripk3-deficient larvae, respectively. The expression of the common product showed that ripk3 was significantly lower expressed in the ripk3-deficient larvae (n ? 10, Student?s t-test). |
|
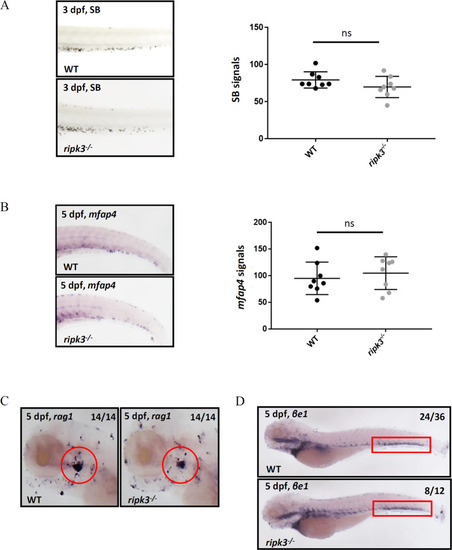
Hematopoiesis was unaltered in ripk3-deficient larvae.
A SB staining showing unchanged neutrophils (n = 8, Student?s t-test). B WISH of mfap4 showing unchanged macrophages (n = 8, Student?s t-test). C WISH of rag1 showing normal T lymphocytes (red circle showing the thymus) (Fisher?s exact tests, n = 14). D WISH of ?e1 showing normal erythrocytes (red box showing the caudal hematopoietic tissue) (Fisher?s exact tests, n > 12). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
The cytokine expressions kept unchanged in ripk3-deficient larvae.
A Normal pro-inflammatory cytokines expression upon ripk3 deficiency. The expression levels of il1b, il6, and cxcl8a were unchanged in 3 dpf ripk3-deficient larvae (n ? 10, Student?s t-test). B Normal anti-inflammatory cytokines expression upon ripk3 deficiency. The expression levels of il4, il10, and il13 were unchanged in 3 dpf ripk3-deficient larvae (n ? 10, Student?s t-test). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
The ripk3 deficiency induced limited changes in non-infectious inflammation.
A Experimental design. The caudal fin folds of 3 dpf larvae were injured by sterile syringe needles, and the local accumulation of neutrophils and cytokines expression were detected at 5 hpi. B, C Normal neutrophils attraction towards the injury site. At 0 hpi, few neutrophils could be found in the injury area (red circle). At 5 hpi, similar numbers of neutrophils (red arrows pointed) were attracted to the caudal fin folds (n ? 12, Student?s t-test). D The expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (il1b, il6, and cxcl8a) (n ? 10, One-way ANOVA). E The expression levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines (il4, il10, and il13) (n ? 10, one-way ANOVA). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
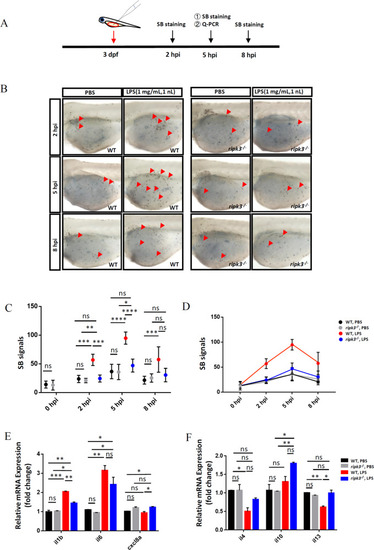
Deficiency of ripk3 attenuated the LPS-induced inflammatory responses.
A Experimental design. The 3 dpf WT and ripk3-deficient larvae were injected with LPS, and collected at 5 hpi for the detection of cytokines. The neutrophil accumulation was evaluated by SB staining at 2, 5, and 8 hpi. B Fewer neutrophils migrated to the injection sites. At 2, 5, and 8 hpi, fewer neutrophils (red arrows pointed) could be found in the yolk sac of the ripk3-deficient larvae. C Quantification of (B) (n ? 6, one-way ANOVA). D Quantification of (B), showing the trends of the accumulated neutrophils. E The expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (il1b, il6, and cxcl8a) at 5 hpi (n ? 10, one-way ANOVA). F The expression levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines (il4, il10, and il13) at 5 hpi (n ? 10, one-way ANOVA). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
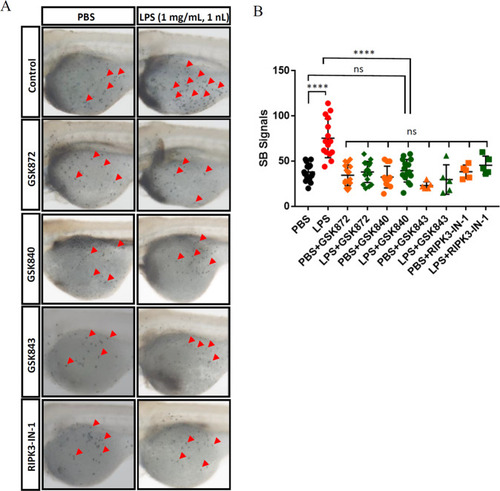
Targeting Ripk3 could inhibit LPS-induced inflammation.
A Attenuated LPS-induced neutrophil accumulation upon Ripk3 inhibition. The WT larvae were pre-treated with Ripk3 inhibitors and then injected with LPS at 3 dpf. The neutrophil accumulation (red arrows pointed) was significantly inhibited by Ripk3 inhibitors at 5 hpi. B Quantification of (A) (n ? 5, one-way ANOVA). |