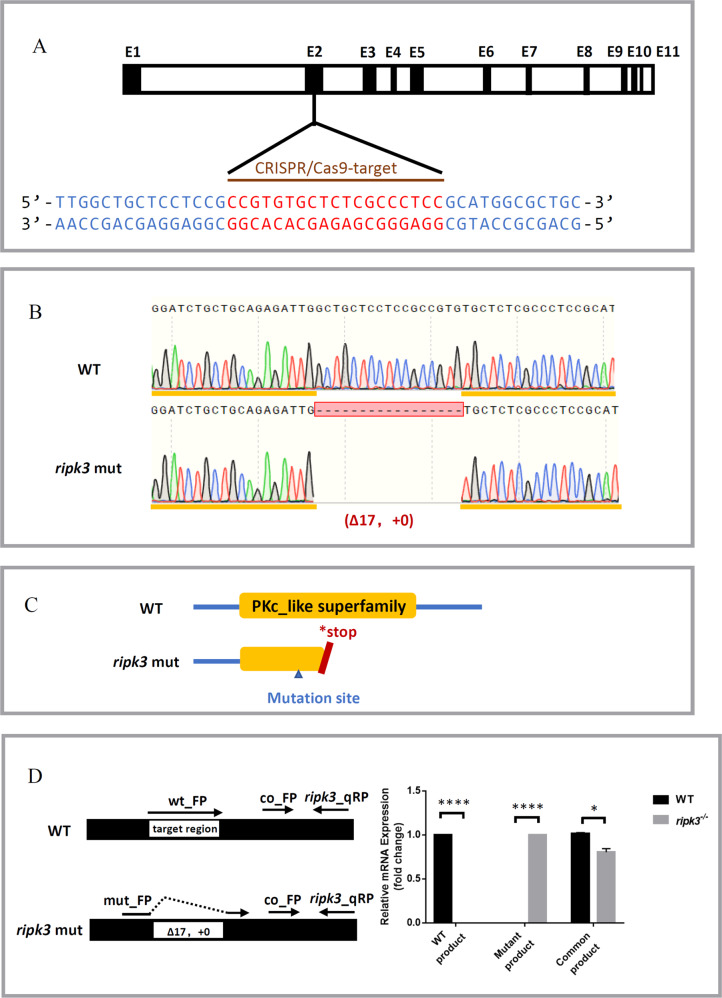
Fig. 1
A CRISPR target of ripk3. The CRISPR/Cas9 target sequence was designed on the second exon of ripk3, and mutations were created using CRISPR-Cas9 technology. B Mutation form of ripk3-deficient larvae. A mutation strain with 17 bp deletion in the ripk3 gene (?17 bp, +0) was applied in this study. C Protein changes upon ripk3 mutation. In the ripk3-deficient larvae, a premature stop codon was generated and disrupted the PKc_like superfamily protein domain. D Validations of the ripk3 mutation. Q-PCR revealed that the WT or mutant product of ripk3 mRNA could only be detected in the WT or ripk3-deficient larvae, respectively. The expression of the common product showed that ripk3 was significantly lower expressed in the ripk3-deficient larvae (n ? 10, Student?s t-test).