- Title
-
Protective Effect of Chlorogenic Acid and Its Analogues on Lead-Induced Developmental Neurotoxicity Through Modulating Oxidative Stress and Autophagy
- Authors
- Ji, X., Wang, B., Paudel, Y.N., Li, Z., Zhang, S., Mou, L., Liu, K., Jin, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Mol Biosci
|
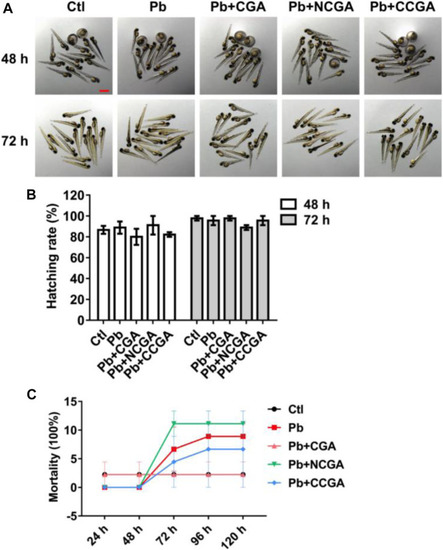
Hatching and mortality rate of zebrafish larvae. |
|
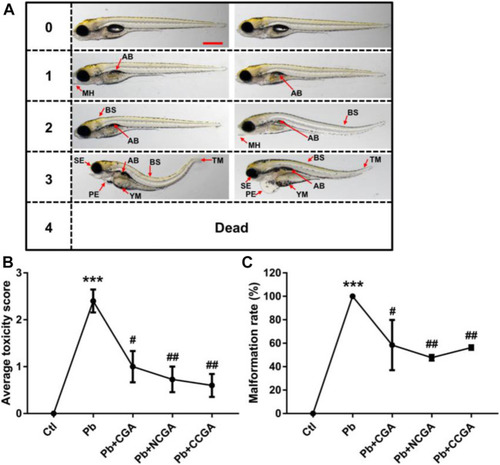
Micrographs, average toxicity scores, and malformation rate. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
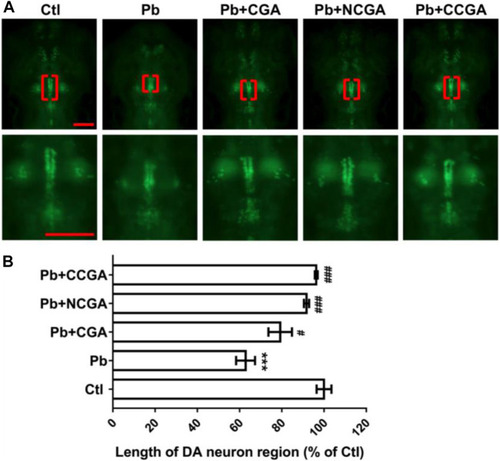
Representative images of DA neuron of zebrafish and its analysis. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Representative fluorescence images of differentiated CNS neuron region of zebrafish and its analysis. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
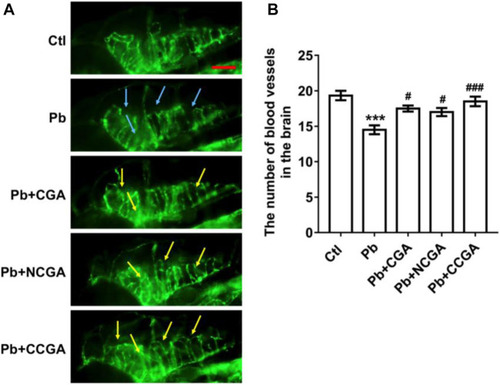
Representative images of blood vasculature of zebrafish and its analysis. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Swimming behavior test of zebrafish at 120 hpf. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Transcription of genes related to neurodevelopment. The graph plot is represented as fold changes in the mRNA expression of c-fos |
|
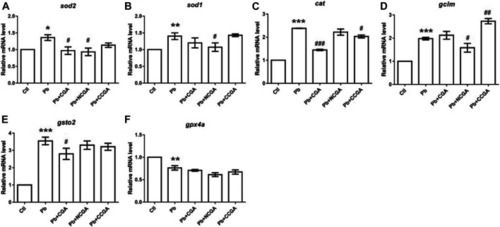
Transcription of genes related to oxidative stress. The graph plot is represented as fold changes in the mRNA expression of sod2 |
|
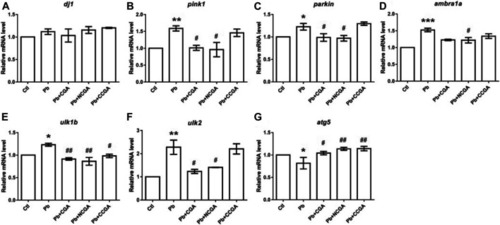
Transcription of genes related to parkinsonian and autophagy. The graph plot is represented as fold changes in the mRNA expression of dj1 |
|
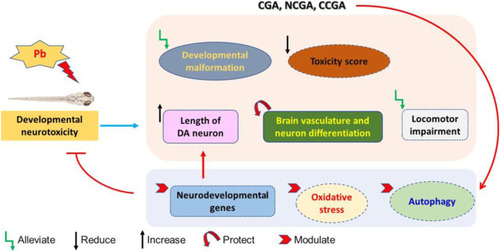
Schematic representation of protective effect of CGA, NCGA, and CCGA against Pb-induced developmental neurotoxicity co-treatment of CGA, NCGA, and CCGA alleviated developmental malformation, reduced toxicity score, increased the length of DA neuron region, protected brain vasculature and neuron differentiation in the CNS, ameliorated locomotor impairment, modulated neurodevelopmental genes ( |