- Title
-
Deletion of morpholino binding sites (DeMOBS) to assess specificity of morphant phenotypes
- Authors
- Cunningham, C.M., Bellipanni, G., Habas, R., Balciunas, D.
- Source
- Full text @ Sci. Rep.
|
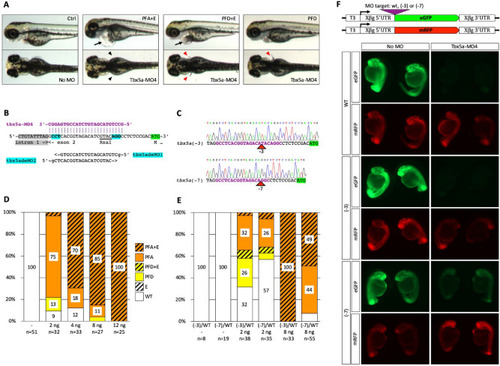
Partial rescue of Tbx5a-MO4 morphant phenotype by (− 3) and (− 7) binding site mutations. ( PHENOTYPE:
|
|
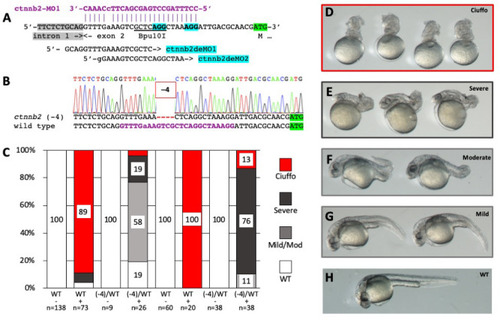
Suppression of a maternal morphant phenotype by DeMOBS. ( PHENOTYPE:
|