- Title
-
The zebrafish HGF receptor met controls migration of myogenic progenitor cells in appendicular development
- Authors
- Nord, H., Dennhag, N., Tydinger, H., von Hofsten, J.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
Pectoral and pelvic fin musculature is affected in adult met-/- mutant zebrafish. Lateral view of mylz2:EGFP transgenic expression in pectoral and pelvic fin musculature of (A) met+/+ (n = 18) and (B) met-/- (n = 15) adult zebrafish, squares indicate areas of enlargement in C-F. Ventral view of mylz2:EGFP transgenic expression in pectoral fin muscle of (G) met+/+ (n = 18) and (H) met-/- (n = 15) adult zebrafish. Ventral view of mylz2:EGFP transgenic expression in pelvic fin muscle of (I) met+/+ (n = 18) and (J) met-/- (n = 15) adult zebrafish. Dashed lines outline muscles as indicated, asterisks indicate areas affected in the hypaxial musculature, arrowheads indicate lack of muscle. Abbreviations: pfm: pectoral fin muscle; plab: abductor pelvicus; plad: adductor pelvicus. Scale bar: 1 mm. |
|
Met mutant embryos display a pectoral fin muscle phenotype. (A) Lateral view of met+/+ and met-/- embryos at 3 dpf. (B) Average anterior-posterior length of embryo and (C) average myotome dorsal-ventral width at the level of the most posterior part of the yolk extension of met+/+ (n = 6) and met-/- (n = 5) embryos at 3 dpf. (D) Transgenic expression of mylz2:EGFP in the pectoral fin of met+/+ siblings and met-/-mutant zebrafish embryos at 3 dpf, dashed line indicate area of transverse section presented to the right, which shows the two separate abductor and adductor muscles of the pectoral fin. (E) Transgenic expression of mylz2:EGFP in the pectoral fin of met+/+siblings and met-/- mutant zebrafish at 14 dpf, dashed line indicate area of transverse section presented to the right, which shows the two separate abductor and adductor muscles of the pectoral fin. Average number of mylz2:EGFP+ fibers in the pectoral (F) abductor and (G) adductor fin muscle of different met+/+ siblings (dark grey) and met-/-mutant (light grey) zebrafish at 3 dpf (n = 6 for met+/+ and n = 5 for met-/-), 6 dpf (n = 5 and n = 5), 10 dpf (n = 5 and n = 5) and 14 dpf (n = 6 and n = 5). Error bars indicate S.E.M. Significance was calculated using students t-test where p<0.05 was considered significant, * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001. (H) Dorsal view and (I) enlargement of pectoral fin of met+/+ siblings (n = 5) and met-/- mutant (n = 5) embryos at 5 dpf stained with alcian blue to visualize cartilage, dashed black lines outline pectoral fins. Abbreviations: add: adductor; abd: abductor. Scale bars: A: 200 μm, D-E: 50 μm, H-I:100 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Met is required for proper sternohyoideus formation. (A) Ventral view of transgenic mylz2:GFP expression in the craniofacial muscles of met+/+ siblings (n = 5) and met-/- mutant (n = 5) embryos at 4 dpf. (B) Average GFP+sternohyoideus area of met-/- mutant embryos (n = 6) in proportion to met+/+ siblings (n = 6) at 4 dpf. (C) Ventral view of transgenic mylz2:EGFP expression in the sternohyoideus of met+/+ siblings and met-/- mutant embryos at 4 dpf. (D) Lateral view of transgenic mylz2:GFP expression in the somites of met+/+ siblings (n = 5) and met-/-mutant embryos (n = 5) at 4 dpf. (E) Lateral view of met+/+ siblings (n = 10) and met-/-mutant larvae (n = 9) fed fluorescent beads at 5 dpf, the average number of beads detected in the stomach is presented in (F). (G) Lateral view of transgenic mylz2:EGFP expression in the oesophagus of met+/+ (n = 5) siblings and met-/- (n = 5) mutant embryos at 4 dpf. Error bars indicate S.E.M. Significance was calculated using students t-test where p<0.05 was considered significant, * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001. Abbreviations: oe: oesophagus; phm: posterior hypaxial muscle; sh: sternohyoideus. Scale bar: 100 μm. |
|
The expression of myogenic markers is severely reduced in MMPs in met-/-mutant embryos. Whole mount in situ hybridization showing the expression of (A) pax3a in met+/+ siblings (n = 5), met+/- heterozygotes (n = 5) and met-/- (n = 8) mutant embryos, (B) myoD in met+/+ siblings (n = 5), met+/- heterozygotes (n = 5) and met-/- mutant embryos (n = 12) and (C) myogenin in met+/+ siblings (n = 5), met+/- heterozygotes (n = 5) and met-/-mutant embryos (n = 10) at 48 hpf. Abbreviations: fb: fin bud; sh: sternohyoideus; phm: posterior hypaxial muscle. Scale bar: 100 μm. |
|
The pax3a:EGFP+ populations of MMPs migrating out from the somites are reduced in met-/- mutants. Lateral view of transgenic pax3a:EGFP expression in (A) met+/+ siblings and (B) met-/-mutant embryos at 28 hpf (n = 6 for met+/+ and n = 9 for met-/-), 36 hpf (n = 7 for met+/+and n = 5 for met-/-) and 48 hpf (n = 5 for met+/+ and n = 5 for met-/-). (C) met+/+ siblings (n = 5) and met-/- mutant (n = 5) pax3a:EGFP (green) embryos treated with BrdU (red) from 24 to 48 hpf to visualize proliferating cells. Dashed line in A indicate yolk-somite border. Abbreviations: sh: sternohyoideus; fb: fin bud; phm: posterior hypaxial muscle. Scale bar: 50 μm. |
|
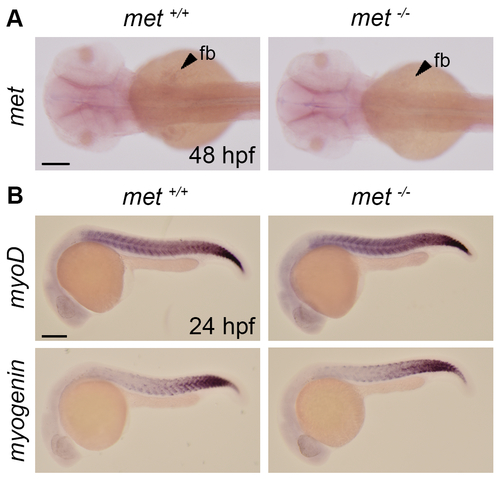
(A) Dorsal view of whole mount in situ showing the expression of met in met+/+ siblings (n = 7) and met-/- (n = 5) mutant embryos at 48 hpf. Scale bar: 100 μm. (B) Lateral view of whole mount in situ showing the expression of myoD and myogenin in met+/+ siblings (n = 7 for myoD and 5 for myogenin) and met-/- (n = 5 for myoD and 5 for myogenin) mutant embryos at 24 hpf. Abbreviation: fb: fin bud. Scale bar: 100 μm. |

Unillustrated author statements PHENOTYPE:
|