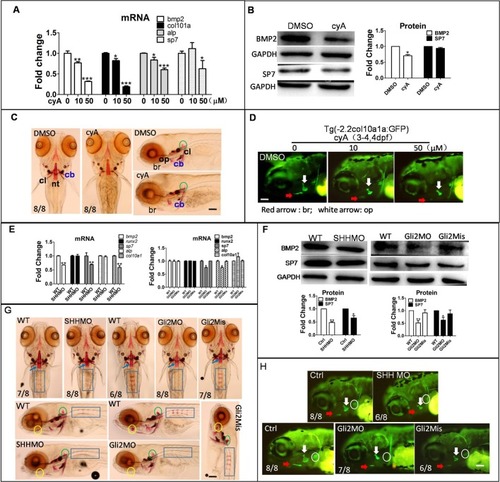
Reduction of Hh signaling inhibited osteoblast differentiation. Larvae were exposed to 10 µM and 50 µM cyA at 3 dpf for 3 days, and were collected to measure osteoblast-related gene mRNA, protein level and mineralization of osteoblasts with DMSO treated as a control. (A) qPCR detected osteoblast genes in transcription level. (B) BMP2 and SP7 proteins were detected by western blot. (C) Alizarin Red staining showed mineralization of osteoblasts. Note that the DMSO panel on the right is reproduced from middle WT panel in Fig. 4E. (D) Transgene larvae Tg (-2.2col10a1a:GFP) were treated with 10 µM and 50 µM cyA at 3 dpf for 1 day, images were obtained by fluorescence microscope at 4 dpf. Embryos were injected with SHHMO, Gli2MO and Gli2Mis at the 1–4 cell stage. Lateral view. (E–H) At 6 dpf, larvae were collected for qPCR, western blot and Alizarin Red staining. (E) Osteoblast genes bmp2, sp7, col10a1, runx2 and alp mRNA were detected by qPCR. (F) Osteoblast-related proteins BMP2 and SP7 were tested by western blot. (G) Alizarin Red staining showed mineralization of osteoblasts including nt (notochord tip, blue arrow), rib (blue rectangle), hm (hyomandibular, yellow circle) and regions delayed in SHHMO- and Gli2MO-injected groups. Green circle, bop (basioccipital articulatory process). The difference in osteoblast name and abbreviation were derived from previous sources (Laue et al., 2008; Aceto et al., 2015). (H) In Tg (-2.2col10a1a:GFP) transgene zebrafish, col10a1a signal was shown. White circle, cb (ceratobranchial 5); red arrow, br; white arrow, op. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 versus untreated groups (one-way ANOVA). The data were from three independent assays. Scale bars: 50 µm.
|