- Title
-
Homozygous frameshift mutations in FAT1 cause a syndrome characterized by colobomatous-microphthalmia, ptosis, nephropathy and syndactyly
- Authors
- Lahrouchi, N., George, A., Ratbi, I., Schneider, R., Elalaoui, S.C., Moosa, S., Bharti, S., Sharma, R., Abu-Asab, M., Onojafe, F., Adadi, N., Lodder, E.M., Laarabi, F.Z., Lamsyah, Y., Elorch, H., Chebbar, I., Postma, A.V., Lougaris, V., Plebani, A., Altmueller, J., Kyrieleis, H., Meiner, V., McNeill, H., Bharti, K., Lyonnet, S., Wollnik, B., Henrion-Caude, A., Berraho, A., Hildebrandt, F., Bezzina, C.R., Brooks, B.P., Sefiani, A.
- Source
- Full text @ Nat. Commun.
|
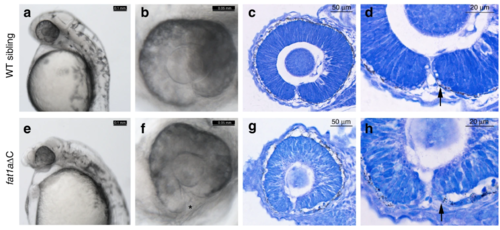
Zebrafish embryos with homozygous alleles of truncated fat1a display coloboma. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated introduction of frame-shift mutations in FAT1 C-terminal resulted in optic fissure closure defects (a and e, scale bar is 0.1 mm). A higher magnification of eye depicting fused margins in WT and unfused margins in homozygous mutant (*, b and f, scale bar is 0.05 mm). Sagittal sections of zebrafish embryos (24–30 hpf) followed by toludene blue staining showing organization of the optic cup (c and g, scale bar is 50 µm). Higher magnification of the optic cup shows morphology of optic fissure margins in WT and homozygous mutant (d, h, scale bar is 20 µm) PHENOTYPE:
|
|
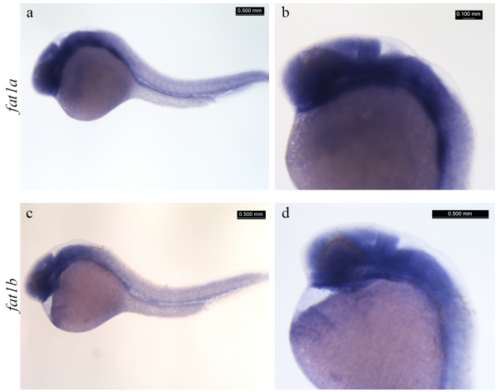
In situ staining of zebrafish embryos. In situ staining of zebrafish embryos (24 hpf) with fat1a (a and b) and fat1b (c and d) riboprobes. Scale bar is 0.5mm EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Morpholino mediated knockdown of zebrafish fat1a causes coloboma Morpholino mediated knockdown of fat1a consistently resulted in coloboma at two different concentrations (a, b, d, f and h), whereas injection of similar amount of control morpholino did not cause coloboma (a, b, c, e and g). Fused optic fissure margins of zebrafish larvae (day 3 post fertilization) can be observed (e and g; sagittal section) after histology and toludene blue staining, whereas the fissure margins remained unfused in fat1a morphant embryos (f, and h). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Variability of coloboma phenotype in fat1a morphant zebrafish embryos. Optic cup morphology of control and fat1a morphant zebrafish embryos. Top panel shows the variability in coloboma phenotype ranging from mild to severe followed by histology in the bottom panel. PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|