- Title
-
A zebrafish model for C9orf72 ALS reveals RNA toxicity as a pathogenic mechanism
- Authors
- Swinnen, B., Bento-Abreu, A., Gendron, T.F., Boeynaems, S., Bogaert, E., Nuyts, R., Timmers, M., Scheveneels, W., Hersmus, N., Wang, J., Mizielinska, S., Isaacs, A.M., Petrucelli, L., Lemmens, R., Van Damme, P., Van Den Bosch, L., Robberecht, W.
- Source
- Full text @ Acta Neuropathol.
|
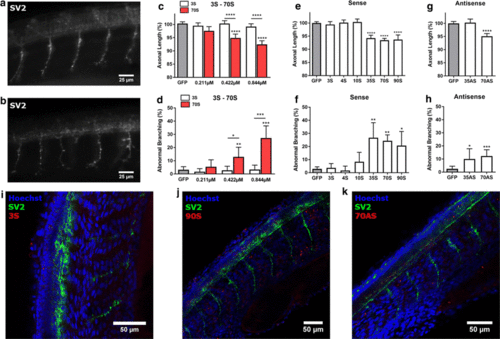
Zebrafish axonopathy induced by C9orf72 sense and antisense repeats. a, b Visualization of motor axons by immunohistochemistry (SV2 antibody) of 30 hpf zebrafish embryos injected with 3S (a) or ~ 70S (b) repeat RNA. c, d Axonal length (c) and aberrant axonal branching (d) of zebrafish embryos injected with increasing doses of 3 and ~ 70 sense repeat RNA, compared to GFP control RNA, n = 5 experiments. c Data represent mean ▒ 95% confidence interval (CI) one-way ANOVA, F(6, 754) = 18.87, ****p < 0.0001. d Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI logistic regression (z values compared to GFP ? 0.796, ? 0.877, ? 0.200, 3.025, 0.104, 5.703; z values for 3S vs 70S: 1.373, 2.480, 4.538), *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. e, f Axonal length (e) and aberrant axonal branching (f) of zebrafish embryos injected with sense repeat RNA with a length of 3 (n = 4 experiments), 4 (n = 4 experiments), 10 (n = 4 experiments), ~ 35 (n = 4 experiments), ~ 70 (n = 24 experiments) and ~ 90 (n = 4 experiments) repeats at equimolar dose (0.844 ÁM). e Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI one-way ANOVA, F(6, 1140) = 57.16, ****p < 0.0001. f Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI logistic regression (z values compared to GFP 1.130, ? 0.573, 1.130, 3.035, 3.063, 2.565), *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. g, h Axonal length (g) and axonal branching (h) of zebrafish embryos injected with antisense repeat RNA with a length of ~ 35 (n = 4 experiments) and ~ 70 (n = 12 experiments) repeats at equimolar dose (0.844 ÁM). g Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI one-way ANOVA, F(2, 474) = 35.66, ****p < 0.0001. h Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI logistic regression (z values compared to GFP 2.450, 3.576), *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. i?k Whole-mount staining (SV2 antibody) of 30 hpf zebrafish embryos injected with fluorescently labeled 3S, ~ 90S and ~ 70AS repeat RNA PHENOTYPE:
|
|
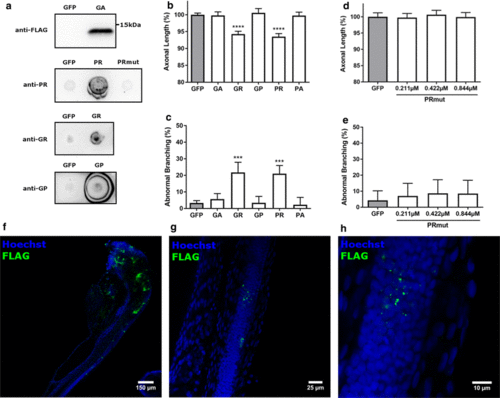
DPR-induced axonopathy in zebrafish. a Western blot using anti-FLAG antibody to detect formation of GA in fish injected with GA-coding mRNA (upper panel) and dot blots using DPR-specific antibodies to detect PR, GR and GP, respectively (three lower panels; pictures for GR and GP are derived from the dot blots in Fig. 3c), n = 3 biological replicates. b, c Quantification of axonal length (b) and aberrant axonal branching (c) of fish injected with equimolar amounts (0.844 ÁM) of codon-optimized RNA encoding a single DPR, compared to GFP control RNA (n = 18 experiments). b Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI one-way ANOVA, F(5, 1390) = 55.07, ****p < 0.0001. c Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI logistic regression (z values compared to GFP 1.693, 7.090, ? 0.177, 7.410, ? 0.533), ***p < 0.001. d, e Quantification of axonal length (d) and aberrant axonal branching (e) of fish injected with increasing doses of PR-encoding RNA with a mutation of the ATG start codon (?PRmut?), n = 3 experiments. d Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI one-way ANOVA, F(3, 179) = 0.3464. e Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI logistic regression (z values compared to GFP 0.828, 0.558, 0.854). f?h Whole-mount staining (FLAG antibody) of 30 hpf zebrafish embryos injected with GA-coding mRNA PHENOTYPE:
|
|
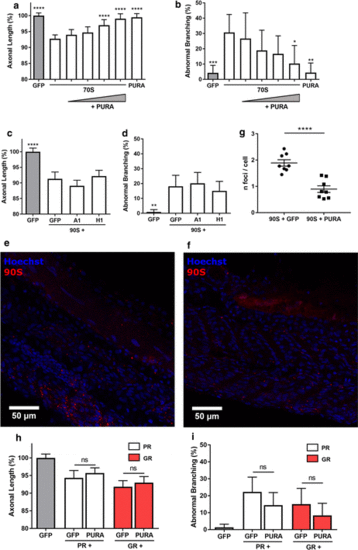
Pur-alpha prevents repeat induced axonopathy in the zebrafish. a, b Dose-dependent effect of injection of Pur-alpha mRNA (0.072?0.143?0.287?0.573 ÁM) on ~ 70S (0.844 ÁM) axonal toxicity, statistics are compared to the second condition, i.e., 70S (n = 3 experiments). a Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI one-way ANOVA, F(6, 310) = 21.56, ****p < 0.0001. b Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI logistic regression (z values ? 3.516, ? 0.393, ? 1.272, ? 1.594, ? 2.007, ? 2.909), *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. c, d Effect of hnRNPA1 (?A1?; 0.108 ÁM) and hnRNPH1 (?H1?; 0.030 ÁM) on ~ 90S (0.844 ÁM) axonal toxicity, statistics are compared to the second condition, i.e., 90S + GFP (n = 8 experiments). c Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI one-way ANOVA, F(3, 460) = 29.63, ****p < 0.0001. d Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI logistic regression (z values ? 3.157, 0.393, ? 0.624), **p < 0.01. e, f Whole-mount staining (Hoechst) of 30 hpf zebrafish embryos injected with fluorescently labeled ~ 90S repeat RNA together with GFP (e) or Pur-alpha (f) Mrna, respectively. g Quantification of number of RNA foci per cell in conditions of panel e and f, n = 8 embryos, data represent mean ▒ SEM, unpaired t test (t14 = 5.677), ****p < 0.0001. h, i Effect of Pur-alpha (0.573 ÁM) on PR and GR (0.844 ÁM) axonal toxicity (n = 6 experiments). h Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI one-way ANOVA, F(4, 444) = 18.49, (PR + GFP vs PR + Pur-alpha: p = 0.7575; GR + GFP vs GR + Pur-alpha: p = 0.9235). i Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI logistic regression (PR + GFP vs PR + Pur-alpha: z value = ? 1.340, p = 0.18; GR + GFP vs GR + Pur-alpha: z value = ? 1.123, p = 0.261) |
|
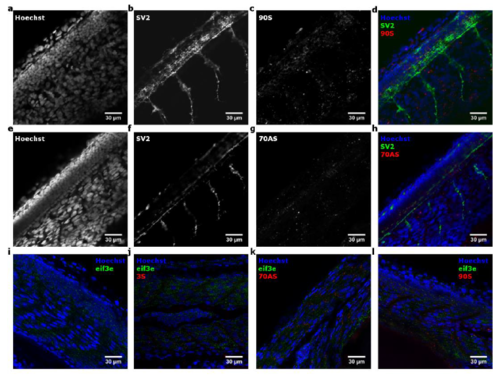
Localization of sense and antisense repeat RNA. (a,b,c,d) Whole mount immunohistochemistry (SV2 antibody, Hoechst) of 30 hpf zebrafish embryos injected with fluorescently labeled ~90S repeat RNA. (e,f,g,h) Whole mount immunohistochemistry (SV2 antibody, Hoechst) of 30 hpf zebrafish embryos injected with fluorescently labeled ~70AS repeat RNA. (i,j,k,l) Whole mount immunohistochemistry (eif3e antibody, Hoechst) of 30 hpf zebrafish embryos injected with 3S (j), ~70AS (k) or ~90S (l) and non-injected embryos (i). |
|
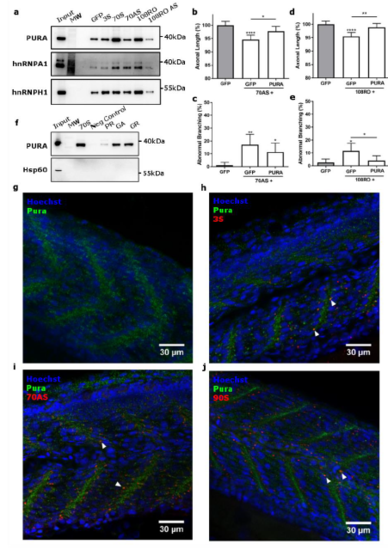
Pura in zebrafish embryos. (a) RNA pull-down from mouse brain lysate. Western blot analysis of Pur-alpha, hnRNPA1 and hnRNPH1, showing the binding affinity to different sense and antisense repeat RNAs, n = 2 biological replicates (Input = brain lysate, MW = molecular weight marker). (b,c) Effect of Pur-alpha (0.573?M) on ~70AS (0.844 ?M) axonal toxicity (n = 6 experiments). (b) Data represent mean +/- 95% CI, one-way ANOVA, F(2, 262) = 10.52, *p<0.05, ****p<0.0001. (c) Data represent mean +/- 95% CI, logistic regression (z-values compared to GFP: 2.782, 2.308; 70AS + GFP vs 70AS + Pur-alpha: z-value = 1.043, p = 0.297), *p<0.05, **p<0.01. (d,e) Effect of Pur-alpha (0.573?M) on 108RO (0.844 ?M) axonal toxicity (n = 8 experiments). (d) Data represent mean +/- 95% CI, one-way ANOVA, F(2, 357) = 10.89, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001. (e) Data represent mean +/- 95% CI, logistic regression (z-values compared to GFP: 2.521, 0.712; 108RO + GFP vs 108RO + Pur-alpha: z-value = -2.065, p = 0.0389), *p<0.05. (f) RNA pull-down from mouse brain lysate. Western blot analysis of Pur-alpha, showing the binding affinity to different DPR coding codon-optimized mRNAs, n = 2 biological replicates. (Input = brain lysate, MW = molecular weight marker, Negative Control = non-biotinylated ~70S repeat RNA). Hsp60 was used as negative control for the RNA pull-down. (g, h, i, j) Whole mount immunohistochemistry (pura antibody, Hoechst) of 30 hpf zebrafish embryos injected with 3S (h), ~70AS (i) or ~90S (j) and non-injected embryos (g). Arrowheads indicate sites of colocalization of pura with repeat RNA. |

Unillustrated author statements PHENOTYPE:
|