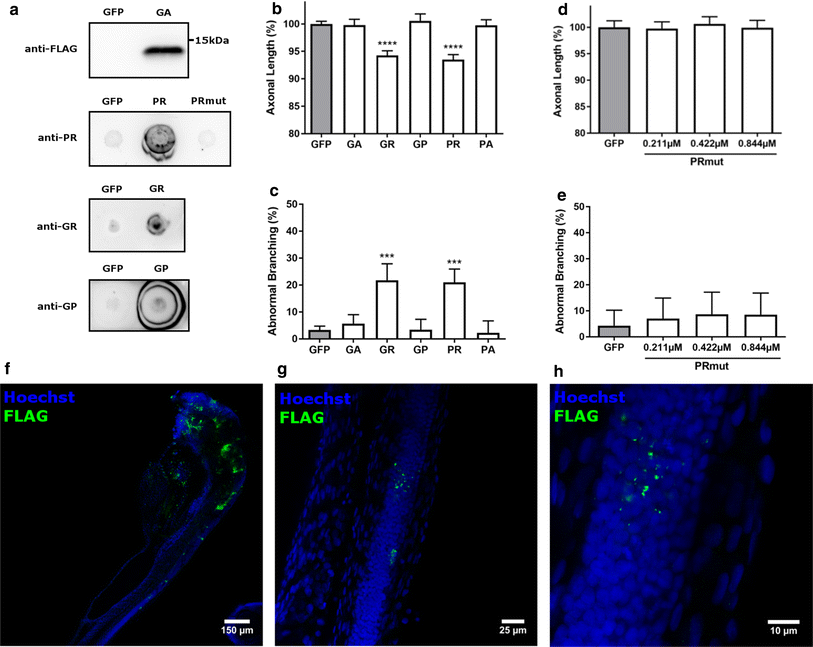
Fig. 2
DPR-induced axonopathy in zebrafish. a Western blot using anti-FLAG antibody to detect formation of GA in fish injected with GA-coding mRNA (upper panel) and dot blots using DPR-specific antibodies to detect PR, GR and GP, respectively (three lower panels; pictures for GR and GP are derived from the dot blots in Fig. 3c), n = 3 biological replicates. b, c Quantification of axonal length (b) and aberrant axonal branching (c) of fish injected with equimolar amounts (0.844 ÁM) of codon-optimized RNA encoding a single DPR, compared to GFP control RNA (n = 18 experiments). b Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI one-way ANOVA, F(5, 1390) = 55.07, ****p < 0.0001. c Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI logistic regression (z values compared to GFP 1.693, 7.090, ? 0.177, 7.410, ? 0.533), ***p < 0.001. d, e Quantification of axonal length (d) and aberrant axonal branching (e) of fish injected with increasing doses of PR-encoding RNA with a mutation of the ATG start codon (?PRmut?), n = 3 experiments. d Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI one-way ANOVA, F(3, 179) = 0.3464. e Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI logistic regression (z values compared to GFP 0.828, 0.558, 0.854). f?h Whole-mount staining (FLAG antibody) of 30 hpf zebrafish embryos injected with GA-coding mRNA