Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-180626-4
- Publication
- Swinnen et al., 2018 - A zebrafish model for C9orf72 ALS reveals RNA toxicity as a pathogenic mechanism
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
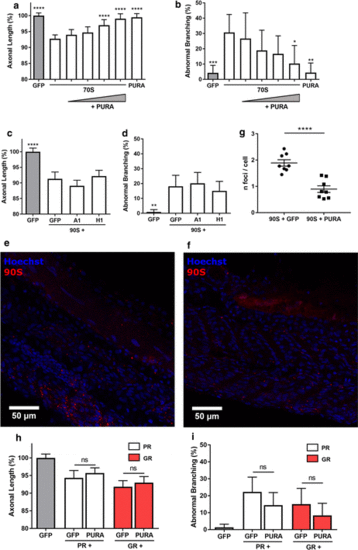
Pur-alpha prevents repeat induced axonopathy in the zebrafish. a, b Dose-dependent effect of injection of Pur-alpha mRNA (0.072?0.143?0.287?0.573 ÁM) on ~ 70S (0.844 ÁM) axonal toxicity, statistics are compared to the second condition, i.e., 70S (n = 3 experiments). a Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI one-way ANOVA, F(6, 310) = 21.56, ****p < 0.0001. b Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI logistic regression (z values ? 3.516, ? 0.393, ? 1.272, ? 1.594, ? 2.007, ? 2.909), *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. c, d Effect of hnRNPA1 (?A1?; 0.108 ÁM) and hnRNPH1 (?H1?; 0.030 ÁM) on ~ 90S (0.844 ÁM) axonal toxicity, statistics are compared to the second condition, i.e., 90S + GFP (n = 8 experiments). c Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI one-way ANOVA, F(3, 460) = 29.63, ****p < 0.0001. d Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI logistic regression (z values ? 3.157, 0.393, ? 0.624), **p < 0.01. e, f Whole-mount staining (Hoechst) of 30 hpf zebrafish embryos injected with fluorescently labeled ~ 90S repeat RNA together with GFP (e) or Pur-alpha (f) Mrna, respectively. g Quantification of number of RNA foci per cell in conditions of panel e and f, n = 8 embryos, data represent mean ▒ SEM, unpaired t test (t14 = 5.677), ****p < 0.0001. h, i Effect of Pur-alpha (0.573 ÁM) on PR and GR (0.844 ÁM) axonal toxicity (n = 6 experiments). h Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI one-way ANOVA, F(4, 444) = 18.49, (PR + GFP vs PR + Pur-alpha: p = 0.7575; GR + GFP vs GR + Pur-alpha: p = 0.9235). i Data represent mean ▒ 95% CI logistic regression (PR + GFP vs PR + Pur-alpha: z value = ? 1.340, p = 0.18; GR + GFP vs GR + Pur-alpha: z value = ? 1.123, p = 0.261) |