- Title
-
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 2 Alpha Is Essential for Hepatic Outgrowth and Functions via the Regulation of leg1 Transcription in the Zebrafish Embryo
- Authors
- Lin, T.Y., Chou, C.F., Chung, H.Y., Chiang, C.Y., Li, C.H., Wu, J.L., Lin, H.J., Pai, T.W., Hu, C.H., Tzou, W.S.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
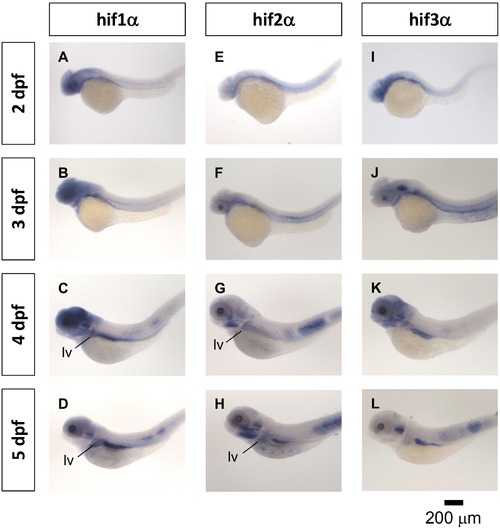
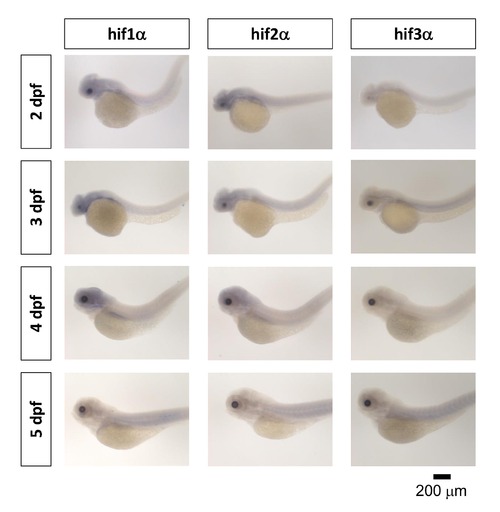
Gene expression pattern of hif-1alpha, hif-2 alpha and hif-3 alpha in zebrafish embryos. The expression patterns of hif1-alpha (A?D), hif2-alpha (E?H) and hif3-alpha (I?L) were performed with anti-sense probes by WISH in zebrafish embryos at 2?5 dpf. WISH, whole-mount in situ hybridization. dpf, days post-fertilization. lv, liver. |
|
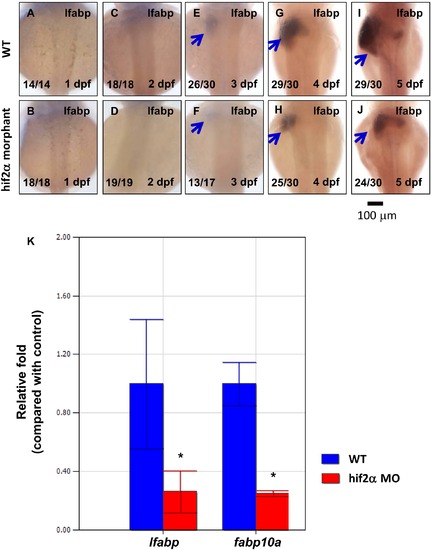
Knockdown of hif2-alpha confers a small liver phenotype. (A?J) Development of the embryonic liver was monitored by the expression pattern of the lfabp gene in wild-type embryos and hif2-alpha ATG-MO-injected embryos at 1?5 dpf by WISH, thereby revealing a small liver phenotype in hif2-alpha morphants. (K) Expression of the lfabp and fabp10a genes was investigated in wild-type embryos and hif2-alpha morphants at 5 dpf by qPCR (n = 30). Expression was normalized to β-actin. WT, wild type. The experiment was performed in triplicate, error bars indicate S.D. *, p<0.05, unpaired t-test. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
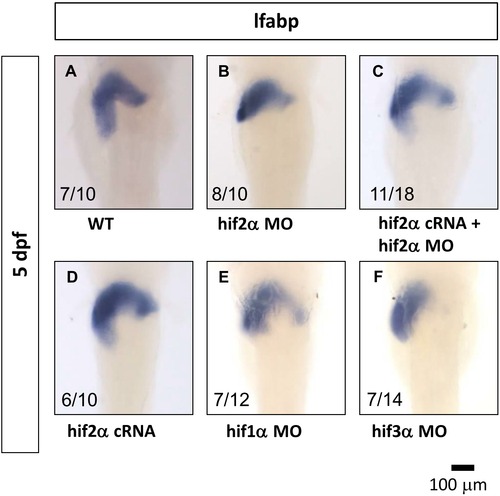
Hif2-alpha plays a major role in liver development. The specificity of knockdown by MO was demonstrated by monitoring lfabp gene expression at 5 pdf by WISH in wild-type embryos (A) and embryos injected with hif2-alpha ATG-MO (B). The small liver phenotype resulting from the knockdown of hif2-alpha can be rescued by co-injection of hif2-alpha mRNA (C). ATG-MO of hif2-alpha but not hif1-alpha caused the small liver phenotype (E). ATG-MO of hif3-alpha also caused a slight effect on liver development (F). |
|
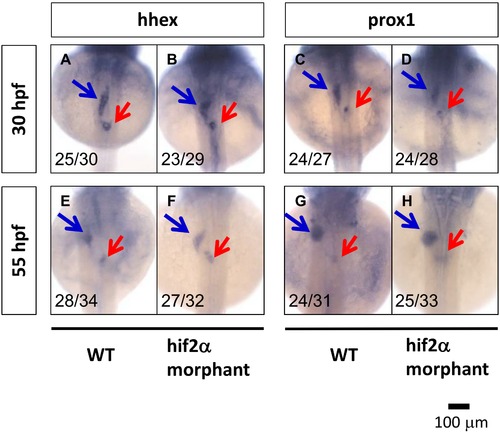
Hif2-alpha is not required for liver specification in zebrafish embryos. Liver specification in hif2-alpha morphants was detected through the expression of the hhex and prox1 genes. The expression of embryonic liver specification genes, hhex (A, B, E, F) and prox1 (C, D, G, H), were examined at 30 hpf (A?D) and 55 hpf (E?H) in wild-type and hif2-alpha ATG-MO-injected embryos by WISH. |
|
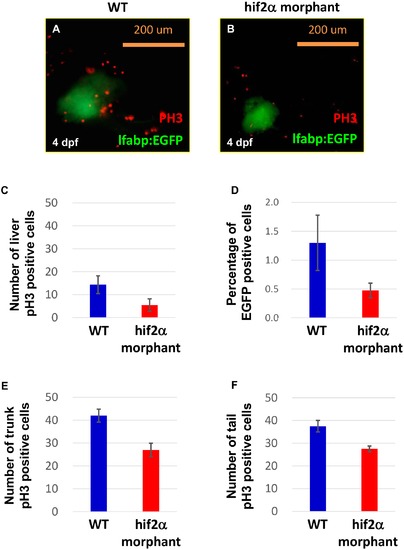
Knockdown of hif2-alpha damages liver cell proliferation. WT (Tg(lfabp:EGFP)) embryos (A) and hif2-alpha ATG-MO-injected embryos (B) were examined for liver cell proliferation using an anti-pH3 antibody at 4 dpf. Cell proliferation in hif2-alpha ATG-MO-injected embryos was reduced compared with WT embryos. (C) Quantification of pH3-positive cells in the liver (n = 11, p<0.05). (D) The EGFP-positive cells were counted by FACS. Quantification of pH3-positive cells in the trunk (E) and tail (F) (n = 4, p<0.05). |
|
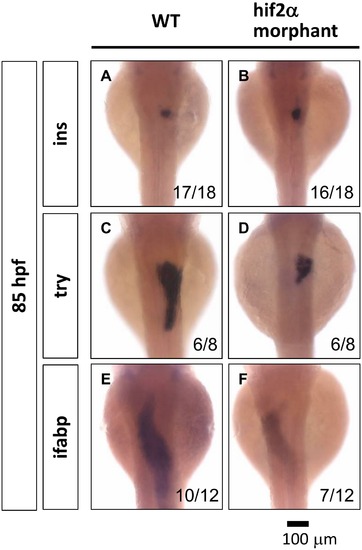
Hif2-alpha is required for the expansion of the exocrine pancreas and the intestine. The development of the embryonic pancreas and the intestine was monitored by examining the gene expression pattern of the endocrine pancreas (ins) (A, B), the exocrine pancreas (try) (C, D), and the intestine (ifabp) (E, F) in wild-type embryos compared with hif2-alpha ATG-MO-injected embryos at 85 hpf by WISH. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
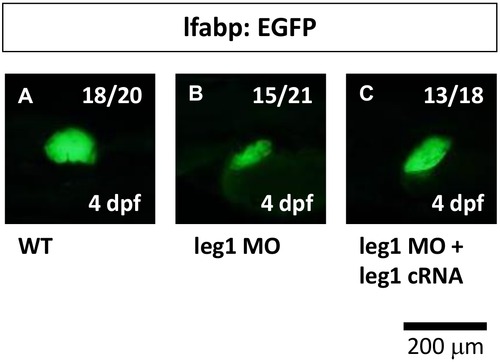
leg1 is required for hepatic outgrowth in zebrafish embryos. The expression pattern of the lfabp gene was examined in Tg(lfabp:EGFP) embryos (A) and compared with leg1 ATG-MO-injected embryos (0.5 μM) (B) as well as embryos co-injected with leg1 ATG-MO (0.5 μM) and leg1 cRNA (C). |
|
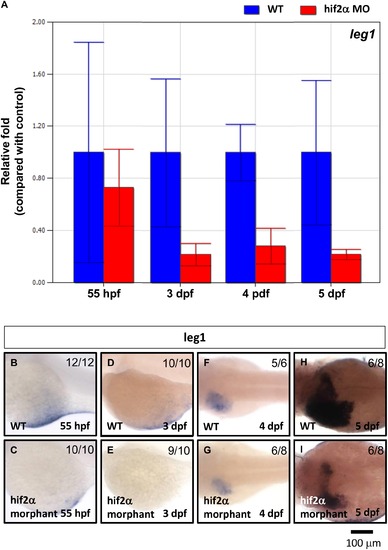
Leg1 expression was down-regulated in hif2-alpha morphants. leg1 gene expression was examined in wild-type embryos and compared with hif2-alpha ATG-MO-injected embryos at 3?5 dpf by qPCR (A) and WISH (B). Expression was normalized to β-actin. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
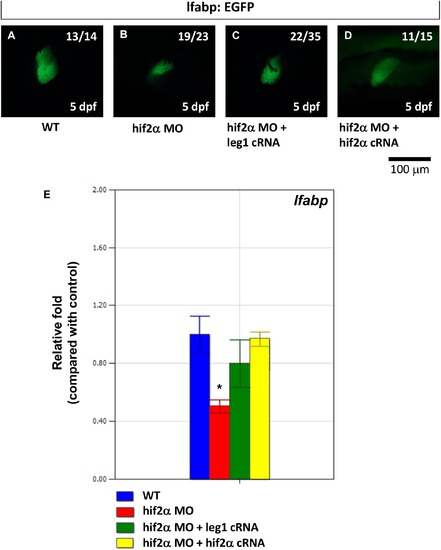
The small liver phenotype caused by hif2-alpha knockdown can be rescued by ectopic leg1 expression. The expression pattern of the lfabp gene was examined in Tg(lfabp:EGFP) embryos (A) and compared with hif2-alpha ATG-MO-injected embryos (8 ng) (B) as well as embryos co-injected with hif2-alpha ATG-MO (8 ng) and leg1 cRNA (C). (D) lfabp mRNA expression was detected by qPCR in wild-type embryos and compared with hif2-alpha ATG-MO-injected embryos, hif2-alpha ATG-MO and leg1 cRNA co-injected embryos, as well as hif2-alpha ATG-MO and hif2-alpha cRNA co-injected embryos. Expression was normalized to β-actin. |
|
Whole-mount in situ hybridization was performed with sense probes of hif1-alpha, hif2-alpha and hif3-alpha. The expression patterns of hif1-alpha (A?D), hif2-alpha (E?H) and hif3-alpha (I?L) were assessed with sense probes by WISH in zebrafish embryos at 2?5 dpf. WISH, whole-mount in situ hybridization. dpf, days post-fertilization. |
|
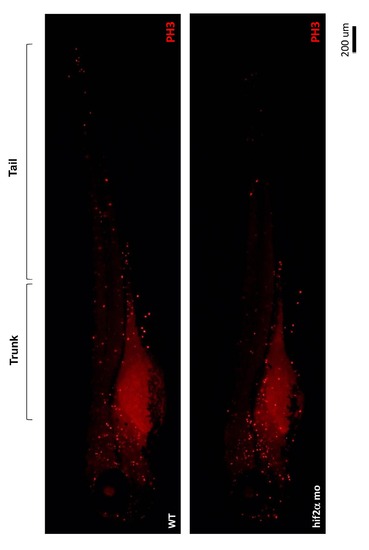
Knockdown of hif2-alpha reduced cell proliferation in the trunk and tail of zebrafish embryos. Cell apoptosis in wild-type embryos (A) and hif2-alpha ATG-MO-injected embryos (B) at 4 dpf by pH3 staining. |
|
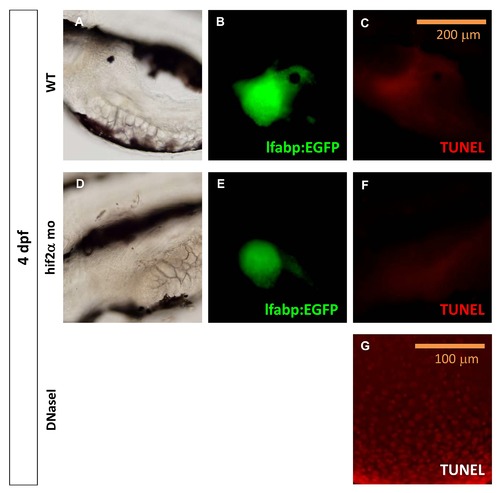
Knockdown of hif2-alpha did not induce cell apoptosis in hepatocytes in the zebrafish embryos. Cell apoptosis in Tg(lfabp:EGFP) embryos (A, B, C) and hif2-alpha ATG-MO-injected Tg(lfabp:EGFP) embryos (D, E, F) at 4 dpf by TUNEL assay. A positive control using Tg(lfabp:EGFP) embryos with DNaseI treatment is also shown (G). |
|
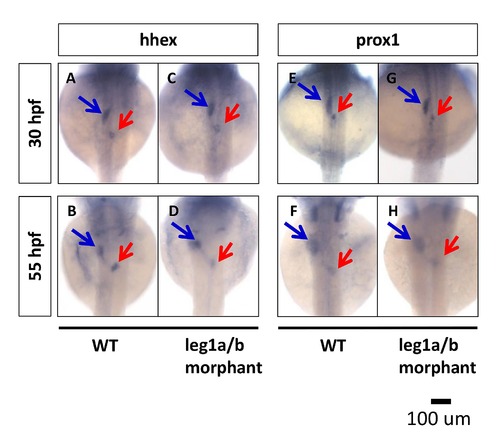
Leg1 is not required for liver specification in zebrafish embryos. Liver specification in leg1 morphants was detected through the expression of the hhex and prox1 genes. The expression of embryonic liver specification genes, hhex (A, B, E, F) and prox1 (C, D, G, H), were examined at 30 hpf (A?D) and 55 hpf (E?H) in wild-type and leg1 ATG-MO-injected embryos by WISH. |